
Presentation Slides
... PCR is used for a variety of different purposes in a multitude of fields. The one example I will be talking about, is forensics. Forensics is scientific tests or techniques used in connection with the detection of crime. So, for example, if a crime is committed inside of a house, the forensics offic ...
... PCR is used for a variety of different purposes in a multitude of fields. The one example I will be talking about, is forensics. Forensics is scientific tests or techniques used in connection with the detection of crime. So, for example, if a crime is committed inside of a house, the forensics offic ...
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is
... (B) synthesis of RNA and some protein (C) synthesis of DNA (D) secretion of enzymes (E) manufacture of lipids 42. One characteristic that all algae have in common is that they (A) contain chlorophyll (B) are unicellular (C) have heterogamous sexual reproduction (D) are aquatic (E) lack alternation o ...
... (B) synthesis of RNA and some protein (C) synthesis of DNA (D) secretion of enzymes (E) manufacture of lipids 42. One characteristic that all algae have in common is that they (A) contain chlorophyll (B) are unicellular (C) have heterogamous sexual reproduction (D) are aquatic (E) lack alternation o ...
Daughter cells are
... • Which type of compound is NOT part of DNA? – Deoxyribose; nitrogen base; phosphate; protein ...
... • Which type of compound is NOT part of DNA? – Deoxyribose; nitrogen base; phosphate; protein ...
Chapter 5 - Scranton Prep Biology
... with their nitrogenous bases pairing and hydrogenbonding together in the inside. Adenine pairs only with thymine; guanine always pairs with cytosine. Thus, the sequencesof nitrogenous baseson the tvvo strands of DNA are complementary. Becauseof this specific base-pairing property, DNA can replicate ...
... with their nitrogenous bases pairing and hydrogenbonding together in the inside. Adenine pairs only with thymine; guanine always pairs with cytosine. Thus, the sequencesof nitrogenous baseson the tvvo strands of DNA are complementary. Becauseof this specific base-pairing property, DNA can replicate ...
Ch 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
BA13.00
... What is a DNA? • A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell and is capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA. • DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix and joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or ...
... What is a DNA? • A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell and is capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA. • DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix and joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or ...
13.3_Mutations
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
... 1 Explain What is a frameshift mutation and give an example Infer The effects of a mutation are not always visible. Choose a species and explain how a biologist might determine whether a mutation has occurred and, if so, what type of mutation it is 2 Review List four effect mutations can have on gen ...
Mastering Biology Genetics Retake
... Contains deoxyribose Contains uracil Contains thymine Composed of a single strand of nucleotides ...
... Contains deoxyribose Contains uracil Contains thymine Composed of a single strand of nucleotides ...
Topic 2: Molecular biology (21 hours)
... not need to be shown, but the two strands should be shown antiparallel. Adenine should be shown paired with thymine and guanine with cytosine, but the relative lengths of the purine and pyrimidine bases do not need to be recalled, nor the numbers of hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
... not need to be shown, but the two strands should be shown antiparallel. Adenine should be shown paired with thymine and guanine with cytosine, but the relative lengths of the purine and pyrimidine bases do not need to be recalled, nor the numbers of hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
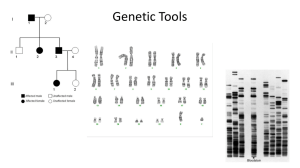
Genetic Tools
... • You will identify the disorder that the child has based on the given karyotype and then research information about that disorder. • You will create a poster that describes aspects of the genetic disorder you have diagnosed. • Information to be included on the poster -What is the disorder (name and ...
... • You will identify the disorder that the child has based on the given karyotype and then research information about that disorder. • You will create a poster that describes aspects of the genetic disorder you have diagnosed. • Information to be included on the poster -What is the disorder (name and ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... Ribose instead of Deoxyribose Uracil instead of Thymine Messenger RNA – carries blueprint Transfer RNA – brings amino acids Ribosomal RNA – reads code ...
... Ribose instead of Deoxyribose Uracil instead of Thymine Messenger RNA – carries blueprint Transfer RNA – brings amino acids Ribosomal RNA – reads code ...
hapCh2 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... number of neutrons,are identified by mass number,and one medical use is as tracers in medical diagnosis.---see.pp. 8 and 9 __________________________________occur whenever atoms combine with or dissociate from other atoms _____________________-2 or more combined chemically;more specifically a co ...
... number of neutrons,are identified by mass number,and one medical use is as tracers in medical diagnosis.---see.pp. 8 and 9 __________________________________occur whenever atoms combine with or dissociate from other atoms _____________________-2 or more combined chemically;more specifically a co ...
Forensic DNA Analysis
... degrees. Now, an enzyme called Taq DNA polymerase is added. This is a very stable enzyme isolated from bacteria living at thermal vents in the ocean (up to 95 oC) In just 32 rounds of PCR, 1 copy of DNA becomes 4.2 billion copies. This would take about 3 hours to perform in lab. ...
... degrees. Now, an enzyme called Taq DNA polymerase is added. This is a very stable enzyme isolated from bacteria living at thermal vents in the ocean (up to 95 oC) In just 32 rounds of PCR, 1 copy of DNA becomes 4.2 billion copies. This would take about 3 hours to perform in lab. ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... substances across cell membranes • Hemoglobin carries oxygen, iron, and other substances through the body. ...
... substances across cell membranes • Hemoglobin carries oxygen, iron, and other substances through the body. ...
[edit]More recent updates
... the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms (with the exception of RNA viruses). The DNA segments carrying this geneticinformation are called genes. Likewise, other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of thi ...
... the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms (with the exception of RNA viruses). The DNA segments carrying this geneticinformation are called genes. Likewise, other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of thi ...
Test Blueprint
... of molecules, disposal of wastes, function of cellular parts, and synthesis of new molecules (TEKS 4B) The student will compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (TEKS 9A) The student will compare the energy flo ...
... of molecules, disposal of wastes, function of cellular parts, and synthesis of new molecules (TEKS 4B) The student will compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (TEKS 9A) The student will compare the energy flo ...
RESTRICTION ENDONUCLEASES
... To incorporate fragments of foreign DNA into a cloning vector, methods for cutting and rejoining of single stranded DNA are necessary. The identification of restriction endonucleases in the 1960s and early 1970s and the recognition that these enzymes act as “molecular scissors”, always cutting DNA a ...
... To incorporate fragments of foreign DNA into a cloning vector, methods for cutting and rejoining of single stranded DNA are necessary. The identification of restriction endonucleases in the 1960s and early 1970s and the recognition that these enzymes act as “molecular scissors”, always cutting DNA a ...
molecular_gene_cloning_restriction
... To incorporate fragments of foreign DNA into a cloning vector, methods for cutting and rejoining of single stranded DNA are necessary. The identification of restriction endonucleases in the 1960s and early 1970s and the recognition that these enzymes act as “molecular scissors”, always cutting DNA a ...
... To incorporate fragments of foreign DNA into a cloning vector, methods for cutting and rejoining of single stranded DNA are necessary. The identification of restriction endonucleases in the 1960s and early 1970s and the recognition that these enzymes act as “molecular scissors”, always cutting DNA a ...
Presentation
... What is the functional significance of the structural differences between bacterial and eukaryotic mRNAs? ...
... What is the functional significance of the structural differences between bacterial and eukaryotic mRNAs? ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.

















![[edit]More recent updates](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022145907_1-8f0620400434ad236b249c9cd08f1aa3-300x300.png)




