The Molecule of Life: DNA
... double helix: a twisted ladder Cells differentiate by turning on and off different genes. DNA is looped and folded so long stretches can be fit into a nucleus Inside the cell, DNA is found in the nucleus ...
... double helix: a twisted ladder Cells differentiate by turning on and off different genes. DNA is looped and folded so long stretches can be fit into a nucleus Inside the cell, DNA is found in the nucleus ...
VII. Molecular Biology Techniques
... Primers, small segments of DNA no more than 20-30 nucleotides long, added. Primers are complementary to segments of opposite strands of that flank the target ...
... Primers, small segments of DNA no more than 20-30 nucleotides long, added. Primers are complementary to segments of opposite strands of that flank the target ...
a15 GenesFormFunc
... • Although mutations are usually lethal, – They are the source of the rich diversity of genes in the living world. – They contribute to the process of evolution by natural selection. ...
... • Although mutations are usually lethal, – They are the source of the rich diversity of genes in the living world. – They contribute to the process of evolution by natural selection. ...
DNA Recombinations
... The major tools of recombinant DNA technology are bacterial enzymes called restriction enzymes. Each enzyme recognizes a short, specific nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules, and cuts the backbones of the molecules at that sequence. The result is a set of doublestranded DNA fragments with singlestra ...
... The major tools of recombinant DNA technology are bacterial enzymes called restriction enzymes. Each enzyme recognizes a short, specific nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules, and cuts the backbones of the molecules at that sequence. The result is a set of doublestranded DNA fragments with singlestra ...
Aim
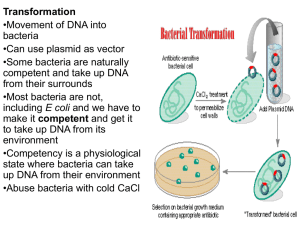
... Transformation (genetic transformation) is a process describing a host cell takes up an exogenous DNA / gene. If the host cell can express the introduced gene, it will then acquire a new trait. As ligation, transformation and the whole DNA cloning process may not be completely efficient and always s ...
... Transformation (genetic transformation) is a process describing a host cell takes up an exogenous DNA / gene. If the host cell can express the introduced gene, it will then acquire a new trait. As ligation, transformation and the whole DNA cloning process may not be completely efficient and always s ...
DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... or enzymes that destroy DNA are present in the cell’s cytoplasm. They are there to protect the cell from invasion by viruses. Once the nuclear membrane is destroyed by the soap the DNA is now susceptible to the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, these enzymes are temperature sensitive and ...
... or enzymes that destroy DNA are present in the cell’s cytoplasm. They are there to protect the cell from invasion by viruses. Once the nuclear membrane is destroyed by the soap the DNA is now susceptible to the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, these enzymes are temperature sensitive and ...
Genetic Engineering - Needham Public Schools
... Selective Breeding • Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits ...
... Selective Breeding • Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits ...
Cloning and selection
... When do the cutting and sticking of plasmid and foreign DNA there are several possible outcomes 1. Successful sticking of the plasmid and foreign DNA 2. Recircularization of plasmid without the foreign DNA 3. Circulization of plasmid with other plasmids or several inserts to make huge circular mol ...
... When do the cutting and sticking of plasmid and foreign DNA there are several possible outcomes 1. Successful sticking of the plasmid and foreign DNA 2. Recircularization of plasmid without the foreign DNA 3. Circulization of plasmid with other plasmids or several inserts to make huge circular mol ...
Biology 155 Practice Exam 3 Name
... 28. If you were to allow a culture of bacteria to replicate for many generations in a medium containing heavy nitrogen (15N) and then transferred a sample of your culture to a medium containing light nitrogen (14N) and allowed the cells to replicate their DNA exactly 2 times, what proportion of the ...
... 28. If you were to allow a culture of bacteria to replicate for many generations in a medium containing heavy nitrogen (15N) and then transferred a sample of your culture to a medium containing light nitrogen (14N) and allowed the cells to replicate their DNA exactly 2 times, what proportion of the ...
Year 13 Winter Revision Guide
... Nucleic acids as condensation products of nucleotides and the release of these on hydrolysis; Nucleotides as condensation products of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base and inorganic phosphate; Helical structure of DNA in terms of two antiparallel chains with specific base pairings; Compari ...
