* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
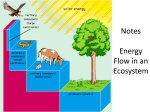
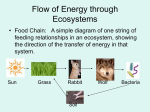
o Ecology Ecology: ________________ among Organisms Interactions between organisms and its ___________________ o ______________ factors are nonliving factors such as temp. soil, air, rocks o _____________ factors are living parts of the ecosystem Communities vs. Populations: A ____________________ is a group of organisms of the same species living in a certain area ___________ populations interacting together in a given area is a ________________ o Ex. Frogs + fish + algae = __________________ Habitats are… o _____________ in the ecosystem where ________ ________________ ______________ o Determined by both biotic and abiotic factors Ex. Earthworm = moist soil, dead organic material Niche: o The ____________ of the organism within its __________________ o Includes feeding habits, reproduction, habitat, and what it ___________________to its surrounding Ecosystem is a community and its physical environment including biotic and abiotic factors Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Nutrition: Autotrophs: Make their own food __________________ Provide food to ____________________ Most carry out ___________________(solar energy being converted into food_______________) o Ex. Green Plants!! Some producers are _____________________________ – ability to create food by using energy stored in inorganic molecules Heterotrophs: __________________ make their own food Must obtain/eat their food from their environment Types of heterotrophs include: o _____________________ eat only plants o ____________________ eat only meat 1. predators- _____________ and eat their prey prey - the animal that is ______________ and __________________ 2. ___________________ feed on dead and decaying meat ex. Buzzards, crows, hyenas o omnivores – eat _________________ plant and animals ex. US, bears and…??? Decomposers (aka. _______________) get nutrients from _______________ ____________ dead plants and animals o Ex. bacteria, fungus, ___________________ Symbiosis (Symbiotic Relationships): 2 organisms living together where at least 1 organism benefits 3 types of symbiotic relationships: 1. ______________________ - both organisms _______________ from the association o Ex. Humans and bacteria in the digestive track o Ex. Fish in sea anemones o Ex. Flower and the bee 2. ____________________- one organism benefits the other is ___________ __________ (not harmed, no benefit) o ex. Remora fish and sharks o ex. Orchids/moss living in tree 3. ___________________ - one organism benefits at the cost of the other (host) o ex. parasites living in animals (tapeworm, tick) o often cause ___________________ Energy Flow in an Ecosystem: o producers (____________________ ) make their own food o _______________________ (heterotrophs) obtain or eat their food from the environment o Decomposers (a.k.a __________________) break down left over remains of plants and animals Food Chains: o Are a transfer or _____________________ of ________________ through an ecosystem o Solar Energy from the sun is converted by ____________________ (photosynthesis) into chemical energy or FOOD o ____________________ eat the producers o Energy is transferred from the producer to the consumer that eats it. o Herbivores are _______________ ______________ consumers gaining the ___________ energy from the producers o Omnivores and Carnivores are secondary consumers getting ______________ ______________ energy o The feeding relationship shows the transfer of energy which forms a ___________ _____________ o The transfer of energy moves from producer to consumer to decomposers o Ex. Sun plant grasshopper bird cat Decomposers Producers (plants) _______ amount of energy consumers (1st level) ________ energy consumers (2nd level) even _________ energy consumers (3rd level) _____________ amount of energy Food Web: food chains (1 ______________of _____________) which are interconnected = food webs Food webs are ______________ food chains _______________ together Each ______________ means consumed (eaten) by… Another way of showing the flow of Energy in an ecosystem is: Energy ______________________: o Each step in a feeding relationship is called a _________________ level o 1st trophic level = __________________ o 2nd trophic level = primary consumers o 3rd trophic level = ______________________ consumers o The greatest amount of energy is at the __________________ of the pyramid (producers), the _____________ amount of __________________ is at the top. 90% of Energy is lost moving at each level; only 10% is transferred to the next level Some of the Energy is used in _____________ _______________ such as growth, and cell division, the rest is lost as _____________. The Carbon Cycle An exchange of materials (carbon dioxide, oxygen) between autotrophs and __________________ Autotrophs: o use the sun’s energy to produce their own food in a process called photosynthesis o In photosynthesis CO2 is ____________________ (taken in) from the environment and O2 (Oxygen) is _______________ as a ______________. Heterotrophs: o Take_________the Oxygen and use it for cellular activities o _________________ CO2 into the environment as a waste o The process is called ____________________ ______________________ The Carbon Cycle is a balance between Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen in the air. Populations: Factors that Limit Populations and Communities: Populations change over time o Most ________________________ rather than continuously grow o As populations increase, its puts more demand on the __________________ available such as food, shelter, and water o Environmental factors that limit the size of a population are called __________________ ______________. Limiting Factors: Environmental factors that limit the size of a population The availability of resources Ex. Food, water, shelter, oxygen, sun Density-____________________________ Factors: limit the growth of a population _____________ the population reaches a certain ____________ Ex. _________________, competition, _____________________, and food Population Density o The _________________ of organisms in a _______________ __________________ o Predation, competition, and the spread of disease all are influenced by population density Question: what happens to the level of competition when the population density increases? Predation? Disease? Ex. Of predator- prey population cycles Density Independent Limiting Factors: o limit growth in a population _____________________ _________ _______________ o These factors are often __________________ events o Ex. Extreme temp, _______________, volcanoes, ___________________ Carrying Capacity: The largest number of __________________(of one species) that ______________ _________ supported for an unlimited amount of time Occurs when the # of deaths and births are about _________________ o If a population goes ________________ the carrying capacity the number of deaths is _________________________ than the # of births o If the population is under the carrying capacity then… Population Growth Rate Involves: • Birth and death rate influences the population growth • Life expectancy o Man-72 years o Woman-79 years o ____________________________-movement of individuals into a population o Emigration -movement of individuals ______________ of a population Graphs and Populations Exponential Model: • Describes a population that _______________________ rapidly after only a few generations • The larger the population gets, the faster it grows • _______ ____________________ _________________ Logistic Model: • Takes into account the influence of ______________ ____________ • Includes carrying capacity -the number of individuals the environment can support over a period of time • Increased birth rates causes ________________ rates to increase • Growth will decrease when a population reaches the ____________________ _____________________ • Increased death __________________ growth • Birth rate = Death rate when a population reaches carrying capacity therefore ____________________ ______________________. Levels of Organization: (from largest to smallest) Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Species Organisms After discussing topics in ecology such as: the flow of energy, balance among organisms and populations, what type of impact do you feel humans have on the environment? Why?