Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... hippocampus, amygdala ● hippocampus: memory processes: spatial memory, consolidation of new info into long term memory ● amygdala: fear response, rage response ●pleasure centers: e.g. where the medial forebrain bundle passes through the hypothalamus ● opiates and stimulants work by exciting this dop ...
... hippocampus, amygdala ● hippocampus: memory processes: spatial memory, consolidation of new info into long term memory ● amygdala: fear response, rage response ●pleasure centers: e.g. where the medial forebrain bundle passes through the hypothalamus ● opiates and stimulants work by exciting this dop ...
Team GALACA Project _3 Presentation
... A recent simple linear circuit with a memristor was used to model adaptive behavior of unicellular organisms The circuit became trained of periodic pulses so that it could anticipate the next pulse Similar to the behavior of slime molds that are subjected to periodic changes in their environment Thi ...
... A recent simple linear circuit with a memristor was used to model adaptive behavior of unicellular organisms The circuit became trained of periodic pulses so that it could anticipate the next pulse Similar to the behavior of slime molds that are subjected to periodic changes in their environment Thi ...
Ling411-01 - OWL-Space
... • Therefore it is a large dynamic network • Not necessarily all in one part of the cortex In fact, we know it is not We know from aphasiology that it • Occupies several different cortical regions • These regions are interconnected ...
... • Therefore it is a large dynamic network • Not necessarily all in one part of the cortex In fact, we know it is not We know from aphasiology that it • Occupies several different cortical regions • These regions are interconnected ...
acetylcholine
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
... Although dopamine is synthesized by only several hundred thousand cells, it fulfils an exceedingly important role in the higher parts of the CNS. These dopaminergic neurons can be divided into three subgroups with different functions. The first group regulates movements: a deficit of dopamine in thi ...
auditory association cortex
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. identify the locations and functions of the primary cortex, secondary cortex, and association areas for the auditory system. 2. discuss the three primary causes of deafness. 3. explain how cochlear implants restore auditory ability. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. identify the locations and functions of the primary cortex, secondary cortex, and association areas for the auditory system. 2. discuss the three primary causes of deafness. 3. explain how cochlear implants restore auditory ability. ...
Slide ()
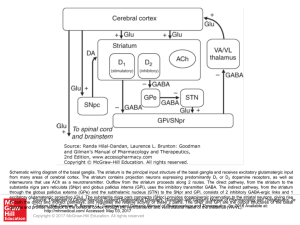
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
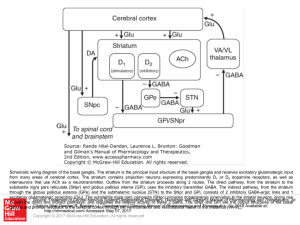
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Motor control
... plans in reverse order of the motions necessary to achieve a goal. In other words, our motor planning is goal based rather than direction based. • This would seem to imply that different parts of the system may be planning different movements at different points in time. • There are also neurons tha ...
... plans in reverse order of the motions necessary to achieve a goal. In other words, our motor planning is goal based rather than direction based. • This would seem to imply that different parts of the system may be planning different movements at different points in time. • There are also neurons tha ...
Why minimal guidance during instruction does not work: An analysis
... • Working memory is the cognitive structure in which conscious processing occurs. • Working memory has two well-known characteristics: when processing novel information, it is very limited in duration and in capacity. • The interactions between working memory and long-term memory may be even more im ...
... • Working memory is the cognitive structure in which conscious processing occurs. • Working memory has two well-known characteristics: when processing novel information, it is very limited in duration and in capacity. • The interactions between working memory and long-term memory may be even more im ...
neurolinguistics: shakespeare and aphasia
... form or the other, as the neural network is hampered. Shakespeare increases brain activity. In other words, it excites a lot of neurons which would not have been excited otherwise. The importance of the associational cortices has been noted earlier. So, if there is excitement of a lot of neurons, re ...
... form or the other, as the neural network is hampered. Shakespeare increases brain activity. In other words, it excites a lot of neurons which would not have been excited otherwise. The importance of the associational cortices has been noted earlier. So, if there is excitement of a lot of neurons, re ...
Prefrontal cortex and diverse functions Keiji Tanaka The prefrontal
... have problems in planning (e.g., in the tower of London task) and in reasoning (e.g., in the Raven’s progressive matrices test). Because the planning and reasoning require working memory, the problems in planning and reasoning may be due to their weaker working memory capacity. Patients with damage ...
... have problems in planning (e.g., in the tower of London task) and in reasoning (e.g., in the Raven’s progressive matrices test). Because the planning and reasoning require working memory, the problems in planning and reasoning may be due to their weaker working memory capacity. Patients with damage ...
Sparse but not `Grandmother-cell` coding in the medial temporal lobe
... processing area – at !130 ms [37] and also long after rapid recognition occurs in the human brain, at !150 ms [38]. Given the direct synaptic connections between the IT cortex and MTL in the monkey [17], response latencies of about 150 ms would have been expected for MTL neurons. This is clearly not ...
