Slide 1
... Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled. • In proteins the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein, which also involves the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary struct ...
... Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled. • In proteins the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein, which also involves the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary struct ...
unit 1: introduction to biology
... Q. 6: Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown? A) Krebs cycle B) electron transport chain C) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid D) conversion of glucose to pyruvate E) none of the above Q. 7: Which of the following is NOT true ...
... Q. 6: Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown? A) Krebs cycle B) electron transport chain C) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid D) conversion of glucose to pyruvate E) none of the above Q. 7: Which of the following is NOT true ...
Microbiology with Diseases Taxonomy
... 28) All of the following bases are found in RNA molecules EXCEPT A) thymine. B) cytosine. C) uracil. D) adenine. 29) The "backbone" of the DNA molecule is composed of A) phosphates. B) nitrogenous bases. C) pentoses. D) alternating phosphates and pentoses. E) amino acids. ...
... 28) All of the following bases are found in RNA molecules EXCEPT A) thymine. B) cytosine. C) uracil. D) adenine. 29) The "backbone" of the DNA molecule is composed of A) phosphates. B) nitrogenous bases. C) pentoses. D) alternating phosphates and pentoses. E) amino acids. ...
WS Chapter 1
... b. Only one variable is tested at a time. c. Scientists always use controlled experiments. d. Controlled experiments cannot be performed on living things. 7. A scientific theory is a. another word for hypothesis. b. a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. c. the same as ...
... b. Only one variable is tested at a time. c. Scientists always use controlled experiments. d. Controlled experiments cannot be performed on living things. 7. A scientific theory is a. another word for hypothesis. b. a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. c. the same as ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
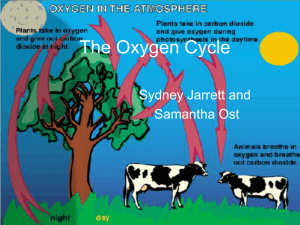
The Oxygen Cycle - EDHSGreenSea.net
... they have been buried in the ground gets absorbed by the soil. ...
... they have been buried in the ground gets absorbed by the soil. ...
No Slide Title
... products, DNA, RNA, enzymes, etc. are all polymers made from a predetermined set of monomers The four primary polymers of interest are: ...
... products, DNA, RNA, enzymes, etc. are all polymers made from a predetermined set of monomers The four primary polymers of interest are: ...
Matrix: Citric Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Oxidation Mitochondrion A
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
... • Production of ATP as a result of electron transfer through carriers in the Electron Transport Chain – Electrons pass through a set of membrane-associated carriers by a series of redox reactions – Energy from electron transport powers the active transport of H+ to the intermembrane compartment of t ...
Title - Iowa State University
... type binds the atoms of a water molecule together? Draw a water molecule and label which parts have a partial positive change and which have a partial negative charge. ...
... type binds the atoms of a water molecule together? Draw a water molecule and label which parts have a partial positive change and which have a partial negative charge. ...
Chemistry, Photosynthesis, Respiration Review
... B—glucose C--light reaction D and E—Chrorophyll and chloroplast F—Electrons from water G—Energy transfer H--Chemiosmosis I—NADPH J—ATP K—Calvin Cycle L—made into PGA M—RuBp N—Glucose ...
... B—glucose C--light reaction D and E—Chrorophyll and chloroplast F—Electrons from water G—Energy transfer H--Chemiosmosis I—NADPH J—ATP K—Calvin Cycle L—made into PGA M—RuBp N—Glucose ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Each gene contains the instructions to build a specific protein. It is the proteins that our bodies make that give us our traits – freckles, brown eyes, blond hair, etc. ...
... Each gene contains the instructions to build a specific protein. It is the proteins that our bodies make that give us our traits – freckles, brown eyes, blond hair, etc. ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... There are two (competing) theories: (1) Organic compounds were delivered to Earth by interplanetary dust, meteorites, comets and asteroids: “Panspermia” (2) Organic compounds were synthesized ...
... There are two (competing) theories: (1) Organic compounds were delivered to Earth by interplanetary dust, meteorites, comets and asteroids: “Panspermia” (2) Organic compounds were synthesized ...
