
Crime Lab Overview
... media to avoid alteration or destruction • Desktops • Tablets • Laptops • Cell Phones • Storage Devices ...
... media to avoid alteration or destruction • Desktops • Tablets • Laptops • Cell Phones • Storage Devices ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 01. Who is called as the father of modern enzymology? Why? 02. Define isoelectric point. 03. How is glycine prepared by strecker synthesis? 04. What are coenzymes? 05. Define rancidity of an oil. 06. Draw the structure of adenine and guanine. 07. How is the presence of ketone group in C-2 position c ...
... 01. Who is called as the father of modern enzymology? Why? 02. Define isoelectric point. 03. How is glycine prepared by strecker synthesis? 04. What are coenzymes? 05. Define rancidity of an oil. 06. Draw the structure of adenine and guanine. 07. How is the presence of ketone group in C-2 position c ...
The Universe and Its Stars / Matter and Its Interactions
... 29) A) 50% dominant trait B) 50% recessive trait 30) The four bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) 31) Adenine and thymine always pair up (A and T) and guanine and cytosine always pair up (C and G). 32) A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can reshape your ent ...
... 29) A) 50% dominant trait B) 50% recessive trait 30) The four bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) 31) Adenine and thymine always pair up (A and T) and guanine and cytosine always pair up (C and G). 32) A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can reshape your ent ...
Molecules of Life
... – Proteins are made up of monomers called amino acids. The sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s shape and function. • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a ...
... – Proteins are made up of monomers called amino acids. The sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s shape and function. • Dipeptides and Polypeptides – Two amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a dipeptide. – A long chain of amino acids is called a ...
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
... nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
... nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
Chapter 13
... to separate molecules in a mixture. Because DNA is negatively charged, the various fragments move through the gel according to their size, forming a pattern of bands The DNA fragments are then split into single-stranded DNA, which is then blotted onto filter paper Afterward, the filter paper is mois ...
... to separate molecules in a mixture. Because DNA is negatively charged, the various fragments move through the gel according to their size, forming a pattern of bands The DNA fragments are then split into single-stranded DNA, which is then blotted onto filter paper Afterward, the filter paper is mois ...
the chemistry of life - Fall River Public Schools
... Enzymes are macromolecules that are biological catalysts. The activation energy of a reaction is the amount of energy it takes to start a reaction – the amount of energy it takes to break the bonds of the reactant molecules. Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy of the reactio ...
... Enzymes are macromolecules that are biological catalysts. The activation energy of a reaction is the amount of energy it takes to start a reaction – the amount of energy it takes to break the bonds of the reactant molecules. Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy of the reactio ...
video slide - Greensburg
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
Biochemistry
... • Chemical substances that neutralize small amounts of acid or base added to a solution • Buffering systems in your body maintain pH values of body fluids at normal and safe levels ...
... • Chemical substances that neutralize small amounts of acid or base added to a solution • Buffering systems in your body maintain pH values of body fluids at normal and safe levels ...
Organization of the eukaryotic genomes
... While the number of genes in prokaryotes correlates well with the sizes of their genome, the number of genes in eukaryotes does not correct well with their genome sizes ...
... While the number of genes in prokaryotes correlates well with the sizes of their genome, the number of genes in eukaryotes does not correct well with their genome sizes ...
Topic Three Chemistry of Life - MrsGorukhomework
... just like petroleum and can store a lot of energy – and not soluble in water When fats are metabolized for energy, it releases a lot more water than if you use glucose. Desert camels can live off that water when they use the fat in their hump. *condensation and hydrolysis equations with words or for ...
... just like petroleum and can store a lot of energy – and not soluble in water When fats are metabolized for energy, it releases a lot more water than if you use glucose. Desert camels can live off that water when they use the fat in their hump. *condensation and hydrolysis equations with words or for ...
Ch. 9 + 10 [genetics]
... 1. Easy to cultivate 2. Has a short generation time 3. Easily cross pollinated ...
... 1. Easy to cultivate 2. Has a short generation time 3. Easily cross pollinated ...
AIM: What are Macromolecules?
... speeding up a chemical reaction and lowering the amount of energy needed for it to start. ...
... speeding up a chemical reaction and lowering the amount of energy needed for it to start. ...
4.04 Workfile
... bullet to see if it was fired from a suspect’s weapon. But out of all the methods, the most reliable forensic technique police use is called DNA fingerprinting. As opposed to traditional fingerprinting in which the actual fingerprints are lifted from the crime scene, this type of fingerprinting look ...
