One Gene - One Polypeptide
... each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids that are eventually folded or joined together in the cell to form proteins. Recall that most proteins usually consist of between 2 and 4 polypeptide chains bonded together. These proteins form the molecular basis of our pheno ...
... each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids that are eventually folded or joined together in the cell to form proteins. Recall that most proteins usually consist of between 2 and 4 polypeptide chains bonded together. These proteins form the molecular basis of our pheno ...
GeneChip Hybridization
... Optimized Hybridization is the process of single stranded nucleic acids binding to another strand with identically complement sequence [We hope] ...
... Optimized Hybridization is the process of single stranded nucleic acids binding to another strand with identically complement sequence [We hope] ...
three possibile models for replication
... they don’t technically “shift the reading frame.” In other words, they do not change the groupings of codons or the amino acids after the mutation.*** ***Note: An example of a frameshift mutation is shown in the image on the next page.*** ...
... they don’t technically “shift the reading frame.” In other words, they do not change the groupings of codons or the amino acids after the mutation.*** ***Note: An example of a frameshift mutation is shown in the image on the next page.*** ...
Uses for transgenic organisms (also called GMO`s or genetically
... testing. Mice given human Huntington’s disease and Alzheimer’s have led to breakthroughs in treatments. Pigs (milk and chickens soon) with omega-3 fatty acids (good for the heart). The natural source of omega-3 fatty acids is some oily fishes like tuna and salmon, but they are overharvested and of ...
... testing. Mice given human Huntington’s disease and Alzheimer’s have led to breakthroughs in treatments. Pigs (milk and chickens soon) with omega-3 fatty acids (good for the heart). The natural source of omega-3 fatty acids is some oily fishes like tuna and salmon, but they are overharvested and of ...
PLASMID ISOLATIONS (MINIPREPS)
... between the stacked bases in DNA, this is termed intercalation. As it does this it forces the bases apart, causing the DNA to unwind and lengthen. However, less of the dye can intercalate into supercoiled DNA than in linear DNA since it is in a covalently closed circle. This is because the ethidium ...
... between the stacked bases in DNA, this is termed intercalation. As it does this it forces the bases apart, causing the DNA to unwind and lengthen. However, less of the dye can intercalate into supercoiled DNA than in linear DNA since it is in a covalently closed circle. This is because the ethidium ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes 2015
... attachment site proteins • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
... attachment site proteins • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
Restriction Enzymes, Gel Electrophoresis and Mapping DNA
... sequences are specific, they should occur at specific locations on every, identical DNA molecule. • Therefore, digestion products are reproducible. • Therefore, we can use the recognition sequence as a “flag” to mark a map. ...
... sequences are specific, they should occur at specific locations on every, identical DNA molecule. • Therefore, digestion products are reproducible. • Therefore, we can use the recognition sequence as a “flag” to mark a map. ...
BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE for Ms.Reep by Keshara Senanayake BIO
... abiotically produced vesicles can reproduce on their own and they can increase in size without dilution of their contents experiments have shown they have a selectively permeable bilayer and can perform metabolic reactions using an external source of reagents First genetic material was mostly li ...
... abiotically produced vesicles can reproduce on their own and they can increase in size without dilution of their contents experiments have shown they have a selectively permeable bilayer and can perform metabolic reactions using an external source of reagents First genetic material was mostly li ...
Document
... • When mRNA leaves nucleus it has a blueprint of DNA’s instructions. • mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm • Ribosomes read the blueprint on mRNA. ...
... • When mRNA leaves nucleus it has a blueprint of DNA’s instructions. • mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm • Ribosomes read the blueprint on mRNA. ...
Print PDF
... isms and new species are still being discove red. Based on Darwin’s theory of evolution, which of the following best describes how millions of species have developed? ...
... isms and new species are still being discove red. Based on Darwin’s theory of evolution, which of the following best describes how millions of species have developed? ...
topic 2 powerpoint
... • Different types of cells use different genes to make the polypeptides that are specific to them. • Humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes in each cell. ...
... • Different types of cells use different genes to make the polypeptides that are specific to them. • Humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes in each cell. ...
