Fundamental niche - Gull Lake Community Schools
... --when sea stars are present, a variety of species are able to live in the same area that the mussels live (intertidal zone) Ex. sea otters (eat sea urchins) --sea urchins eat kelp --kelp forests provide habitat for many aquatic animals --predict what would happen if the sea otters were removed fr ...
... --when sea stars are present, a variety of species are able to live in the same area that the mussels live (intertidal zone) Ex. sea otters (eat sea urchins) --sea urchins eat kelp --kelp forests provide habitat for many aquatic animals --predict what would happen if the sea otters were removed fr ...
Section 4.2 Powerpoint
... IMPORTANT WAYS IN WHICH ORGANISMS INTERACT. Intraspecific competition - occurring within one species Interspecific competition - occurring between species ...
... IMPORTANT WAYS IN WHICH ORGANISMS INTERACT. Intraspecific competition - occurring within one species Interspecific competition - occurring between species ...
Population Ecology
... A. ________________ – populations grow in number by birth or __________________ (going into an area). B ________________ – populations decrease in number by death or __________________ (leaving an area). C. Calculating percentage population change: Percent change = change in population X 100 % Total ...
... A. ________________ – populations grow in number by birth or __________________ (going into an area). B ________________ – populations decrease in number by death or __________________ (leaving an area). C. Calculating percentage population change: Percent change = change in population X 100 % Total ...
Invasive Species 2010-2011
... those that evolved within the ecosystems where they are found. Natural controls to limit: ...
... those that evolved within the ecosystems where they are found. Natural controls to limit: ...
22-3 interactions among living things notes
... specific living conditions. • An organism’s particular role, or how it makes its living is called its niche. ...
... specific living conditions. • An organism’s particular role, or how it makes its living is called its niche. ...
Part 1 - glenbrook s hs
... How do organisms interact in a community? Properties of a community: • Diversity - variety of different kinds of organisms - richness and relative abundance of organisms (see left) • Form of Vegetation -types and features of plants determine kinds of animals in a community • Stability - community’s ...
... How do organisms interact in a community? Properties of a community: • Diversity - variety of different kinds of organisms - richness and relative abundance of organisms (see left) • Form of Vegetation -types and features of plants determine kinds of animals in a community • Stability - community’s ...
Evolution
... Extinct: When no more individuals of a species remain. Biodiversity: The variety of living things. It is measured as the differences between individuals of the same species, or the number of different species in an ecosystem. A6 ...
... Extinct: When no more individuals of a species remain. Biodiversity: The variety of living things. It is measured as the differences between individuals of the same species, or the number of different species in an ecosystem. A6 ...
Lecture 10
... Mechanisms of Competition • Species can compete directly by fighting to gain access to resources (interference competition) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EOB5S5IXCFg&feature=related ...
... Mechanisms of Competition • Species can compete directly by fighting to gain access to resources (interference competition) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EOB5S5IXCFg&feature=related ...
APES 9 Week Review Sheet
... Coevolution: species evolve together (symbiosis, mutualism, parasitism, commensalism) Parasitism: take resources from another while keeping it alive Symbiosis: close association between organism (mutualism, parasitism, commensalism) Mutualism: symbiosis where both species benefit Fundamental Niche: ...
... Coevolution: species evolve together (symbiosis, mutualism, parasitism, commensalism) Parasitism: take resources from another while keeping it alive Symbiosis: close association between organism (mutualism, parasitism, commensalism) Mutualism: symbiosis where both species benefit Fundamental Niche: ...
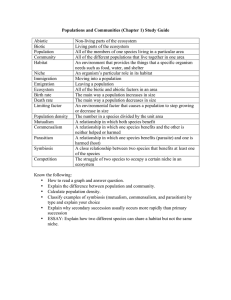
Populations and Communities (Chapter 1) Study Guide Abiotic Non
... An environment that provides the things that a specific organism needs such as food, water, and shelter An organism’s particular role in its habitat Moving into a population Leaving a population All of the biotic and abiotic factors in an area The main way a population increases in size The main way ...
... An environment that provides the things that a specific organism needs such as food, water, and shelter An organism’s particular role in its habitat Moving into a population Leaving a population All of the biotic and abiotic factors in an area The main way a population increases in size The main way ...
Community Ecology
... As global climates are shifted it may change the dynamics in local communities I.e. increased production in some places, decreased production in others ...
... As global climates are shifted it may change the dynamics in local communities I.e. increased production in some places, decreased production in others ...