... processing area – at !130 ms [37] and also long after rapid recognition occurs in the human brain, at !150 ms [38]. Given the direct synaptic connections between the IT cortex and MTL in the monkey [17], response latencies of about 150 ms would have been expected for MTL neurons. This is clearly not ...
Terminology and Diagnoses - Academy for Coaching Parents
... interactions triggered and controlled by chemical signals in the brain when danger or threat is perceived in the environment, resulting in complex responses throughout the body and brain which cause the person to run away, freeze or hide, or prepare to fight for their life. Limbic System – The Life ...
... interactions triggered and controlled by chemical signals in the brain when danger or threat is perceived in the environment, resulting in complex responses throughout the body and brain which cause the person to run away, freeze or hide, or prepare to fight for their life. Limbic System – The Life ...
Chapter3ID
... quickly as possible? Set the thermostat to be at its highest or to the desired temperature? (b) You arrive home starving hungry. You look in the fridge and find all that is left is an uncooked pizza. You have an electric oven. Do you warm it up to 375 degrees first and then put it in (as specified b ...
... quickly as possible? Set the thermostat to be at its highest or to the desired temperature? (b) You arrive home starving hungry. You look in the fridge and find all that is left is an uncooked pizza. You have an electric oven. Do you warm it up to 375 degrees first and then put it in (as specified b ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... - response is automatic (involuntary) - controls smooth and cardiac muscles and glands ...
... - response is automatic (involuntary) - controls smooth and cardiac muscles and glands ...
Cognition and Emotion November 12
... explaining what has just happened. Two things are important in this: whether we interpret the event as good or bad for us, and what we believe is the cause of the event. • In primary appraisal, we consider how the situation affects our personal well-being. In secondary appraisal we consider how we m ...
... explaining what has just happened. Two things are important in this: whether we interpret the event as good or bad for us, and what we believe is the cause of the event. • In primary appraisal, we consider how the situation affects our personal well-being. In secondary appraisal we consider how we m ...
Dissociative Disorders
... away from home Often involves the creation of a new identity Fugue state usually ends abruptly – then amnesic for events during the fugue ...
... away from home Often involves the creation of a new identity Fugue state usually ends abruptly – then amnesic for events during the fugue ...
Neuroanatomy The central nervous system (CNS)
... suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood-brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to many types of damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of c ...
... suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood-brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to many types of damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of c ...
THE CEREBRUM (sah REB brum) LOCATION The cerebrum is the
... a. Voluntary muscles. Cells in the right hemisphere activate the left side of the body; the left hemisphere controls the right side. b. Speech. usually in the left hemisphere Damage to this area means that you may know what to say, but you cannot vocalize the words. 2. Parietal lobe - in the middle ...
... a. Voluntary muscles. Cells in the right hemisphere activate the left side of the body; the left hemisphere controls the right side. b. Speech. usually in the left hemisphere Damage to this area means that you may know what to say, but you cannot vocalize the words. 2. Parietal lobe - in the middle ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations
... III. Tour through the Brain Frontal Lobes – Located just behind the forehead – Control voluntary movement and speech – Involved with self – awareness, planning ability, social skills and working memory Working memory is located in the very front of the frontal lobes ...
... III. Tour through the Brain Frontal Lobes – Located just behind the forehead – Control voluntary movement and speech – Involved with self – awareness, planning ability, social skills and working memory Working memory is located in the very front of the frontal lobes ...
Anatomical Terminology
... act on sensory in puts. They have multiple inputs and outputs. In addition to those association areas discussed above; there are: i. Prefrontal cortex ii. Gnostic area iii. Language areas i. Prefrontal cortex (Brodmann 11 & 47): Located on the anterior portion of frontal lobe. It concerns intelligen ...
... act on sensory in puts. They have multiple inputs and outputs. In addition to those association areas discussed above; there are: i. Prefrontal cortex ii. Gnostic area iii. Language areas i. Prefrontal cortex (Brodmann 11 & 47): Located on the anterior portion of frontal lobe. It concerns intelligen ...
glossary of terms
... Deductive schemas that refer to repeated, internalized and commonly shared ways of acting by an individual or a group towards an object, event or situation. Cultural patterns Shared patterns of behav ...
... Deductive schemas that refer to repeated, internalized and commonly shared ways of acting by an individual or a group towards an object, event or situation. Cultural patterns Shared patterns of behav ...
The Nervous System
... The more convoluted the surface of the neocortex the more surface area the more neurons. ...
... The more convoluted the surface of the neocortex the more surface area the more neurons. ...
Self-Guided Study for Chapter 12 and Review
... II. Additional Information to Cover (some may be covered in your notes) 1. Cerebral Cortex – Motor Areas Area Primary Motor Cortex ...
... II. Additional Information to Cover (some may be covered in your notes) 1. Cerebral Cortex – Motor Areas Area Primary Motor Cortex ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.