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
... What is gene? Genes – the information-containing elements that determine the characteristics of a species as a whole and of the individuals within it. A gene is usually defined as a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for making a particular protein (or, in some cases, a set of closely re ...
... What is gene? Genes – the information-containing elements that determine the characteristics of a species as a whole and of the individuals within it. A gene is usually defined as a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for making a particular protein (or, in some cases, a set of closely re ...
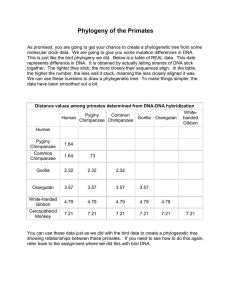
Phylogeny of the Primates
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
36_sequencing
... • Make a DNA copy (“cDNA”) of the mRNA using Reverse Transcriptase • Use that to probe for clones that contain coding sequences ...
... • Make a DNA copy (“cDNA”) of the mRNA using Reverse Transcriptase • Use that to probe for clones that contain coding sequences ...
Connectivity of Earth`s largest biomes: the deep Atlantic to the
... • Method used to identify organisms • Much like assigning a “numerical barcode” to shopping item • Sequence a ~600 base pair segment of DNA to reveal an organism “barcode” • Organisms have unique DNA sequences for each species ...
... • Method used to identify organisms • Much like assigning a “numerical barcode” to shopping item • Sequence a ~600 base pair segment of DNA to reveal an organism “barcode” • Organisms have unique DNA sequences for each species ...
Fluorescent dye, SYBR Green, is incorporated into PCR reaction
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
BIOLOGY Cells Unit GUIDE SHEET
... 1. What are some ways in which genes are altered and analyzed in organisms? 2. What are the risks and benefits of altering the genes of existing organisms? ...
... 1. What are some ways in which genes are altered and analyzed in organisms? 2. What are the risks and benefits of altering the genes of existing organisms? ...
General Biochemistry Exam – 2002 Excess Acetyl
... replaced with T in humans, the enzyme improved its ability, and when T was replaced with S in the frog, its affinity decreased. On the other hand, when a mutation occurred and S or T was replaced with valine (V) the enzyme lost catalytic activity. Mark the correct answer: a. The S and the T are foun ...
... replaced with T in humans, the enzyme improved its ability, and when T was replaced with S in the frog, its affinity decreased. On the other hand, when a mutation occurred and S or T was replaced with valine (V) the enzyme lost catalytic activity. Mark the correct answer: a. The S and the T are foun ...
learning objectives
... A. The first step of genetic engineering is to cleave the DNA that the geneticist wishes to transfer. B. This process involves the use of restriction enzymes that bind specific sequences of nucleotides and split the DNA in that position. C. Since DNA is made up of complementary bases, both strands d ...
... A. The first step of genetic engineering is to cleave the DNA that the geneticist wishes to transfer. B. This process involves the use of restriction enzymes that bind specific sequences of nucleotides and split the DNA in that position. C. Since DNA is made up of complementary bases, both strands d ...
Exam3-1406_Fall2007ch9-10-11.doc
... C) an animal cell undergoing cytokinesis D) a plant cell in metaphase E) a plant cell undergoing cytokinesis 50) Cytokinesis refers to the division of the A) cytoplasm. B) nucleus. C) mitochondria. D) centrioles. E) chromosomes. 51) Sister chromatids are A) duplicate chromosomes held together by a ...
... C) an animal cell undergoing cytokinesis D) a plant cell in metaphase E) a plant cell undergoing cytokinesis 50) Cytokinesis refers to the division of the A) cytoplasm. B) nucleus. C) mitochondria. D) centrioles. E) chromosomes. 51) Sister chromatids are A) duplicate chromosomes held together by a ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Base Composition of Some
... The mean base compositions are seen to cover a wide range (35'1-5706 % GC) indicating a pronounced genetic heterogeneity among the species investigated. The lowest % GC values are seen for Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. clausenii and C. stellatoidea. These four species which, from a conventiona ...
... The mean base compositions are seen to cover a wide range (35'1-5706 % GC) indicating a pronounced genetic heterogeneity among the species investigated. The lowest % GC values are seen for Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. clausenii and C. stellatoidea. These four species which, from a conventiona ...
Living things are energy rich complex chemical structures
... endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
... endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.