The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
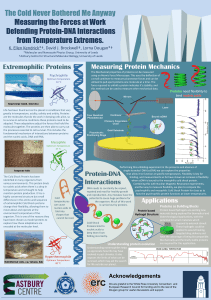
... to survive in extreme conditions these proteins need to be adapted. These adaptations adjust the forces that hold the molecules together. The proteins are then able to carry out the processes essential to cell survival. This includes the fundamental mechanism of interactions between proteins and the ...
... to survive in extreme conditions these proteins need to be adapted. These adaptations adjust the forces that hold the molecules together. The proteins are then able to carry out the processes essential to cell survival. This includes the fundamental mechanism of interactions between proteins and the ...
Supplemental Material
... primers FrzG-C-1 and wspR-6, which flank the non-coding region between wspF and wspR. Primers wspR-1 and wspR-5, which lie within wspR, were used as controls to confirm transcription of wspR and accuracy of the RT-PCR. The location and orientation of primers are marked as arrows. The expected PCR pr ...
... primers FrzG-C-1 and wspR-6, which flank the non-coding region between wspF and wspR. Primers wspR-1 and wspR-5, which lie within wspR, were used as controls to confirm transcription of wspR and accuracy of the RT-PCR. The location and orientation of primers are marked as arrows. The expected PCR pr ...
What is the Structure of DNA?
... Results of their experiment can only be explained by the semiconservative model. If it was conservative, the first generation of individuals would have all been high or low density, but not intermediate. ...
... Results of their experiment can only be explained by the semiconservative model. If it was conservative, the first generation of individuals would have all been high or low density, but not intermediate. ...
DNA Keychains: Spell Your Initials Using the Genetic Code!!!!! This
... 2. If your last bead was a sugar, then you will need to add a phosphate bead. Add a phosphate bead to each strand. Make sure to thread BOTH wires through these beads. 3. If your l ...
... 2. If your last bead was a sugar, then you will need to add a phosphate bead. Add a phosphate bead to each strand. Make sure to thread BOTH wires through these beads. 3. If your l ...
Microbial GeneticsIII MB - E
... (1) DNA topoisomerases (2) D-loops (3) 5? ? 3? exonucleases 18Which of the following is mismatched? (1) Semiconservative replication: hybrid of original template plus new polynucleotide strand (2) Displacement replication: D-loop (3) Linking number: the number of times one strand crosses the other i ...
... (1) DNA topoisomerases (2) D-loops (3) 5? ? 3? exonucleases 18Which of the following is mismatched? (1) Semiconservative replication: hybrid of original template plus new polynucleotide strand (2) Displacement replication: D-loop (3) Linking number: the number of times one strand crosses the other i ...
Document
... The other crucial contributing factor is that interaction between two hydrophobic surfaces in a solution reduces the hydrophobic surface area and therby INCREASES the number of water-to-water solvent hydrogen bonds!!! ...
... The other crucial contributing factor is that interaction between two hydrophobic surfaces in a solution reduces the hydrophobic surface area and therby INCREASES the number of water-to-water solvent hydrogen bonds!!! ...
Challenging traditional approaches to
... transducer. 'r' represents the 'read' symbol and 'p' represents the 'printed‘ symbol. B. Transition rules of this transducer. For each transition rule there is a transition molecule. ...
... transducer. 'r' represents the 'read' symbol and 'p' represents the 'printed‘ symbol. B. Transition rules of this transducer. For each transition rule there is a transition molecule. ...
Spring Semester Test Review KEY
... Evidence that considers homologous structures, vestigial organs and embryological development of organisms and how these may be linked to a common ancestor. Evidence that shows how organisms living widely apart may be similar because they shared a common ancestor. ...
... Evidence that considers homologous structures, vestigial organs and embryological development of organisms and how these may be linked to a common ancestor. Evidence that shows how organisms living widely apart may be similar because they shared a common ancestor. ...
The human genome of is found where in the human body?
... Living things are extremely complex • Cellular machinery is sophisticated and required for life • Cellular machinery is made largely of proteins • Blueprints for all cellular machinery are contained in genes • Genes are inherited from parents • Humans have ~30,000 genes ...
... Living things are extremely complex • Cellular machinery is sophisticated and required for life • Cellular machinery is made largely of proteins • Blueprints for all cellular machinery are contained in genes • Genes are inherited from parents • Humans have ~30,000 genes ...
Section 8 – The human genome project
... 5. Different restriction enzymes cut the DNA at different points as each recognises a particular short sequence of bases occurring in the DNA. Where the sequence is recognised, the enzyme cuts the DNA so that it is cut into fragments. 6. By using combinations of restriction enzymes and working out ...
... 5. Different restriction enzymes cut the DNA at different points as each recognises a particular short sequence of bases occurring in the DNA. Where the sequence is recognised, the enzyme cuts the DNA so that it is cut into fragments. 6. By using combinations of restriction enzymes and working out ...
DNA PROFILING
... STAGES OF DNA PROFILING DNA is negatively charged so it is attracted to the positive end of the gel. The shorter DNA fragments move faster than the ...
... STAGES OF DNA PROFILING DNA is negatively charged so it is attracted to the positive end of the gel. The shorter DNA fragments move faster than the ...
dna testing workshop 2005
... a. Which cancers have the highest incidence of p53 mutation associated with them? b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated in human cancers? d. How does this information help us to design treatments for can ...
... a. Which cancers have the highest incidence of p53 mutation associated with them? b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated in human cancers? d. How does this information help us to design treatments for can ...
organic reading ws
... of many structures in organisms. Your contain large amounts of protein, Proteins are scattered throughout ...
