Chapter 53: Community Ecology
... accidentally crushed the egg during incubation; some eggs also didn’t hatch eagle population; the population of eagles’ prey increased, so competition for those prey isn’t as intense. ...
... accidentally crushed the egg during incubation; some eggs also didn’t hatch eagle population; the population of eagles’ prey increased, so competition for those prey isn’t as intense. ...
Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
... Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere What is Ecology? The scientific study of how living things interact with each other and with their environment • An environment consists of biotic factors which are living things such as plants and animals and abiotic factors which are nonliving things such ...
... Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere What is Ecology? The scientific study of how living things interact with each other and with their environment • An environment consists of biotic factors which are living things such as plants and animals and abiotic factors which are nonliving things such ...
worksheet - Holy Spirit High School
... What two factors explain why the birth rates and death rates for each stage are the way they are? _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. At which stage of the Demographic Transition Model of Human Population Growth is Canada ? _______________________________ ...
... What two factors explain why the birth rates and death rates for each stage are the way they are? _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. At which stage of the Demographic Transition Model of Human Population Growth is Canada ? _______________________________ ...
Ecology
... • Population: all individuals of a certain species within a certain area • Community: all the populations of different species within an area ...
... • Population: all individuals of a certain species within a certain area • Community: all the populations of different species within an area ...
Natural selection
... ways. Symbiotic relationships are those in which two species live in physical contact and at least one species derives benefit from the relationship. In an ecosystem, energy is trapped by producers and flows from producers through various trophic levels of consumers. ...
... ways. Symbiotic relationships are those in which two species live in physical contact and at least one species derives benefit from the relationship. In an ecosystem, energy is trapped by producers and flows from producers through various trophic levels of consumers. ...
Notes 30: Community and Ecosystem Ecology I
... • A population is the set of all members of one species in a defined area. • A community is the set of all populations in a defined area. • An ecosystem includes a community, together with the non-living factors that affect it. – In a land ecosystem, these might include temperature, rainfall, ...
... • A population is the set of all members of one species in a defined area. • A community is the set of all populations in a defined area. • An ecosystem includes a community, together with the non-living factors that affect it. – In a land ecosystem, these might include temperature, rainfall, ...
Natural Selection, Adaptations, and Niches
... Explain how adaptations benefit an organism Identify and describe the three types of interactions between organisms in a community ...
... Explain how adaptations benefit an organism Identify and describe the three types of interactions between organisms in a community ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 4. The study of how things interact with each other and with their environment is called a. ecology. b. community. c. photosynthesis. d. biotic studies. 5. The struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources is called a. competition. b. symbiosis. c. predation. d. parasitis ...
... 4. The study of how things interact with each other and with their environment is called a. ecology. b. community. c. photosynthesis. d. biotic studies. 5. The struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources is called a. competition. b. symbiosis. c. predation. d. parasitis ...
Section 4.1 Population Dynamics pg.91
... Ex. Introducing organisms into a controlled environment with abundant resources; observe how the organisms react How fast do populations grow? Starts out slowly then increases rapidly; resembles a J shape on a chart of population growth Starts out small because the number of individuals reproducing ...
... Ex. Introducing organisms into a controlled environment with abundant resources; observe how the organisms react How fast do populations grow? Starts out slowly then increases rapidly; resembles a J shape on a chart of population growth Starts out small because the number of individuals reproducing ...
Ecology
... o Energy is transferred from the producer to the consumer that eats it. o Herbivores are _______________ ______________ consumers gaining the ___________ energy from the producers o Omnivores and Carnivores are secondary consumers getting ______________ ______________ energy o The feeding relationsh ...
... o Energy is transferred from the producer to the consumer that eats it. o Herbivores are _______________ ______________ consumers gaining the ___________ energy from the producers o Omnivores and Carnivores are secondary consumers getting ______________ ______________ energy o The feeding relationsh ...
Name - Humble ISD
... o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Omnivores: ___________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Detritivores: _______________________________________________________________________ ...
... o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Omnivores: ___________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: _________________________________________________ o Detritivores: _______________________________________________________________________ ...
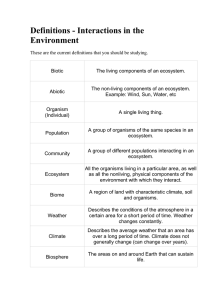
Definitions - Interactions in the Environment These are the current
... Describes the conditions of the atmosphere in a certain area for a short period of time. Weather changes constantly. ...
... Describes the conditions of the atmosphere in a certain area for a short period of time. Weather changes constantly. ...
Unit 5
... accurate when there are more numerous or larger sample plots and when the habitat is homogenous. In some cases, population sizes are estimated not by counts of organisms but by indirect indicaters. Another sampling technique commonly used to estimate wildlife population is the mark-recapture method. ...
... accurate when there are more numerous or larger sample plots and when the habitat is homogenous. In some cases, population sizes are estimated not by counts of organisms but by indirect indicaters. Another sampling technique commonly used to estimate wildlife population is the mark-recapture method. ...
Population ecology
... Population density - # of individuals per unit area (can be misleading) Population distribution – pattern of dispersal across an area (controlled by resources and limiting factors) clumped, random, uniform ...
... Population density - # of individuals per unit area (can be misleading) Population distribution – pattern of dispersal across an area (controlled by resources and limiting factors) clumped, random, uniform ...
Land Resource Issues - Winona State University
... Elected officials spend too much time raising money to be reelected ...
... Elected officials spend too much time raising money to be reelected ...
Ecology Review Sheet. KEY
... Use Ecological Succession Notes to help answer the following questions. 25. When observing an area where Primary Succession is occurring, like after a glacier melts or a volcano erupts, what type of organism(s) would be the pioneer species? Lichens and other ground hugging plants 26. After what type ...
... Use Ecological Succession Notes to help answer the following questions. 25. When observing an area where Primary Succession is occurring, like after a glacier melts or a volcano erupts, what type of organism(s) would be the pioneer species? Lichens and other ground hugging plants 26. After what type ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.