What you need to Know for Chapter 1 Quiz
... o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypeptides? o Describe the general structure of amino acids – what is the R group? o Describe the 4 levels ...
... o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypeptides? o Describe the general structure of amino acids – what is the R group? o Describe the 4 levels ...
Biotechnology Labs Makeup Assignment
... and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how does electrophoresis work? On what basis does it separate mixtures of molecules? What kinds of things could you use electrophoresis to do? (1 page) DNA Crime Scene Lab Only: -what are RFLP’s? How do they relate to doing ...
... and what is the function of each reagent? (1 page) Dye/Indicator Lab Only: -how does electrophoresis work? On what basis does it separate mixtures of molecules? What kinds of things could you use electrophoresis to do? (1 page) DNA Crime Scene Lab Only: -what are RFLP’s? How do they relate to doing ...
BSCA Questions: Biochemistry
... Steroid hormones are typically made from ____. A. Arachidonic acid B. Tyrosine C. Cholesterol D. Second messengers ...
... Steroid hormones are typically made from ____. A. Arachidonic acid B. Tyrosine C. Cholesterol D. Second messengers ...
Test 2
... 9. In class you were shown that NADH generates 2.5 ATP and each FADH2 generates 1.5 ATP. A. (5 points) Show me the math. For each complex involved in electron transport, tell me how many protons are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix. Also, for the ATPsynthase, how many protons must be let into ...
... 9. In class you were shown that NADH generates 2.5 ATP and each FADH2 generates 1.5 ATP. A. (5 points) Show me the math. For each complex involved in electron transport, tell me how many protons are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix. Also, for the ATPsynthase, how many protons must be let into ...
Unit Plan Template - Gates County Schools
... Bio.3.2.1 Explain the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction and genetic variation. Bio.3.2 Understand how the environment, and/or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits. Bio.3.2.2 Predict offspring ratios based on a variety of inheritance patterns (including: domina ...
... Bio.3.2.1 Explain the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction and genetic variation. Bio.3.2 Understand how the environment, and/or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits. Bio.3.2.2 Predict offspring ratios based on a variety of inheritance patterns (including: domina ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... genetic information). The 21st century is an era of life science. Lots of wonders are being created, and explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of c ...
... genetic information). The 21st century is an era of life science. Lots of wonders are being created, and explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of c ...
1. There are many different views on the ethics of reproductive
... There are many different views on the ethics of reproductive cloning in humans. Which is a valid argument against cloning in humans? A. ...
... There are many different views on the ethics of reproductive cloning in humans. Which is a valid argument against cloning in humans? A. ...
Section 11.2 Summary – pages 288 - 295
... • The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of messenger RNA acts as a genetic message, the complete information for the building of a protein. • As you know, proteins contain chains of amino acids. You could say that the language of proteins uses an alphabet of amino acids. ...
... • The nucleotide sequence transcribed from DNA to a strand of messenger RNA acts as a genetic message, the complete information for the building of a protein. • As you know, proteins contain chains of amino acids. You could say that the language of proteins uses an alphabet of amino acids. ...
Mutations - TeacherWeb
... What do mutations do to the protein? Are they all bad or all good? The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called ...
... What do mutations do to the protein? Are they all bad or all good? The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called ...
Name Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological
... 3. Anabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called dehydration synthesis; catabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called hydrolysis. Compare the outcomes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, with an example for each. 4. How is it possible to construct millions of different macromolecules from only a few ...
... 3. Anabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called dehydration synthesis; catabolic enzymes catalyze reactions called hydrolysis. Compare the outcomes of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, with an example for each. 4. How is it possible to construct millions of different macromolecules from only a few ...
Word Work File L_2.tmp
... hydroxyl at another end. 7. The two DNA strands are antiparallel, that is, their sugar phosphate backbones run in opposite directions. 8. DNA polymerases catalyze the linking together of the nucleotide subunits. There are at least eleven DNA polymerases involved in eukaryote replication. 9. Nucleoti ...