... of many structures in organisms. Your contain large amounts of protein, Proteins are scattered throughout ...
Chapter 20: Biotechnology - Biology E
... The gene ampR makes E. coli cells resistant to the antibiotic ampicillin, while lacZ encodes the enzyme β-galactosidase, which hydrolyzes lactose. This enzyme can also hydrolyze a similar synthetic molecule called X-gal to form a blue product. The plasmid contains only one copy of the restriction si ...
... The gene ampR makes E. coli cells resistant to the antibiotic ampicillin, while lacZ encodes the enzyme β-galactosidase, which hydrolyzes lactose. This enzyme can also hydrolyze a similar synthetic molecule called X-gal to form a blue product. The plasmid contains only one copy of the restriction si ...
Replication Study Guide
... chromosome - the entire collection of a cell’s DNA, which contains all of the cell’s genetic information cytidine - one of the nucleotide bases in which cells store their genetic code. Cytidine bonds with guanosine in both DNA and RNA. DNA - the molecule that stores and encodes an organism’s genetic ...
... chromosome - the entire collection of a cell’s DNA, which contains all of the cell’s genetic information cytidine - one of the nucleotide bases in which cells store their genetic code. Cytidine bonds with guanosine in both DNA and RNA. DNA - the molecule that stores and encodes an organism’s genetic ...
Fundamentals of Biotechnology
... the bases found in nucleic acids to a pseudopeptide backbone. The normal phosphodiester backbone is entirely replaced with a ...
... the bases found in nucleic acids to a pseudopeptide backbone. The normal phosphodiester backbone is entirely replaced with a ...
Macromolecules College Notes
... amino acids are hooked together) ______________________- formed by hydrogen bonding between the amino acid R groups. (β-pleated sheets and α helix). ______________________ - formed when the polypeptide chain folds and the R groups of different amino acids form covalent and ionic bonds with each othe ...
... amino acids are hooked together) ______________________- formed by hydrogen bonding between the amino acid R groups. (β-pleated sheets and α helix). ______________________ - formed when the polypeptide chain folds and the R groups of different amino acids form covalent and ionic bonds with each othe ...
Restriction Enzyme Worksheet
... You may notice that the EcoR1 enzyme does not cut straight across the DNA molecule. When EcoR1 cuts DNA, it leaves single stranded “tails” called sticky ends, because they could stick (although not very tightly) to other segments of DNA that have been cut with the same enzyme. (Remember this trait o ...
... You may notice that the EcoR1 enzyme does not cut straight across the DNA molecule. When EcoR1 cuts DNA, it leaves single stranded “tails” called sticky ends, because they could stick (although not very tightly) to other segments of DNA that have been cut with the same enzyme. (Remember this trait o ...
Voices - Indiana University Bloomington
... to annotate cis-regulatory elements enabled a large number of recent epigenome mapping efforts across a myriad of cell types and organisms. The picture that emerges from these studies elucidates the astounding degree to which our genome, including the repetitive regions derived from transposon eleme ...
... to annotate cis-regulatory elements enabled a large number of recent epigenome mapping efforts across a myriad of cell types and organisms. The picture that emerges from these studies elucidates the astounding degree to which our genome, including the repetitive regions derived from transposon eleme ...
Types of Genetic Mutations
... Silent Mutations • Cause no detectable change in the corresponding protein sequence • Most amino acids are encoded by several different codons so sometimes a change in the third base of a codon will have no affect on which amino acid in encoded. • For example, if the third base in the TCT codon for ...
... Silent Mutations • Cause no detectable change in the corresponding protein sequence • Most amino acids are encoded by several different codons so sometimes a change in the third base of a codon will have no affect on which amino acid in encoded. • For example, if the third base in the TCT codon for ...
File
... type of incorrect base., which then cleaves the Nglycosyl bond to remove the defective nitrogen base and generating an apurinicor apyrimidinic (AP) site. Different DNA glycosylasesrecognize different types of defective bases. Each DNA glycosylase is generally specific for one type of lesion. Uracil ...
... type of incorrect base., which then cleaves the Nglycosyl bond to remove the defective nitrogen base and generating an apurinicor apyrimidinic (AP) site. Different DNA glycosylasesrecognize different types of defective bases. Each DNA glycosylase is generally specific for one type of lesion. Uracil ...
Human Physiology Quiz Questions: 1) Purines degrade into what
... 8) What two membrane transporters absorb monosaccharides into the absorptive cell? 9) What is ‘gluconeogenesis’? 10) What causes salivary amylase inactivation? 11) What two monosaccharides is sucrose made up of and what enzyme digests sucrose? 12) What two monosaccharides is maltose made up of and w ...
... 8) What two membrane transporters absorb monosaccharides into the absorptive cell? 9) What is ‘gluconeogenesis’? 10) What causes salivary amylase inactivation? 11) What two monosaccharides is sucrose made up of and what enzyme digests sucrose? 12) What two monosaccharides is maltose made up of and w ...
One Gene - One Polypeptide
... each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids that are eventually folded or joined together in the cell to form proteins. Recall that most proteins usually consist of between 2 and 4 polypeptide chains bonded together. These proteins form the molecular basis of our pheno ...
... each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids that are eventually folded or joined together in the cell to form proteins. Recall that most proteins usually consist of between 2 and 4 polypeptide chains bonded together. These proteins form the molecular basis of our pheno ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.























