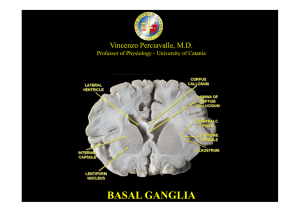
Role of Basal Ganglia in the Regulation of Motor Activities by the
... motor activities and has a well established link with movement disorders like Parkinsonism, Chorea/ Huntington’s ...
... motor activities and has a well established link with movement disorders like Parkinsonism, Chorea/ Huntington’s ...
Function
... serotonergic neurons in the CNS (also in GIT). Function: regulation of anger, aggression, body ...
... serotonergic neurons in the CNS (also in GIT). Function: regulation of anger, aggression, body ...
2_Neuro-Bio_Review
... Frontal Lobes: Contain the motor cortex which control voluntary movement. In the LEFT frontal lobe is Broca's Area which controls our ability to speak. Parietal Lobes: Contain the somatosensory cortex which registers bodily sensations (touch). Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (aud ...
... Frontal Lobes: Contain the motor cortex which control voluntary movement. In the LEFT frontal lobe is Broca's Area which controls our ability to speak. Parietal Lobes: Contain the somatosensory cortex which registers bodily sensations (touch). Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (aud ...
copyright 2004 scientific american, inc.
... frequencies. The cochlea then transmits this information along separately tuned fibers of the auditory nerve as trains of neural discharges. Eventually these trains reach the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Different cells in the auditory system of the brain respond best to certain frequencies ...
... frequencies. The cochlea then transmits this information along separately tuned fibers of the auditory nerve as trains of neural discharges. Eventually these trains reach the auditory cortex in the temporal lobe. Different cells in the auditory system of the brain respond best to certain frequencies ...
basal ganglia
... the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are colo ...
... the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are colo ...
Smell - Brain Day Association of U of T
... A broken arm or bruise can recover but damaged neurons cannot. The best cure for brain damage is prevention. ...
... A broken arm or bruise can recover but damaged neurons cannot. The best cure for brain damage is prevention. ...
Ch. 10: Technology and Learning
... a seat usually having four legs for support and a rest for the back and often having rests for the arms ...
... a seat usually having four legs for support and a rest for the back and often having rests for the arms ...
Module 07_lecture
... • Regions available for general processing, including mathematical reasoning • Designated as the association lobes • Behind the frontal lobes ...
... • Regions available for general processing, including mathematical reasoning • Designated as the association lobes • Behind the frontal lobes ...
Neurons- We will be making neurons out of different color pipe
... The most common way to view some of the key internal structures of the brain either in dissection or in images is to look at a mid-sagittal section of the brain. Imagine dividing the brain in half between its left and right hemispheres. Important brain regions that can now be seen include the pons, ...
... The most common way to view some of the key internal structures of the brain either in dissection or in images is to look at a mid-sagittal section of the brain. Imagine dividing the brain in half between its left and right hemispheres. Important brain regions that can now be seen include the pons, ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... • Located at superior edge of the temporal lobe • Conscious awareness of sound • Impulses transmitted to primary auditory cortex ...
... • Located at superior edge of the temporal lobe • Conscious awareness of sound • Impulses transmitted to primary auditory cortex ...
Completed Notes
... • Spatial memory – prefrontal cortex & visual cortex/association areas 2. Long-term (> 30 sec – to years) • Non-declarative (hard to describe if you were asked) For ex., could you verbally describe how to tie a shoelace? = memory of simple motor skills & conditioning stored in basal ganglia, cerebel ...
... • Spatial memory – prefrontal cortex & visual cortex/association areas 2. Long-term (> 30 sec – to years) • Non-declarative (hard to describe if you were asked) For ex., could you verbally describe how to tie a shoelace? = memory of simple motor skills & conditioning stored in basal ganglia, cerebel ...
7 - smw15.org
... Brain Mechanisms of Movement Role of Cerebral Cortex • Important for complex actions such as writing • Stimulation of primary motor cortex elicits certain outcome movements in corresponding body area ▫ 500 msec stimulation of arm region of monkey results in grasping movement and moving hand ...