Study Guide
... chlorophyll within its membrane. 19. A combination of reactions that use light energy and atmospheric carbon dioxide to synthesize large energy-rich molecules. 21. The incorporation of atmospheric CO2 into a carbohydrate molecule. 22. These hold atoms together in an arranged order to form molecules. ...
... chlorophyll within its membrane. 19. A combination of reactions that use light energy and atmospheric carbon dioxide to synthesize large energy-rich molecules. 21. The incorporation of atmospheric CO2 into a carbohydrate molecule. 22. These hold atoms together in an arranged order to form molecules. ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... Its 3-dimensional shape Some amino acids have a negative charge that bind onto an amino acid in the string that has a positive charge, causing a 3-dimensional fold in the string. It is essential to a protein’s physiological function. If it does not fold properly, it will not be in the proper shape t ...
... Its 3-dimensional shape Some amino acids have a negative charge that bind onto an amino acid in the string that has a positive charge, causing a 3-dimensional fold in the string. It is essential to a protein’s physiological function. If it does not fold properly, it will not be in the proper shape t ...
Alcoholic fermentation
... Complete the notes sheets below. Where you see a blank (…………………..), decide which word/phrase is most appropriate. ………………………. (which takes place in the ……………………) produces …… molecules of pyruvate. The fate of the pyruvate depends on …………………… availability. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentat ...
... Complete the notes sheets below. Where you see a blank (…………………..), decide which word/phrase is most appropriate. ………………………. (which takes place in the ……………………) produces …… molecules of pyruvate. The fate of the pyruvate depends on …………………… availability. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentat ...
T Dx test II
... a. their target cells must formulate new proteins before an effect can take place b. second messengers act slowly c. they are large molecules and move slowly through the blood d. because they are large polar molecules, they do not enter cells easily e. they are synthesized in very small quantities b ...
... a. their target cells must formulate new proteins before an effect can take place b. second messengers act slowly c. they are large molecules and move slowly through the blood d. because they are large polar molecules, they do not enter cells easily e. they are synthesized in very small quantities b ...
05- macromolecules
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
File
... Acid: A chemical compound that releases H+ atoms Base: A chemical compound that attracts H+ atoms, causing OH ions to accumulate. Organic Compounds found in living things ...
... Acid: A chemical compound that releases H+ atoms Base: A chemical compound that attracts H+ atoms, causing OH ions to accumulate. Organic Compounds found in living things ...
Amino Acids
... Organic compounds with amino and carboxylate functional groups Each AA has unique side chain (R) attached to alpha (α) carbon Crystalline solids with high MP’s Highly-soluble in water Exist as dipolar, charged zwitterions (ionic form) Exist as either L- or D- enantiomers Almost without exception, bi ...
... Organic compounds with amino and carboxylate functional groups Each AA has unique side chain (R) attached to alpha (α) carbon Crystalline solids with high MP’s Highly-soluble in water Exist as dipolar, charged zwitterions (ionic form) Exist as either L- or D- enantiomers Almost without exception, bi ...
Gene Expression
... DNA in cells controls all sorts of things such as the color of your eyes, the color of your hair, and whether or not you can digest milk. These characteristics are called traits. DNA also controls your responses to stimuli in the environment to keep you alive. For example, when you are frightened, t ...
... DNA in cells controls all sorts of things such as the color of your eyes, the color of your hair, and whether or not you can digest milk. These characteristics are called traits. DNA also controls your responses to stimuli in the environment to keep you alive. For example, when you are frightened, t ...
Atomic Structure (Bohr or Planetary Model)
... are grouped into two general classes: – Catabolic (exergonic) reactions • decomposition reactions that release energy (due to bonds breaking) in the form of HEAT into the environment of the reaction • reactants contain more energy than the products – Anabolic (endergonic) reactions • synthesis react ...
... are grouped into two general classes: – Catabolic (exergonic) reactions • decomposition reactions that release energy (due to bonds breaking) in the form of HEAT into the environment of the reaction • reactants contain more energy than the products – Anabolic (endergonic) reactions • synthesis react ...
BINF6201/8201 Basics of Molecular Biology
... Ø However, the complementary parts in a RNA molecule can form local double-stranded structures, thus, causing loops in the non-complementary regions. ...
... Ø However, the complementary parts in a RNA molecule can form local double-stranded structures, thus, causing loops in the non-complementary regions. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.