Document
... stops Chain termination resulting in different DNA fragment lengths Separate different DNA lengths by gel electrophoresis, loading each reaction tube in a separate well/lane Sequence can be read from the gel in ascending order ...
... stops Chain termination resulting in different DNA fragment lengths Separate different DNA lengths by gel electrophoresis, loading each reaction tube in a separate well/lane Sequence can be read from the gel in ascending order ...
(3) Ch 6 Review Game
... • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in the parent cell at the BEGINNING of the process. • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in each cell at the END of the process. ...
... • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in the parent cell at the BEGINNING of the process. • This term refers to the number of chromosomes in each cell at the END of the process. ...
Chapter 20 Notes
... Often carry resistance genes Isolated genes of interest can be inserted into the plasmid How is this insertion done? Restriction endonucleases (enzymes) ...
... Often carry resistance genes Isolated genes of interest can be inserted into the plasmid How is this insertion done? Restriction endonucleases (enzymes) ...
DNA Profiling
... ‘relentless evolution’ • O157 strains have increased geographically and in diversity – Viruses are responsible for insertions into the bacterial DNA adding toxins that cause HUS – The 2006 spinach outbreak is an example – it demonstrated that the pathogen could subsist on produce as well as meat Man ...
... ‘relentless evolution’ • O157 strains have increased geographically and in diversity – Viruses are responsible for insertions into the bacterial DNA adding toxins that cause HUS – The 2006 spinach outbreak is an example – it demonstrated that the pathogen could subsist on produce as well as meat Man ...
Introduction To Molecular Biology
... Nitrogenous base; these bases are classified based on their chemical structures into two groups: ...
... Nitrogenous base; these bases are classified based on their chemical structures into two groups: ...
BIOFINALRVW
... 1. Who were the scientists responsible for discovering that DNA was the heredity material? ...
... 1. Who were the scientists responsible for discovering that DNA was the heredity material? ...
GENETICS: BIOLOGY HSA REVIEW
... b 1. If a homozygous German Shepherd with brown eyes is bred with a heterozygous German Shepherd with blue eyes, is it possible to have puppies with brown eyes? a. Yes, and all potential offspring will be carriers of the allele for blue eyes. b. Yes; 50% of the offspring would be heterozygous for bl ...
... b 1. If a homozygous German Shepherd with brown eyes is bred with a heterozygous German Shepherd with blue eyes, is it possible to have puppies with brown eyes? a. Yes, and all potential offspring will be carriers of the allele for blue eyes. b. Yes; 50% of the offspring would be heterozygous for bl ...
Biological Molecules
... acids – not the foods that contain them, but specific lipids. How are carbohydrates and lipids different from one another? ...
... acids – not the foods that contain them, but specific lipids. How are carbohydrates and lipids different from one another? ...
QUIZ #1 - Introduction, Water, pH, buffers, Amino Acids, Proteins
... a. When the pH = pI, the amino acid has no net charge b. When the pH = pI, the amino acid will not migrate in an electric field c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = pI, the pK of each ionizable group is unchanged 14. Concerning buffers, which of ...
... a. When the pH = pI, the amino acid has no net charge b. When the pH = pI, the amino acid will not migrate in an electric field c. When the pH = pI, the amino acid is at its greatest buffering capacity d. When the pH = pI, the pK of each ionizable group is unchanged 14. Concerning buffers, which of ...
THE FUNCTION OF DNA AND GENETIC ENGINEERING By
... into another organism to carry on those traits. Cells make copies of themselves to reproduce, they must copy their genetic information and transfer a copy to the new cell before cell division may commence. There are two main types of cellular reproduction, mitosis, and meiosis. Mutation is when the ...
... into another organism to carry on those traits. Cells make copies of themselves to reproduce, they must copy their genetic information and transfer a copy to the new cell before cell division may commence. There are two main types of cellular reproduction, mitosis, and meiosis. Mutation is when the ...
a 1
... increase in substitution rate in nonfunctional, but also in functional, regions, leading to a pattern similar to the HAR pattern. Furthermore, several aspects of the evolution of HARs seem to be consistent with the BGC model, as discussed by Pollard et al. [3]. 1) Substitutions are mostly AT> GC cha ...
... increase in substitution rate in nonfunctional, but also in functional, regions, leading to a pattern similar to the HAR pattern. Furthermore, several aspects of the evolution of HARs seem to be consistent with the BGC model, as discussed by Pollard et al. [3]. 1) Substitutions are mostly AT> GC cha ...
Thermo Scientific Gene Modulation
... Non-catalytic strand: Same as the sense, passenger, or nontargeting strand in siRNA/miRNA. Northern Blot: A method for detecting specific mRNAs using radioor chemiluminescent-labeled DNA probes. Nuclease: Enzyme that degrades nucleic acids; specific enzymes can be DNA or RNA specific, act on single ...
