Document
... (1) Normal DNA and amino acid sequence makes a wild-type protein. (2) Mutation in DNA changes Trp to Stop to make a short, mutant protein. Mutations in DNA can be Caused by: • Mistakes made when the DNA is replicated (wrong base inserted) • Ultra violet (UV) light and ionizing radiation (X-rays) dam ...
... (1) Normal DNA and amino acid sequence makes a wild-type protein. (2) Mutation in DNA changes Trp to Stop to make a short, mutant protein. Mutations in DNA can be Caused by: • Mistakes made when the DNA is replicated (wrong base inserted) • Ultra violet (UV) light and ionizing radiation (X-rays) dam ...
Exam #3 (final)
... 30. Carbon and nitrogen fixation in photosynthetic bacteria 31. DNA content of bacteria 32. Phenotypes of bacteria – visible, selectable, differential 33. Phenotypes of bacteria – visible, selectable, differential 34. Wild type, prototroph, and auxotroph 35. Genotypic and phenotypic designations in ...
... 30. Carbon and nitrogen fixation in photosynthetic bacteria 31. DNA content of bacteria 32. Phenotypes of bacteria – visible, selectable, differential 33. Phenotypes of bacteria – visible, selectable, differential 34. Wild type, prototroph, and auxotroph 35. Genotypic and phenotypic designations in ...
Bio_Ch7 - Faustina Academy
... Telophase II- plasma membrane constricts along equatorial plane, forming two pairs of haploid cells ...
... Telophase II- plasma membrane constricts along equatorial plane, forming two pairs of haploid cells ...
Chapter 7 Cellular control
... you first need to think back to the structure of proteins. Proteins are made of polypeptides, which are long chains of amino acids. There are about 20 different amino acids, and the sequence in which they are strung together determines the structure – and therefore the function – of the protein mole ...
... you first need to think back to the structure of proteins. Proteins are made of polypeptides, which are long chains of amino acids. There are about 20 different amino acids, and the sequence in which they are strung together determines the structure – and therefore the function – of the protein mole ...
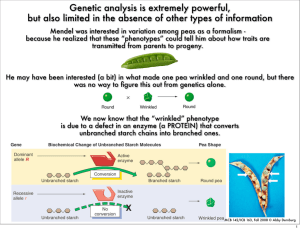
Genetic analysis is extremely powerful, but also limited in the
... This “Fluctuation Test” revealed that mutations arise spontaneously in a population, presumably due to some “natural” mutagenic process(es). This provided strong support for Darwin’s ideas about natural selection acting on naturally arising variation. Salvador Luria and Max Delbrück received the Nob ...
... This “Fluctuation Test” revealed that mutations arise spontaneously in a population, presumably due to some “natural” mutagenic process(es). This provided strong support for Darwin’s ideas about natural selection acting on naturally arising variation. Salvador Luria and Max Delbrück received the Nob ...
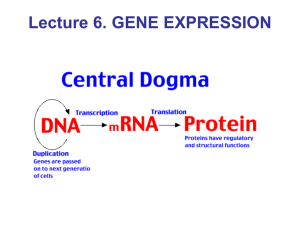
Regulation of Gene Expression
... translated into protein. RNA - Three types Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - as name suggests found in ribosomes which function to synthesise proteins Messenger RNA (mRNA) - This type of RNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein by triplet codon bases. The mRNA sequence is translated into a protei ...
... translated into protein. RNA - Three types Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - as name suggests found in ribosomes which function to synthesise proteins Messenger RNA (mRNA) - This type of RNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein by triplet codon bases. The mRNA sequence is translated into a protei ...
5.1.1 Cellular Control MS
... so unable to, accept / transport, HCO3-; unable to bind ATP; so increase in acidity / decrease in pH; effect on mucus; effect on enzyme(s) /ref pH optimum of enzyme(s); poor digestion of, protein / lipid / starch; AVP; e.g. ...
... so unable to, accept / transport, HCO3-; unable to bind ATP; so increase in acidity / decrease in pH; effect on mucus; effect on enzyme(s) /ref pH optimum of enzyme(s); poor digestion of, protein / lipid / starch; AVP; e.g. ...
doc
... 18. Suppose you inserted a U between the G and the C. What would be the sequence of the new peptide? (remember to read the message in the correct direction!) (A) ArgArgGlyGlyIleLeu, (B) GlyGlyValGluTyrLys, (C) LeuGluArgGlyValIle, (D) GlyLysArgGlyGlyTyrAla, or (E) none of the above. 19. Suppose you d ...
... 18. Suppose you inserted a U between the G and the C. What would be the sequence of the new peptide? (remember to read the message in the correct direction!) (A) ArgArgGlyGlyIleLeu, (B) GlyGlyValGluTyrLys, (C) LeuGluArgGlyValIle, (D) GlyLysArgGlyGlyTyrAla, or (E) none of the above. 19. Suppose you d ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Detect sequences of DNA in an organism’s genome Used in gene discovery and gene mapping To analyze the genetic patterns in an organism’s DNA To identify gene mutations, deletions, duplications, and gene rearrangements involved in diseases To determine the number of copies of a particular DNA sequenc ...
