Amino acid Metabolism 2
... B) glutamate C) fumarate D) acetoacetate 5. T/F It is possible for an amino acid to be both ketogenic and glucogenic. ...
... B) glutamate C) fumarate D) acetoacetate 5. T/F It is possible for an amino acid to be both ketogenic and glucogenic. ...
UNIT 1: Cell Biology Chemical Foundations of Life ALL matter is
... Chemical Foundations of Life ALL matter is composed of atoms and molecules. Compounds are made up of different elements combined chemically There are four large groups of compounds needed for life: o ______________________________ o ______________________________ o ______________________________ ...
... Chemical Foundations of Life ALL matter is composed of atoms and molecules. Compounds are made up of different elements combined chemically There are four large groups of compounds needed for life: o ______________________________ o ______________________________ o ______________________________ ...
Biology 12 Mr. Kruger - Kevan Kruger
... 1. Illustrate the structure of water molecules: Show bonding within and between molecules 2. Describe the important functions water plays in the body & the property of water they are related to 3. Describe the pH scale; Give examples of typical pH values in different areas of the body 4. What is a b ...
... 1. Illustrate the structure of water molecules: Show bonding within and between molecules 2. Describe the important functions water plays in the body & the property of water they are related to 3. Describe the pH scale; Give examples of typical pH values in different areas of the body 4. What is a b ...
Organic Molecules
... •Always contain carbon and hydrogen •Always covalent bonding •Often quite large, with many atoms ...
... •Always contain carbon and hydrogen •Always covalent bonding •Often quite large, with many atoms ...
Macromolecule Jeopardy
... 200- What is an example of a nucleic acid? DNA or RNA 300- What are nucleic acids used for in living things? Storing genetic information\ 400- What are the subunits that combine to form nucleic acids? Nucleotides 500- Nucleic acids contain the instructions on how to make which other type of macromol ...
... 200- What is an example of a nucleic acid? DNA or RNA 300- What are nucleic acids used for in living things? Storing genetic information\ 400- What are the subunits that combine to form nucleic acids? Nucleotides 500- Nucleic acids contain the instructions on how to make which other type of macromol ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
Macromolecules Part 2
... C. The monomer “building blocks” are called Amino Acids (There are 20 different Amino Acids that can be involved in making proteins. Proteins and enzymes usually have hundreds to thousands of Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – Thi ...
... C. The monomer “building blocks” are called Amino Acids (There are 20 different Amino Acids that can be involved in making proteins. Proteins and enzymes usually have hundreds to thousands of Amino acids in their structure.) D. Amino Acids have 4 different parts to them: 1. Carboxyl end (COOH) – Thi ...
2 Carboxyl Groups
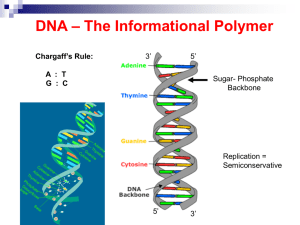
... Consists of two nucleotide chains wrapped around each other to form a double helix. Sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules make up the backbone and pairs of nitrogen bases make up the ...
... Consists of two nucleotide chains wrapped around each other to form a double helix. Sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules make up the backbone and pairs of nitrogen bases make up the ...
Unit 3 Biology - moleculesoflife2
... In medicine,…………………………………….of all drugs are proteins. Examples of proteins include hormones, enzymes and blood hemoglobin. They are used to build cell structure. ...
... In medicine,…………………………………….of all drugs are proteins. Examples of proteins include hormones, enzymes and blood hemoglobin. They are used to build cell structure. ...
Ch 2 BS
... Organic Compounds Found in all living things Always contain carbon Can combine with other elements to form a large number of organic compounds. 4 Major Groups ...
... Organic Compounds Found in all living things Always contain carbon Can combine with other elements to form a large number of organic compounds. 4 Major Groups ...
Biochemistry Notes
... B. Four types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things 1. Carbohydrates – starches and sugars a. monosaccharide – simple sugars (fructose and glucose) b. disaccharide – two sugars bonded together c. polysaccharide – polymers of monosaccharide (starch and cellulose) 2. Lipids – nonpolar ...
... B. Four types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things 1. Carbohydrates – starches and sugars a. monosaccharide – simple sugars (fructose and glucose) b. disaccharide – two sugars bonded together c. polysaccharide – polymers of monosaccharide (starch and cellulose) 2. Lipids – nonpolar ...
Guide 1406 Ch, 1-5
... Tetra valence, hydrocarbon, the functional groups Polysaccharides important in an organism ...
... Tetra valence, hydrocarbon, the functional groups Polysaccharides important in an organism ...
Biomacromolecules ppt
... shell. • Carbon can form covalent bonds with as many as 4 other atoms (elements). ...
... shell. • Carbon can form covalent bonds with as many as 4 other atoms (elements). ...
monosaccharides
... overview of the four biological molecules that we will be discussing. Read through the information. ...
... overview of the four biological molecules that we will be discussing. Read through the information. ...
Atomic Number
... Nucleic Acids- Very Large and complex organic molecules that store important information in the cell Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acid polymers, composed of thousands of linked monomers called nucleotides. ...
... Nucleic Acids- Very Large and complex organic molecules that store important information in the cell Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acid polymers, composed of thousands of linked monomers called nucleotides. ...
Inorganic/Organic Chemistry
... Primary: The order in which the different amino acids are linked together in the polypeptide Secondary: the coiling of the polypeptide chain into an alpha helix, held by hydrogen bonds Tertiary : The bending and twisting of the helix in three dimensions, held in place by a combination of covalent, i ...
... Primary: The order in which the different amino acids are linked together in the polypeptide Secondary: the coiling of the polypeptide chain into an alpha helix, held by hydrogen bonds Tertiary : The bending and twisting of the helix in three dimensions, held in place by a combination of covalent, i ...
The biomolecules of terrestrial life
... Biological macromolecules Macromolecules are created by polymerization of a large number of subunits (monomers) Heterogeneous class of organic molecules with common solubility properties Soluble in certain types of non-polar solvents Insoluble in water Larger number of C H bonds with respect to carb ...
... Biological macromolecules Macromolecules are created by polymerization of a large number of subunits (monomers) Heterogeneous class of organic molecules with common solubility properties Soluble in certain types of non-polar solvents Insoluble in water Larger number of C H bonds with respect to carb ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 8. Describe the building-block molecules, structure, and biological importance of fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Know common examples. 9. Identify an ester linkage and describe how it is formed. 10. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fats. 11. Name the principal energy storage molecul ...
... 8. Describe the building-block molecules, structure, and biological importance of fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Know common examples. 9. Identify an ester linkage and describe how it is formed. 10. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fats. 11. Name the principal energy storage molecul ...
Biomolecule Discussion Guide KEY
... dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagram based on the animations shown in class). b. How are polymers broken apa ...
... dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagram based on the animations shown in class). b. How are polymers broken apa ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.