... Non-catalytic strand: Same as the sense, passenger, or nontargeting strand in siRNA/miRNA. Northern Blot: A method for detecting specific mRNAs using radioor chemiluminescent-labeled DNA probes. Nuclease: Enzyme that degrades nucleic acids; specific enzymes can be DNA or RNA specific, act on single ...
tRNA and Translation
... 3. The proper arrangement of almost 600 amino acids results in normal formation of the hemoglobin molecule. According to the question above, one mistake involving the replacement of the amino acid ______________________________________ by the amino acid ____________________________________ can resul ...
... 3. The proper arrangement of almost 600 amino acids results in normal formation of the hemoglobin molecule. According to the question above, one mistake involving the replacement of the amino acid ______________________________________ by the amino acid ____________________________________ can resul ...
From http://www
... Once the DNA double helix had been discovered, the next big challenge was to work out how the four letters of DNA could code for each of the twenty amino acids that make protein. The first question was how many DNA letters coded for each amino acid? If it was one DNA letter for one amino acid then y ...
... Once the DNA double helix had been discovered, the next big challenge was to work out how the four letters of DNA could code for each of the twenty amino acids that make protein. The first question was how many DNA letters coded for each amino acid? If it was one DNA letter for one amino acid then y ...
Chemical Evolution of Life on the Early Earth All organisms on Earth
... All organisms on Earth today use the same four bases in the same genetic code and the same 20 amino acids (out of the hundreds possible). Furthermore they all use the same basic mechanism of DNA-protein conversion (transcription and translation). Even more surprising is that the genes that specify c ...
... All organisms on Earth today use the same four bases in the same genetic code and the same 20 amino acids (out of the hundreds possible). Furthermore they all use the same basic mechanism of DNA-protein conversion (transcription and translation). Even more surprising is that the genes that specify c ...
A-level Biology B Question paper Unit 2 - Genes and Genetic
... (2 marks) (b) The sea-fir is a marine animal. It has two body forms in its life cycle, the polyp and the medusa. The polyp lives its whole life attached to a rock. The polyp reproduces asexually. All its offspring have the medusa body form. These offspring can swim. A mature medusa reproduces sexual ...
... (2 marks) (b) The sea-fir is a marine animal. It has two body forms in its life cycle, the polyp and the medusa. The polyp lives its whole life attached to a rock. The polyp reproduces asexually. All its offspring have the medusa body form. These offspring can swim. A mature medusa reproduces sexual ...
Viruses Nonliving Structure Reproduction
... Influenza infects cells lining the respiratory tracts. Poliomyelitis virus infects nerve cells. Tobacco mosaic virus infects tobacco leaves. Protein Synthesis In a normal cell, DNA is copied to make mRNA by a process called transcription. The information stored in mRNA is used by ribosomes to assemb ...
... Influenza infects cells lining the respiratory tracts. Poliomyelitis virus infects nerve cells. Tobacco mosaic virus infects tobacco leaves. Protein Synthesis In a normal cell, DNA is copied to make mRNA by a process called transcription. The information stored in mRNA is used by ribosomes to assemb ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations
... The change in free energy ∆G is the most useful measure for predicting the direction of chemical reactions in biological systems. Chemical reactions tend to proceed in the direction for which ∆G is negative. A chemical reaction having a positive ∆G can proceed if it is coupled with a reaction having ...
... The change in free energy ∆G is the most useful measure for predicting the direction of chemical reactions in biological systems. Chemical reactions tend to proceed in the direction for which ∆G is negative. A chemical reaction having a positive ∆G can proceed if it is coupled with a reaction having ...
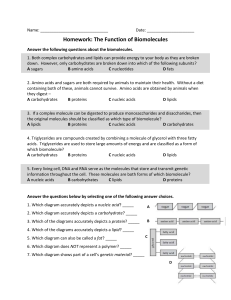
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B nucleic acids and lipids C carbohydrates and lipids D nucleic acids and proteins 13. Which set of biomole ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B nucleic acids and lipids C carbohydrates and lipids D nucleic acids and proteins 13. Which set of biomole ...
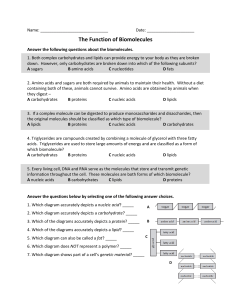
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
... Use the information in the diagrams to determine which biomolecules are being compared 12. Which set of biomolecules is being compared in the diagram to the right? A carbohydrates and proteins B n ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.