... Detect sequences of DNA in an organism’s genome Used in gene discovery and gene mapping To analyze the genetic patterns in an organism’s DNA To identify gene mutations, deletions, duplications, and gene rearrangements involved in diseases To determine the number of copies of a particular DNA sequenc ...
BLOTTING TECHNIQUES - University of Kufa
... Disadvantage of Nourthern plotting 1.The standard northern blot method is relatively less sensitive than nuclease protection assays and RT-PCR ...
... Disadvantage of Nourthern plotting 1.The standard northern blot method is relatively less sensitive than nuclease protection assays and RT-PCR ...
Document
... Occurs after exposure to a physical or chemical agent called a mutagen Modes of action 1. Incorporation of base analogs-structurally similar to the normal bases that get incorporated into the growing chain during replication. Typically they base pair with different bases and thus replace the normal ...
... Occurs after exposure to a physical or chemical agent called a mutagen Modes of action 1. Incorporation of base analogs-structurally similar to the normal bases that get incorporated into the growing chain during replication. Typically they base pair with different bases and thus replace the normal ...
Medical Biochemistry at a Glance. 3rd Edition. At a Glance Brochure
... Offering a concise, illustrated summary of biochemistry and its relevance to clinical medicine, Medical Biochemistry at a Glance is intended for students of medicine and the biomedical sciences such as nutrition, biochemistry, sports science, medical laboratory sciences, physiotherapy, pharmacy, phy ...
... Offering a concise, illustrated summary of biochemistry and its relevance to clinical medicine, Medical Biochemistry at a Glance is intended for students of medicine and the biomedical sciences such as nutrition, biochemistry, sports science, medical laboratory sciences, physiotherapy, pharmacy, phy ...
101 -- 2006
... __ 46. What is the general process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones called? a) catalysis b) metabolism c) anabolism d) dehydration e) catabolism __ 47. Photosynthesis is exergonic. a) True b) False __ 48. Which of the following statements is true concerning catabolic pathways? a) ...
... __ 46. What is the general process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones called? a) catalysis b) metabolism c) anabolism d) dehydration e) catabolism __ 47. Photosynthesis is exergonic. a) True b) False __ 48. Which of the following statements is true concerning catabolic pathways? a) ...
Notes - Dr. Bruce Owen
... of a long, narrow molecule just 20 angstroms (20 x 10-10 meters) wide − 38,000 strands of DNA next to each other would be about as wide as one human hair − yet each strand is up to 12 cm (4 ¾ inches) long, with all 46 strands totaling about 2 meters (6 ½ feet) long! − if the DNA in one cell in your ...
... of a long, narrow molecule just 20 angstroms (20 x 10-10 meters) wide − 38,000 strands of DNA next to each other would be about as wide as one human hair − yet each strand is up to 12 cm (4 ¾ inches) long, with all 46 strands totaling about 2 meters (6 ½ feet) long! − if the DNA in one cell in your ...
control biological machines
... • Control biological activity – external – reversible – on molecular scale (selective) – direct – in vitro/ in vivo – universal ...
... • Control biological activity – external – reversible – on molecular scale (selective) – direct – in vitro/ in vivo – universal ...
DNA Technology
... What other effects will it have besides the one intended They can mutate Examples of GMOs (genetically modified organisms) that we have now……… Sterile male crop pests Plants that have an insecticide in them ...
... What other effects will it have besides the one intended They can mutate Examples of GMOs (genetically modified organisms) that we have now……… Sterile male crop pests Plants that have an insecticide in them ...
Exam3fall2005ch9-12.doc
... Remote number __ 1) According to Griffith’s experiments, bacteria could be _______________, as shown when they were injected into____________. a) Dangerous/ rabbits b) Transformed/mice c) Prokaryotes/dogs d) Deleterious/DNA 2) Nucleic acids are made up of ____-carbon sugar, phosphate groups and eith ...
... Remote number __ 1) According to Griffith’s experiments, bacteria could be _______________, as shown when they were injected into____________. a) Dangerous/ rabbits b) Transformed/mice c) Prokaryotes/dogs d) Deleterious/DNA 2) Nucleic acids are made up of ____-carbon sugar, phosphate groups and eith ...
(3) Ch 6 Review Game
... • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in the parent cell at the BEGINNING of the process. • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in each cell at the END of the process. ...
... • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in the parent cell at the BEGINNING of the process. • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in each cell at the END of the process. ...
Chapter 20 Notes
... Often carry resistance genes Isolated genes of interest can be inserted into the plasmid How is this insertion done? Restriction endonucleases (enzymes) ...
... Often carry resistance genes Isolated genes of interest can be inserted into the plasmid How is this insertion done? Restriction endonucleases (enzymes) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.