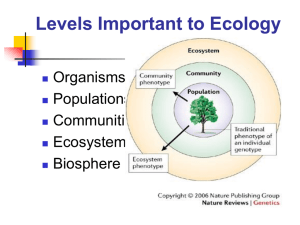
Ecology - bulldog biology
... Richness and Diversity Species richness – the number of species in a community Species diversity – number of species in a community relative to the abundance of each species ...
... Richness and Diversity Species richness – the number of species in a community Species diversity – number of species in a community relative to the abundance of each species ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... 33.3 Regulation of Population Growth Members of opportunistic populations are small in size, mature early, and have a short life span. Equilibrium pattern organisms are fairly large, slow to mature, and have a fairly long life span. Abiotic factors, such as weather and natural diseases, are density- ...
... 33.3 Regulation of Population Growth Members of opportunistic populations are small in size, mature early, and have a short life span. Equilibrium pattern organisms are fairly large, slow to mature, and have a fairly long life span. Abiotic factors, such as weather and natural diseases, are density- ...
Marine Communities
... A a factor that limits and organisms success in a community. Prevents organism from feeding, growing, reproducing, defending itself, or sensing danger. ...
... A a factor that limits and organisms success in a community. Prevents organism from feeding, growing, reproducing, defending itself, or sensing danger. ...
Interactions among species
... No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time. If there are two species, one will be better at competing for limited resources and will eventually exclude the other species. ...
... No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time. If there are two species, one will be better at competing for limited resources and will eventually exclude the other species. ...
COMMUNITY AND POPULATION ECOLOGY
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
Sc9 - a 1.2 (teacher notes)
... 1 Identify examples of niches and describe how closely related living things can survive in the same ecosystem. 1.2 - Interdependence Each and every species depends on many other species within an environment in order to survive and prosper. Food chains and Food webs represent different types of ong ...
... 1 Identify examples of niches and describe how closely related living things can survive in the same ecosystem. 1.2 - Interdependence Each and every species depends on many other species within an environment in order to survive and prosper. Food chains and Food webs represent different types of ong ...
Evolution Project File
... This project ties together the Ecology and Evolution units. You may work by yourself or with a partner. No more than TWO people may work together! You will have several days in class to work on this assignment. This project will count as a test grade and is due on Friday, October 18. Components A ...
... This project ties together the Ecology and Evolution units. You may work by yourself or with a partner. No more than TWO people may work together! You will have several days in class to work on this assignment. This project will count as a test grade and is due on Friday, October 18. Components A ...
12/9/10 Practice Test Exam 4
... 12. All nonliving factors, such as temperature, light, water and nutrients are considered ____ factors influencing an environment. a. abiotic b. rocks c. biotic d. soil 13. If you place two species of bacteria that use the same food sources in a single flask, over time one will thrive and other wil ...
... 12. All nonliving factors, such as temperature, light, water and nutrients are considered ____ factors influencing an environment. a. abiotic b. rocks c. biotic d. soil 13. If you place two species of bacteria that use the same food sources in a single flask, over time one will thrive and other wil ...
notes
... Community interactions 3. Symbiosis---two different species live together Mutualism- both species benefit Commensalism- one benefits without harming ...
... Community interactions 3. Symbiosis---two different species live together Mutualism- both species benefit Commensalism- one benefits without harming ...
Ecosystem Notes
... Ecosystem- A system consisting of all of the interactions that occur between abiotic and biotic factors within an environment. ...
... Ecosystem- A system consisting of all of the interactions that occur between abiotic and biotic factors within an environment. ...
Ch 37 HW - TeacherWeb
... 3. Review questions- number each one and answer on a separate sheet of paper. You do not need to rewrite the questions. 1. Describe the characteristics of a community & how interspecific interactions affect the dynamics of populations (p 742) 2. Explain 5 different aspects of ecological niche of hip ...
... 3. Review questions- number each one and answer on a separate sheet of paper. You do not need to rewrite the questions. 1. Describe the characteristics of a community & how interspecific interactions affect the dynamics of populations (p 742) 2. Explain 5 different aspects of ecological niche of hip ...
community interactions
... coloration that allows an otherwise visible organism or object to remain indiscernible from the surrounding environment. ...
... coloration that allows an otherwise visible organism or object to remain indiscernible from the surrounding environment. ...
3.4 Ecosystem Changes
... b. endangered - too few individuals, extinction soon Species need 10,000 organisms to maintain evolutionary potential. c. extinct - means gone forever - when numbers drop below 1,000 for animal species and 120 species for plants, the species is considered extinct because of the problems finding mate ...
... b. endangered - too few individuals, extinction soon Species need 10,000 organisms to maintain evolutionary potential. c. extinct - means gone forever - when numbers drop below 1,000 for animal species and 120 species for plants, the species is considered extinct because of the problems finding mate ...
4-1 What roles do species play in an ecosystem
... The size of a species’ population is influenced by the following four variables: births, deaths, immigration, and emigration. CONCEPT 4-5A Population size increases because of births and immigration, and decreases through deaths and emigration. CONCEPT 4-5B The average number of children born to wom ...
... The size of a species’ population is influenced by the following four variables: births, deaths, immigration, and emigration. CONCEPT 4-5A Population size increases because of births and immigration, and decreases through deaths and emigration. CONCEPT 4-5B The average number of children born to wom ...
How Populations Grow - Brookwood High School
... B. Population growth: increase in size of population with time. ...
... B. Population growth: increase in size of population with time. ...