Community Ecology
... Community Interactions: competition, predation, mutualism and commensalism Predation +/- ...
... Community Interactions: competition, predation, mutualism and commensalism Predation +/- ...
Population Interactions
... – Competitive interactions can get interesting when two species compete for more than one resource with differing capabilities. ...
... – Competitive interactions can get interesting when two species compete for more than one resource with differing capabilities. ...
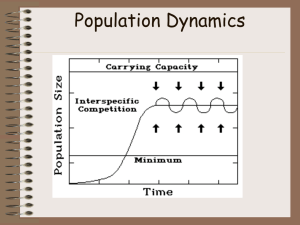
Population Dynamics
... Factors which work best with a large dense population Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Predation Disease Parasitism Density Independent Limiting Factors Tornado, hurricane, drought, temperature Human disturbance (Clear-cutting forests or damming rivers) ...
... Factors which work best with a large dense population Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Predation Disease Parasitism Density Independent Limiting Factors Tornado, hurricane, drought, temperature Human disturbance (Clear-cutting forests or damming rivers) ...
Study Guide Noncumulative part of Final
... habitat destruction, biodiversity crisis, introduction/competition of exotic species, ESA, endangered species, fragmentation and edges, movement corridor, establishing protected areas, biodiversity hot spot, case study: sustainable development in Costa Rica? Sample Essays 1. Discuss 3 points made by ...
... habitat destruction, biodiversity crisis, introduction/competition of exotic species, ESA, endangered species, fragmentation and edges, movement corridor, establishing protected areas, biodiversity hot spot, case study: sustainable development in Costa Rica? Sample Essays 1. Discuss 3 points made by ...
14.4 Interactions within Communities
... – An organisms use of and interaction with abiotic and biotic resources in its environment that influences its growth, survival and reproduction. ...
... – An organisms use of and interaction with abiotic and biotic resources in its environment that influences its growth, survival and reproduction. ...
Quiz 5 Key
... a. a predator keeps the death rate of its prey constant by eating more of them when the population is larger b. a predator keeps the population of its prey species well below its carrying capacity. c. an early frost kills a large fraction of the insects in a population d. food limitation reduces the ...
... a. a predator keeps the death rate of its prey constant by eating more of them when the population is larger b. a predator keeps the population of its prey species well below its carrying capacity. c. an early frost kills a large fraction of the insects in a population d. food limitation reduces the ...
Community Interactions and Disturbances PPT
... A close interaction between species that live in or on each other: Parasitism- One organism (parasite) obtains its nourishment at the expense of the other (host) Ex: tapeworm in intestine Mutualism- Both species benefit Ex: bees and flowers Commensalism- One organism benefits and the other is ...
... A close interaction between species that live in or on each other: Parasitism- One organism (parasite) obtains its nourishment at the expense of the other (host) Ex: tapeworm in intestine Mutualism- Both species benefit Ex: bees and flowers Commensalism- One organism benefits and the other is ...
Symbiosis Activity
... Two individuals of the same or different species may interact in a variety of different ways. A very specific interaction that may occur between the organisms is defined as symbiosis, a close, coevolutionary association between one species (host) and another species (symbiont). Species may interact ...
... Two individuals of the same or different species may interact in a variety of different ways. A very specific interaction that may occur between the organisms is defined as symbiosis, a close, coevolutionary association between one species (host) and another species (symbiont). Species may interact ...
Ecology - Cobb Learning
... • Diversity- measure of the number of different species there are in an area • (Ecosystems flourish more with more diversity) ...
... • Diversity- measure of the number of different species there are in an area • (Ecosystems flourish more with more diversity) ...
16.5 Conservation - Brookwood High School
... • The timber industry has started to adopt sustainable practices. • Global fisheries have adopted several sustainable practices. – rotation of catches – fishing gear review – harvest reduction – fishing bans ...
... • The timber industry has started to adopt sustainable practices. • Global fisheries have adopted several sustainable practices. – rotation of catches – fishing gear review – harvest reduction – fishing bans ...
Biodiversity_and_HIPPO
... particular environment. • Habitat- The environment in which a population or individual lives; includes not only the place where a species is found, but also the particular characteristics of the place (e.g., climate or the availability of suitable food and shelter) that make it especially well suite ...
... particular environment. • Habitat- The environment in which a population or individual lives; includes not only the place where a species is found, but also the particular characteristics of the place (e.g., climate or the availability of suitable food and shelter) that make it especially well suite ...
Chapter 14 Interactions in Ecosystems Review
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
11.17-Community-Interactions-and-Succession
... tree stumps Analogy: baseball players can be pitchers, catchers, shortstops, etc. ...
... tree stumps Analogy: baseball players can be pitchers, catchers, shortstops, etc. ...
Notes: Populations and Carrying Capacity
... Example: Seychelles Paradise Flycatcher needs one acre of mixed forest per breeding pair. They live on the little island of _______________________. A population remains at its ________________ capacity when it’s in ________________ (number of individuals added and the number of individuals that lea ...
... Example: Seychelles Paradise Flycatcher needs one acre of mixed forest per breeding pair. They live on the little island of _______________________. A population remains at its ________________ capacity when it’s in ________________ (number of individuals added and the number of individuals that lea ...
Ecology
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
... Energetic Hypothesis—food chain can’t be long because there is an insufficient transfer of energy (10% Rule) ...
100
... an organism lives is its _______, and the role the organism plays in an ecosystem is its _______. ...
... an organism lives is its _______, and the role the organism plays in an ecosystem is its _______. ...
Ecology
... Realized niche - the portion of the fundamental niche actually utilized due to interactions with other species ...
... Realized niche - the portion of the fundamental niche actually utilized due to interactions with other species ...
Chapter 14 Questions 14.1 1. Three parts of a niche include food
... No, population density simply describes the number of individuals per unit area, not the dispersion pattern. Three dispersion diagrams: clumped, uniform and random (see “Visual Vocab” on p.411) Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. If the curve shows a low ...
... No, population density simply describes the number of individuals per unit area, not the dispersion pattern. Three dispersion diagrams: clumped, uniform and random (see “Visual Vocab” on p.411) Survivorship curves help to describe the reproductive strategy of a species. If the curve shows a low ...
Chapter 5
... help regulate populations. Foundation species affect the community’s habitat to benefit other species. ...
... help regulate populations. Foundation species affect the community’s habitat to benefit other species. ...
Population Interactions
... • Meaning living together. • Two different species live close, usually in physical contact. • There are three types: 1) mutualism 2) commensalism 3) parasitism ...
... • Meaning living together. • Two different species live close, usually in physical contact. • There are three types: 1) mutualism 2) commensalism 3) parasitism ...