... bullet to see if it was fired from a suspect’s weapon. But out of all the methods, the most reliable forensic technique police use is called DNA fingerprinting. As opposed to traditional fingerprinting in which the actual fingerprints are lifted from the crime scene, this type of fingerprinting look ...
Section 4 – Molecules
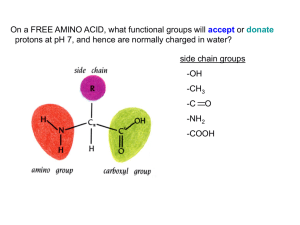
... The type of side chain is very important as it affects the solubility of the amino acid. Hydrophobic features include long non-polar (uncharged) chains or complex aromatic rings. Hydrophilic features include additional carboxyl groups or amino groups not involved in peptide bonding which are ionised ...
... The type of side chain is very important as it affects the solubility of the amino acid. Hydrophobic features include long non-polar (uncharged) chains or complex aromatic rings. Hydrophilic features include additional carboxyl groups or amino groups not involved in peptide bonding which are ionised ...
Slide 1
... (STAR) test are based on the California Standards. There are five major categories and they include: Investigation and Experimentation, Cell Biology, Genetics, Evolution and Ecology, and Physiology. Each of the categories includes a number of topics that you should know about. I am including each of ...
... (STAR) test are based on the California Standards. There are five major categories and they include: Investigation and Experimentation, Cell Biology, Genetics, Evolution and Ecology, and Physiology. Each of the categories includes a number of topics that you should know about. I am including each of ...
March 21, 1968, Number 12, Page Number 659
... Acyl sRNA + Enzyme + AMP. The first step is the amino acid activation step in which a specific amino acyl sRNA synthetase forms a complex with its amino acid in the presence of ATP. This step is known to be magnesium dependent.54-56 Optimal activity of each of the amino acyl RNA synthetases occurs a ...
... Acyl sRNA + Enzyme + AMP. The first step is the amino acid activation step in which a specific amino acyl sRNA synthetase forms a complex with its amino acid in the presence of ATP. This step is known to be magnesium dependent.54-56 Optimal activity of each of the amino acyl RNA synthetases occurs a ...
Document
... (T) as compared to the amount of adenine (A)? What is said about the amount of cytosine (C) as compared to guanine (G)? ...
... (T) as compared to the amount of adenine (A)? What is said about the amount of cytosine (C) as compared to guanine (G)? ...
FoundationACT – Physician FAQs 1. What is cell
... We do this to avoid charging patients for results that are not likely beneficial to them and to avoid providing false negative results. This may be a more stringent standard than other liquid biopsy ...
... We do this to avoid charging patients for results that are not likely beneficial to them and to avoid providing false negative results. This may be a more stringent standard than other liquid biopsy ...
Genetic Engineering Notes
... Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) = are organisms with artificially altered DNA. They can be created by: Inserting a foreign gene: Organisms that are altered in this way are known as transgenic organisms. ...
... Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) = are organisms with artificially altered DNA. They can be created by: Inserting a foreign gene: Organisms that are altered in this way are known as transgenic organisms. ...
Comparative study for establishing the efficiency of some methods
... temperatures, with a hard cell membrane difficult to cleave, which had enlarged surviving strategies to protect themselves at lower temperatures. Common methods used for chrDNA extraction, as microwave method or FastDNA® Kit, were not suitable to develop good yield of DNA, as much as necessary for p ...
... temperatures, with a hard cell membrane difficult to cleave, which had enlarged surviving strategies to protect themselves at lower temperatures. Common methods used for chrDNA extraction, as microwave method or FastDNA® Kit, were not suitable to develop good yield of DNA, as much as necessary for p ...
MB207Jan2010
... - ionizing radiation because it removes electrons from biological molecules. - generating highly reactive intermediates that cause various types of DNA damage. ...
... - ionizing radiation because it removes electrons from biological molecules. - generating highly reactive intermediates that cause various types of DNA damage. ...
The amino acids
... Di-peptide Amino acids bind, to form a protein. Upon binding, two protons from the NH3 and one oxygen from the carboxyl join to form a water. So the peptide bond has at the one side a C=O and at the other side an N-H. Only the ends of the chain are NH3 or carboxylic. ...
... Di-peptide Amino acids bind, to form a protein. Upon binding, two protons from the NH3 and one oxygen from the carboxyl join to form a water. So the peptide bond has at the one side a C=O and at the other side an N-H. Only the ends of the chain are NH3 or carboxylic. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.










![Ch. 9 + 10 [genetics]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008315130_1-77d900a848f59bba71a4600153ed2e6c-300x300.png)











