Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
Running head: AGING BRAIN
... (Hasher & Zacks 1988, p. 196), is a necessary component of everyday functioning. Also called short-term memory, it allows us to continually relate one experience to the next as we navigate through time. Many times, the information we are grappling with is presented in front of us so that we do not h ...
... (Hasher & Zacks 1988, p. 196), is a necessary component of everyday functioning. Also called short-term memory, it allows us to continually relate one experience to the next as we navigate through time. Many times, the information we are grappling with is presented in front of us so that we do not h ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_ekversion
... growing problem for most users – Who have vast numbers of documents, images, music files, video clips, emails, attachments, bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of e ...
... growing problem for most users – Who have vast numbers of documents, images, music files, video clips, emails, attachments, bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what they were called and where to find them again – Naming most common means of e ...
CNS_notes
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
... receiving sensory information from the environment via the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, position in space, and nerve endings throughout our body. This information is then sent to other parts of the body via the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system. Subsequently, the central nervous system (CNS) ...
... receiving sensory information from the environment via the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, position in space, and nerve endings throughout our body. This information is then sent to other parts of the body via the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system. Subsequently, the central nervous system (CNS) ...
Chapters 13, and 14
... The limbic system is a functional grouping rather than an anatomical one. Within the limbic system, the hippocampus makes the prefrontal area aware of past experiences, and the amygdala causes such experiences to have emotions associated with them. Higher Mental Functions Memory and Learning Memory ...
... The limbic system is a functional grouping rather than an anatomical one. Within the limbic system, the hippocampus makes the prefrontal area aware of past experiences, and the amygdala causes such experiences to have emotions associated with them. Higher Mental Functions Memory and Learning Memory ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
... receiving sensory information from the environment via the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, position in space, and nerve endings throughout our body. This information is then sent to other parts of the body via the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system. Subsequently, the central nervous system (CNS) ...
... receiving sensory information from the environment via the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, position in space, and nerve endings throughout our body. This information is then sent to other parts of the body via the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system. Subsequently, the central nervous system (CNS) ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... left hemisphere – Pain felt in left foot, Information processed by right hemisphere ...
... left hemisphere – Pain felt in left foot, Information processed by right hemisphere ...
Nerves, structures, and organs of the head 1. Left cerebral
... Spinal cord (19) A soft oval-shaped cylinder about 45 cm long, and about as big around as the little finger. This structure is protected by the spinal column and is composed of afferent and efferent neurons and internucial neurons. Thalamus (8) Two rounded lobes of gray matter that serves as a major ...
... Spinal cord (19) A soft oval-shaped cylinder about 45 cm long, and about as big around as the little finger. This structure is protected by the spinal column and is composed of afferent and efferent neurons and internucial neurons. Thalamus (8) Two rounded lobes of gray matter that serves as a major ...
Moran Furman
... FIGURE 19.6 Spatial stability during eye movements is achieved through integration of visual and motor signals. During eye movements, the visual system “compensates” for shifts in the location of the retinal image, to generate visual representations in externally based coordinates (“spatial stabili ...
... FIGURE 19.6 Spatial stability during eye movements is achieved through integration of visual and motor signals. During eye movements, the visual system “compensates” for shifts in the location of the retinal image, to generate visual representations in externally based coordinates (“spatial stabili ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_slides - Interaction Design
... • Cognition involves several processes including attention, memory, perception and learning • The way an interface is designed can greatly affect how well users can perceive, attend, learn and remember how to do their tasks • Theoretical frameworks such as mental models and external cognition provid ...
... • Cognition involves several processes including attention, memory, perception and learning • The way an interface is designed can greatly affect how well users can perceive, attend, learn and remember how to do their tasks • Theoretical frameworks such as mental models and external cognition provid ...
sms7new
... cerebellum may be viewed as key elements in two parallel reentrant systems that receive input from and return their influences to the cerebral cortex through discrete and separate portions of the ventrolateral thalamus. They also influence the brain stem and, ultimately, spinal mechanisms. ...
... cerebellum may be viewed as key elements in two parallel reentrant systems that receive input from and return their influences to the cerebral cortex through discrete and separate portions of the ventrolateral thalamus. They also influence the brain stem and, ultimately, spinal mechanisms. ...
Psychology Lecture 02 - Biological Basis
... ◦ Vibrations of the oval window cause the perilymph of the cochlea to move in waves. ◦ Waves move to the scala vestibuli, the scala tympani, then to the round window. ◦ The waves cause the round window to bulge into the middle ear & the walls fo the scala vestibuli & scala tympani to change. ◦ Wall ...
