Chapter 5
... – Can grow two feet per day – Require cool water – Host many species – high biodiversity – Fight beach erosion – Algin ...
... – Can grow two feet per day – Require cool water – Host many species – high biodiversity – Fight beach erosion – Algin ...
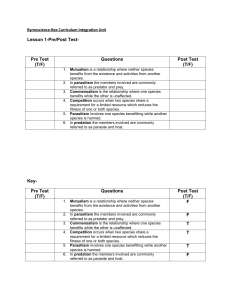
Unit 7 practice test
... b. Has a high r c. Grows fastest at an intermediate population density d. Grows fastest as it approaches carrying capacity ...
... b. Has a high r c. Grows fastest at an intermediate population density d. Grows fastest as it approaches carrying capacity ...
species. - Kelso High School
... Biodiversity within an ecosystem refers to the range of species present within that ecosystem’s community. ...
... Biodiversity within an ecosystem refers to the range of species present within that ecosystem’s community. ...
Lecture 8 - Community Interactions and Niche Diversity
... 4. The main consequence of competition between two species is competitive exclusion. a. Two species compete only if their niches overlap. b. Two species with similar requirements cannot coexist in the same community. The more efficient species should drive other to extinction. c. Test with 2 closely ...
... 4. The main consequence of competition between two species is competitive exclusion. a. Two species compete only if their niches overlap. b. Two species with similar requirements cannot coexist in the same community. The more efficient species should drive other to extinction. c. Test with 2 closely ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... grown separately. In the third graph, they were grown in the same test tube. Explain the difference between the first two graphs and the third graph and how the third graph demonstrates competitive exclusion. ...
... grown separately. In the third graph, they were grown in the same test tube. Explain the difference between the first two graphs and the third graph and how the third graph demonstrates competitive exclusion. ...
evolution: natural selection
... • Share common ancestor – as organisms divide and evolve they split from common ancestors which helps explain similarities between them; gives rise to new species • Evolutionary change is slow – supported by fossil record and lack of sudden appearance of new species ...
... • Share common ancestor – as organisms divide and evolve they split from common ancestors which helps explain similarities between them; gives rise to new species • Evolutionary change is slow – supported by fossil record and lack of sudden appearance of new species ...
limiting factor notes
... organisms can adapt to changes (in available resources and their environment) and reproduce If an entire species is unable to respond to changes, it could face extinction Extinct species – no living organism of the species exists Endangered species – small population of the species exists with ...
... organisms can adapt to changes (in available resources and their environment) and reproduce If an entire species is unable to respond to changes, it could face extinction Extinct species – no living organism of the species exists Endangered species – small population of the species exists with ...
PowerPoint slide show on ecological modelling concepts
... Forms of interaction - two species (say H and S) are linked by: • neutralism • competition • mutualism • commensalism • amensalism • parasitism • predation ...
... Forms of interaction - two species (say H and S) are linked by: • neutralism • competition • mutualism • commensalism • amensalism • parasitism • predation ...
Competition, lecture 10a (extra)
... Within a community you have interactions among the species themselves that can lead to: Predation Symbiosis COMPETITION ...
... Within a community you have interactions among the species themselves that can lead to: Predation Symbiosis COMPETITION ...
Species interactions and symbiotic relationships
... Population – group of individuals of the same species living in the same area, potentially interacting ...
... Population – group of individuals of the same species living in the same area, potentially interacting ...
Chapter 19
... • Niche – all the ways in which an organism uses its habitat • Habitat – the place where an organism lives • Competition – when two organisms attempt to use the same resource – Interspecific – between two different species – Intraspecific – between the same species ...
... • Niche – all the ways in which an organism uses its habitat • Habitat – the place where an organism lives • Competition – when two organisms attempt to use the same resource – Interspecific – between two different species – Intraspecific – between the same species ...
POPULATION DYNAMICS
... Carrying capacity is dynamic; environmental conditions are always changing ...
... Carrying capacity is dynamic; environmental conditions are always changing ...
Types of Species Interactions
... Species interactions • In every ecosystem species interact in a variety of ways. – They can be positive (+) , negative (-) , or have no effect (0). • Each species develops adaptations to deal with these interactions. • If a species cannot adjust to it’s community members (two species in the same ni ...
... Species interactions • In every ecosystem species interact in a variety of ways. – They can be positive (+) , negative (-) , or have no effect (0). • Each species develops adaptations to deal with these interactions. • If a species cannot adjust to it’s community members (two species in the same ni ...
R - UNL Math
... ‘Theorem’: Without inter-specific competition (c_0 = 0) but with intra-specific competition (m_0 > 0), all species will eventually become competitive and coexist at an equilibrium state as the resources become sufficiently abundant. ‘Theorem’: With both types of competitions, competitive species can ...
... ‘Theorem’: Without inter-specific competition (c_0 = 0) but with intra-specific competition (m_0 > 0), all species will eventually become competitive and coexist at an equilibrium state as the resources become sufficiently abundant. ‘Theorem’: With both types of competitions, competitive species can ...
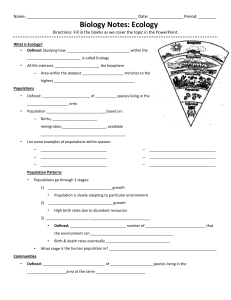
Biology Notes: Ecology
... 2. What are two reasons that populations will increase?__________________________ , ________________________ 3. What are two reasons that populations will decrease?_________________________ , ________________________ 4. What are factors that control population growth called? ______________________ ...
... 2. What are two reasons that populations will increase?__________________________ , ________________________ 3. What are two reasons that populations will decrease?_________________________ , ________________________ 4. What are factors that control population growth called? ______________________ ...