Population - AP Subjects
... Food, predation, disease, migration, parasitism affect species population o Population Growth J shaped curve = exponential growth r-selected species (“reproduce rapidly like rabbits”) S shaped curve = logistic growth K-selected species o Survivorship Curve Type I- Death greatest at old a ...
... Food, predation, disease, migration, parasitism affect species population o Population Growth J shaped curve = exponential growth r-selected species (“reproduce rapidly like rabbits”) S shaped curve = logistic growth K-selected species o Survivorship Curve Type I- Death greatest at old a ...
Unit 6 Ecology Study Guide Behavioral ecology: study of interaction
... Survivorship curves: show survival rates for different-aged members of a population o Type I: live long life, until age is reached where death rate increases rapidly – humans, large mammals o Type II: constant death rate across the age spectrum – lizards, small mammals o Type III: steep downward dea ...
... Survivorship curves: show survival rates for different-aged members of a population o Type I: live long life, until age is reached where death rate increases rapidly – humans, large mammals o Type II: constant death rate across the age spectrum – lizards, small mammals o Type III: steep downward dea ...
Species Interactions in Biological Communities
... The Viceroy butterfly uses mimicry to look like the Monarch butterfly. Can you tell them apart? ...
... The Viceroy butterfly uses mimicry to look like the Monarch butterfly. Can you tell them apart? ...
Population Ecology
... type of growth happens when resources are limited. As the population grows, births decline and death rises. Eventually birth=death so the population stops ...
... type of growth happens when resources are limited. As the population grows, births decline and death rises. Eventually birth=death so the population stops ...
Ecology Test Study Guide: Students will be expected to… Identify
... Ecology Test Study Guide: Students will be expected to… ...
... Ecology Test Study Guide: Students will be expected to… ...
Document
... (considering the logarithm of body size relative to that of the autotroph). The coefficients μ and σγ represent the optimal trait ratio of predator to prey and the dietary breadth of the predator. The natural mortality is also assumed to be trait-mediated, Di = d0exp(-ri/4) (Peters, 1983). The inten ...
... (considering the logarithm of body size relative to that of the autotroph). The coefficients μ and σγ represent the optimal trait ratio of predator to prey and the dietary breadth of the predator. The natural mortality is also assumed to be trait-mediated, Di = d0exp(-ri/4) (Peters, 1983). The inten ...
AP® Biology Scoring Guidelines Question 5 According to fossil
... 4. Identification of the niche “Competitive Exclusion Principle” (1 point): by name or description. (c) Predict the population density of species C in 2014. Provide a biological explanation for your prediction. (2 points) 1. Prediction (1 point): The population will increase, decrease, or stabilize ...
... 4. Identification of the niche “Competitive Exclusion Principle” (1 point): by name or description. (c) Predict the population density of species C in 2014. Provide a biological explanation for your prediction. (2 points) 1. Prediction (1 point): The population will increase, decrease, or stabilize ...
AP Biology: Chapter 53-Community Ecology Give the definition and
... Effects on population density Example Predation Herbivory Parasitism Disease Mutualism Commensalism ...
... Effects on population density Example Predation Herbivory Parasitism Disease Mutualism Commensalism ...
Species Interaction
... Symbiosis and Adaptations (No picture necessary) Predation Parasitism Competition Mutualism Commensalism ...
... Symbiosis and Adaptations (No picture necessary) Predation Parasitism Competition Mutualism Commensalism ...
Ecology Unit Test review
... Know the following terms/processes o Populations, communities, ecosystems o Survivorship curves o Population growth – factors that attribute to growth and decline o Age structures o Carrying capacity o Density dependent/independent factors o Competition, interspecific competition o Symbiosis o Mut ...
... Know the following terms/processes o Populations, communities, ecosystems o Survivorship curves o Population growth – factors that attribute to growth and decline o Age structures o Carrying capacity o Density dependent/independent factors o Competition, interspecific competition o Symbiosis o Mut ...
Bio 4 - Study Guide 4
... What is a population? What is density? What are density dependent and density independent factors? What is dispersion? What are the three types of dispersion patterns? Which is the most common? What are the two types of population growth models? What is carrying capacity? What are the two types of o ...
... What is a population? What is density? What are density dependent and density independent factors? What is dispersion? What are the three types of dispersion patterns? Which is the most common? What are the two types of population growth models? What is carrying capacity? What are the two types of o ...