... ◦ Vibrations of the oval window cause the perilymph of the cochlea to move in waves. ◦ Waves move to the scala vestibuli, the scala tympani, then to the round window. ◦ The waves cause the round window to bulge into the middle ear & the walls fo the scala vestibuli & scala tympani to change. ◦ Wall ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... emotions and higher mental functions. The limbic system is a complex network of tracts and nuclei involving cerebral lobes, basal nuclei and the diencephalon. Two structures, the hippocampus and amygdala are essential for learning and memory. ...
... emotions and higher mental functions. The limbic system is a complex network of tracts and nuclei involving cerebral lobes, basal nuclei and the diencephalon. Two structures, the hippocampus and amygdala are essential for learning and memory. ...
Exponential Growth By Joe Zakhary Slide 2 Target Audience 10th
... Spatial- The spatial learner will be engaged with all the different graphs. The students will also have to compare graphs and determine whether it is increasing or decreasing at a faster rate. Bodily-Kinesthetic- Students will learn how to use their hands to model the exponential equation given. Mus ...
... Spatial- The spatial learner will be engaged with all the different graphs. The students will also have to compare graphs and determine whether it is increasing or decreasing at a faster rate. Bodily-Kinesthetic- Students will learn how to use their hands to model the exponential equation given. Mus ...
sample - McLoon Lab
... temporal lobe. D. Broca’s aphasia is often accompanied by weakness of the left arm. 51. Which statement is true about language areas? A. For almost everyone, language areas are found only on the left side of the frontal lobe. B. When chimpanzees use manual gestures to communicate, no areas in the le ...
... temporal lobe. D. Broca’s aphasia is often accompanied by weakness of the left arm. 51. Which statement is true about language areas? A. For almost everyone, language areas are found only on the left side of the frontal lobe. B. When chimpanzees use manual gestures to communicate, no areas in the le ...
Understanding the Brain and Mental Illness
... neurotransmitters (e.g. production of neurotransmitters cannot keep up with the body’s demands or the neurotransmitters are not effectively removed from the system). ...
... neurotransmitters (e.g. production of neurotransmitters cannot keep up with the body’s demands or the neurotransmitters are not effectively removed from the system). ...
Cranial nerve of smell, plus olfactory pathway
... secondary cortical olfactory areas, and their relationship to limbic system ...
... secondary cortical olfactory areas, and their relationship to limbic system ...
module b6: brain and mind – overview
... illustrates specialised areas of the brain, methods scientists have used to map the cerebral cortex and introduces a basic understanding of memory. Finally the effects of drugs on synapses in the brain are explored (for example, Ecstasy) ...
... illustrates specialised areas of the brain, methods scientists have used to map the cerebral cortex and introduces a basic understanding of memory. Finally the effects of drugs on synapses in the brain are explored (for example, Ecstasy) ...
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
... of action extensively connected with the parietal lobes. Both the prefrontal and the parietal cortex send axons that converge on cortical area 6 and this plays an important role in higher-order motor planning ...
... of action extensively connected with the parietal lobes. Both the prefrontal and the parietal cortex send axons that converge on cortical area 6 and this plays an important role in higher-order motor planning ...
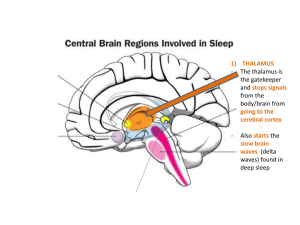
Sleep Brain Labelling
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
Final review quiz
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
... Which brain structure is implicated in procedural learning? _______________________________ A rat is trained to run a T-maze. When the maze is rotated 180º, will the rat go to the specific place or make the same turn as it was trained to get the reward? When the maze is flipped early in training (in ...
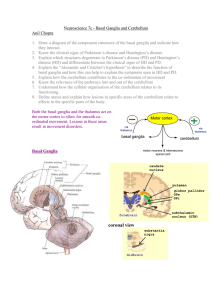
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... Pars compacta of substantia nigra stimulates striatum Striatum inhibit external globus pallidus, internal globus pallidus and pars reticular of the substantia nigra DIRECTLY. Striatum also inhibit internal globus pallidus INDIRECTLY via the external globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus inte ...
... Pars compacta of substantia nigra stimulates striatum Striatum inhibit external globus pallidus, internal globus pallidus and pars reticular of the substantia nigra DIRECTLY. Striatum also inhibit internal globus pallidus INDIRECTLY via the external globus pallidus subthalamic nucleus inte ...
Baddeley 1966 - the Department of Psychology
... environment as a controlled laboratory experiment. The aim was to investigate the influence of acoustic and semantic word similarity on learning and recall in STM and LTM. The IV present in this experiment was the type of similarity between words in a list and the DV was the recall of the list seque ...
... environment as a controlled laboratory experiment. The aim was to investigate the influence of acoustic and semantic word similarity on learning and recall in STM and LTM. The IV present in this experiment was the type of similarity between words in a list and the DV was the recall of the list seque ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.