... Nucleic acids as condensation products of nucleotides and the release of these on hydrolysis; Nucleotides as condensation products of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base and inorganic phosphate; Helical structure of DNA in terms of two antiparallel chains with specific base pairings; Compari ...
problem set
... Paralogous genes are derived from gene duplications and have diverged to perform different functions in a given organism. Orthologous genes typically perform the same function in different organisms, and have diverged in sequence due to mutations associated with speciation (Fig. 6.26b). The complexi ...
... Paralogous genes are derived from gene duplications and have diverged to perform different functions in a given organism. Orthologous genes typically perform the same function in different organisms, and have diverged in sequence due to mutations associated with speciation (Fig. 6.26b). The complexi ...
Test 4
... Apatamer An RNA molecule that will bind some other small molecule restrictive ground state. A cell in which most of the genes are turned off unless specifically turned on. 2. Describe the system by which a tRNA gets charged with an amino acid. In your description be sure to included details like: Wh ...
... Apatamer An RNA molecule that will bind some other small molecule restrictive ground state. A cell in which most of the genes are turned off unless specifically turned on. 2. Describe the system by which a tRNA gets charged with an amino acid. In your description be sure to included details like: Wh ...
PART
... m. RNA is similar to DNA except it has a single polynucleotide chain, has ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has uracil instead of thymine. ...
... m. RNA is similar to DNA except it has a single polynucleotide chain, has ribose instead of deoxyribose, and has uracil instead of thymine. ...
Genetics 314 – Spring 2007
... genetic information in a cell. Describe one of these experiments and how the results demonstrated that DNA carried genetic information. The two experiments were: 1) The Avery, Macleod and McCarty experiment where they repeated the Griffith’s experiment with heat-killed Pneumoccocus but used enzymes ...
... genetic information in a cell. Describe one of these experiments and how the results demonstrated that DNA carried genetic information. The two experiments were: 1) The Avery, Macleod and McCarty experiment where they repeated the Griffith’s experiment with heat-killed Pneumoccocus but used enzymes ...
Unit 2 Terms
... fetus by removing and analyzing a sample of the fetal portion of the placenta In DNA, the separation of the two strands of the double helix. A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA A process of communication that deals with the occurrence or risk ...
... fetus by removing and analyzing a sample of the fetal portion of the placenta In DNA, the separation of the two strands of the double helix. A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence of DNA A process of communication that deals with the occurrence or risk ...
Chapter 5 - SchoolRack
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins Organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups 20 types of AAs that make up 1000s of different proteins AAs are linked together by peptide bonds ...
... Amino acids are the monomers of proteins Organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups 20 types of AAs that make up 1000s of different proteins AAs are linked together by peptide bonds ...
Virus - Homework Market
... The extreme simplicity of viruses eliminates most of the vulnerable features found in cellular organisms such as bacteria. Antibacterial products commonly attack cell walls, plasma membranes, and cytoplasm, none of which are present in viruses. Using two or three sentences, explain in your own words ...
... The extreme simplicity of viruses eliminates most of the vulnerable features found in cellular organisms such as bacteria. Antibacterial products commonly attack cell walls, plasma membranes, and cytoplasm, none of which are present in viruses. Using two or three sentences, explain in your own words ...
Document
... concern when designing primers • Actually not a single primer for each but a mixture of primers (oligoprimers) if the sequence of the target is not known • If amino acid sequence of gene product is used then degenerate primers must be used • Initial forward primer is GABTATGTTGTTGARTCTTCWGG B=G/T/C ...
... concern when designing primers • Actually not a single primer for each but a mixture of primers (oligoprimers) if the sequence of the target is not known • If amino acid sequence of gene product is used then degenerate primers must be used • Initial forward primer is GABTATGTTGTTGARTCTTCWGG B=G/T/C ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: Explain how an oxygen molecule obeys the octet rule. ANSWER: Oxygen has six electrons in its outer shell. When two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell, at least part of the time. Figure 2.11 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUEST ...
... BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: Explain how an oxygen molecule obeys the octet rule. ANSWER: Oxygen has six electrons in its outer shell. When two oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, each atom has eight electrons in its outer shell, at least part of the time. Figure 2.11 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUEST ...
2770 October 2007 Mid-Term Test
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.