... Brain Mechanisms of Movement Role of Cerebral Cortex • Important for complex actions such as writing • Stimulation of primary motor cortex elicits certain outcome movements in corresponding body area ▫ 500 msec stimulation of arm region of monkey results in grasping movement and moving hand ...
Motor Systems II Loops and Tracts
... Four major descending pathways: two in the dorsolateral region of the spinal cord; two in the ventromedial region. In each region, one is direct and one is indirect. ...
... Four major descending pathways: two in the dorsolateral region of the spinal cord; two in the ventromedial region. In each region, one is direct and one is indirect. ...
Chapter 13
... Most output from basal ganglia is directed to premotor cortex and supplementary motor area (involved in planning and execution of movements) ...
... Most output from basal ganglia is directed to premotor cortex and supplementary motor area (involved in planning and execution of movements) ...
The Brain
... What are Frontal Lobes? • Abstract thought and emotional control and planning. • Contains Motor Cortex, Broca’s area. • Broca’s Aphasia • Lobotomies damage this. • Suppresses the Amygdala. ...
... What are Frontal Lobes? • Abstract thought and emotional control and planning. • Contains Motor Cortex, Broca’s area. • Broca’s Aphasia • Lobotomies damage this. • Suppresses the Amygdala. ...
8.7 Learning and Memory
... Compare habituation and sensitisation in terms of• After repeated stimuli habituation decreases the awareness and response to that stimulus. Sensitisation will result in an increase in awareness to all stimuli. • Two neurons are involved in habituation- the Ca2+ channels in the pre-synaptic neuron ...
... Compare habituation and sensitisation in terms of• After repeated stimuli habituation decreases the awareness and response to that stimulus. Sensitisation will result in an increase in awareness to all stimuli. • Two neurons are involved in habituation- the Ca2+ channels in the pre-synaptic neuron ...
Consciousness and Creativity in Brain
... problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. ...
... problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction once set - identify the most important problems and focus on them - is still important. ...
November 12
... Premotor areas (PMA, SMA) – plan the motor activity Primary motor cortex (M1) – initiates motor activity: ...
... Premotor areas (PMA, SMA) – plan the motor activity Primary motor cortex (M1) – initiates motor activity: ...
the Unit 2 study guide in RTF format (which you may re
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
the Unit 2 study guide in PDF format.
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
... 5. Describe the function of the primary sensory cortex. What lobe is it in? 6. Where are the parietal lobes located? Learning Objective 6 (pp.99-101): Temporal — Occipital Lobes ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... 40. The hypothalamus is associated with both the anterior and the posterior lobes of the pituitary gland. Which of the following statements correctly describes this system? A. Magnocellular neurons in the supraoptic nucleus contain antidiuretic hormone and project their axons to the anterior pituita ...
... 40. The hypothalamus is associated with both the anterior and the posterior lobes of the pituitary gland. Which of the following statements correctly describes this system? A. Magnocellular neurons in the supraoptic nucleus contain antidiuretic hormone and project their axons to the anterior pituita ...
14/15 April 2008
... How many memories can be stored in the network? To store M memories, each of length N bits, in a network of N neurons, we first ask how many stable patterns can be reached? In 1987, McEliece et al derived an upper limit for the number of memories that can be stored accurately: M = N/(2 logN). e.g. f ...
... How many memories can be stored in the network? To store M memories, each of length N bits, in a network of N neurons, we first ask how many stable patterns can be reached? In 1987, McEliece et al derived an upper limit for the number of memories that can be stored accurately: M = N/(2 logN). e.g. f ...
Descending Spinal Tracts
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... homonymous hemianopia is the loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes. It occurs frequently in traumatic brain injuries, because of the manner in which the nasal nerve fibers from each eye cross as they pass to the back of the brain. The visual images that we see to the right ...
... homonymous hemianopia is the loss of half of the field of view on the same side in both eyes. It occurs frequently in traumatic brain injuries, because of the manner in which the nasal nerve fibers from each eye cross as they pass to the back of the brain. The visual images that we see to the right ...
Neuroanatomy of memory

The neuroanatomy of memory encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the brain.