... hydroxyl at another end. 7. The two DNA strands are antiparallel, that is, their sugar phosphate backbones run in opposite directions. 8. DNA polymerases catalyze the linking together of the nucleotide subunits. There are at least eleven DNA polymerases involved in eukaryote replication. 9. Nucleoti ...
The chemical constituents of cells
... Nucleotide is formed by further condensation between nucleoside and phosphoric acid. Different nucleotides are formed according to the sugars and base used. ...
... Nucleotide is formed by further condensation between nucleoside and phosphoric acid. Different nucleotides are formed according to the sugars and base used. ...
Chemistry 100 Name
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
Name Date Ch 3. Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... Concept 3.2 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 7. Explain the difference between a dehydration (condensation) reaction and a hydrolysis reaction. Give an example of each. ...
... Concept 3.2 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 7. Explain the difference between a dehydration (condensation) reaction and a hydrolysis reaction. Give an example of each. ...
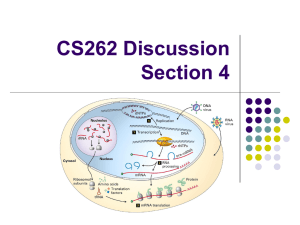
CS262 Discussion Section 4
... passed on to the next generation. A mutation in a somatic cell is not transmitted to the organism’s offspring. ...
... passed on to the next generation. A mutation in a somatic cell is not transmitted to the organism’s offspring. ...
pdf version
... published in the revue Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. Each of our cells contains two huge DNA strands, segmented into parts that are packaged within chromosomes. Each chromosome end, however, becomes vulnerable to specific enzymes that target accidental DNA breaks in need of repair. The cell ...
... published in the revue Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. Each of our cells contains two huge DNA strands, segmented into parts that are packaged within chromosomes. Each chromosome end, however, becomes vulnerable to specific enzymes that target accidental DNA breaks in need of repair. The cell ...
Bacterial Transformation of pGLO
... (catabolism) of food are good examples of highly regulated genes. For example, the sugar arabinose is both a source of energy and a source of carbon. • E. coli bacteria produce three enzymes (proteins) needed to digest arabinose as a food source. The genes which code for these enzymes are not expres ...
... (catabolism) of food are good examples of highly regulated genes. For example, the sugar arabinose is both a source of energy and a source of carbon. • E. coli bacteria produce three enzymes (proteins) needed to digest arabinose as a food source. The genes which code for these enzymes are not expres ...
Worksheet 16
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
... 1. What is the name of the individual units that make up the chain of polypeptides? ...
lipid3 - ChemEd DL
... There is almost no free space in the interior of the protein. The various sizes and shapes of the hydrophobic amino acids ensure that every space is filled. As in the interiors of water-soluble proteins, the polar hydrogen-bonding main-chain carbonyl and amine groups have to be kept satisfied by the ...
... There is almost no free space in the interior of the protein. The various sizes and shapes of the hydrophobic amino acids ensure that every space is filled. As in the interiors of water-soluble proteins, the polar hydrogen-bonding main-chain carbonyl and amine groups have to be kept satisfied by the ...
Gene Expression and DNA Copy Number Analysis in Plants
... with 650 mE of light. p-values based on the difference between both transgenic lines and wildtype control. * p#0.05. Where error bars are not visible they are smaller than the data points. Reprinted from Preuss SB, et al., Expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana BBX32 gene in soybean increases grain ...
... with 650 mE of light. p-values based on the difference between both transgenic lines and wildtype control. * p#0.05. Where error bars are not visible they are smaller than the data points. Reprinted from Preuss SB, et al., Expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana BBX32 gene in soybean increases grain ...
ppt link
... Dispersive replication: At completion, both strands of both double helices contain both original and newly synthesized material. ...
... Dispersive replication: At completion, both strands of both double helices contain both original and newly synthesized material. ...
Solutions to Molecular Biology Unit Exam
... and end at the stop codon. This is about 2600 nucleotides, which represents about 866 codons. SO the two proteins expected would be about 866 amino acids long and about 533 amino acids long. ...
... and end at the stop codon. This is about 2600 nucleotides, which represents about 866 codons. SO the two proteins expected would be about 866 amino acids long and about 533 amino acids long. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.