Energy and Respiration
... 4 carbon compound to make a 6 carbon compound. A series of steps now transfer the 6C (citrate) back to the 4C (oxaloacetate) These steps include more decarboxylation and dehydrogenation ...
... 4 carbon compound to make a 6 carbon compound. A series of steps now transfer the 6C (citrate) back to the 4C (oxaloacetate) These steps include more decarboxylation and dehydrogenation ...
9/19
... Most phototrophs reduce nitrate to ammonia and then use ammonia Some bacteria can reduce and assimilate atmospheric nitrogen ...
... Most phototrophs reduce nitrate to ammonia and then use ammonia Some bacteria can reduce and assimilate atmospheric nitrogen ...
PPT
... Salt bridges – ionic bonds form between acidic and basic residues Hydrogen bonds – form between polar residues ...
... Salt bridges – ionic bonds form between acidic and basic residues Hydrogen bonds – form between polar residues ...
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis
... enzymes that degrade RNA from the 5′ end; • serves as an assembly point for the proteins needed to recruit the small subunit of the ribosome to begin translation. ...
... enzymes that degrade RNA from the 5′ end; • serves as an assembly point for the proteins needed to recruit the small subunit of the ribosome to begin translation. ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... urine or used to synthesize other compounds. ...
... urine or used to synthesize other compounds. ...
Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... urine or used to synthesize other compounds. ...
... urine or used to synthesize other compounds. ...
Printing – LAB Organic Molecule – Lipid
... 2. A wide variety of proteins are located in and around membranes. These proteins can associate with membranes in a variety of ways. 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. ...
... 2. A wide variety of proteins are located in and around membranes. These proteins can associate with membranes in a variety of ways. 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. ...
1 glucose 2 molecules acetyl CoA
... • Lipids and proteins can also be used for energy via the same pathways used for the metabolism of pyruvate. ...
... • Lipids and proteins can also be used for energy via the same pathways used for the metabolism of pyruvate. ...
amino acids - CRCBiologyY11
... contain sulphur and may form complexes with other molecules. Proteins are made of small units called amino acids. These link together by peptide bonds to form chains of polypeptides. Musical Proteins ...
... contain sulphur and may form complexes with other molecules. Proteins are made of small units called amino acids. These link together by peptide bonds to form chains of polypeptides. Musical Proteins ...
Use food products in two ways
... Occurs in liver & muscle cells Process of joining glucose molecules together > glycogen (animal starch) ...
... Occurs in liver & muscle cells Process of joining glucose molecules together > glycogen (animal starch) ...
Energy and Metabolism
... (1) occurs in cytoplasm; anaerobic (2) rearranges the bonds in glucose molecules, releasing free energy to form ATP from ADP through substrate-level phosphorylation resulting in the production of pyruvate. c. Kreb’s cycle (1) occurs in mitochondrial matrix (2) also called the citric acid cycle (3) o ...
... (1) occurs in cytoplasm; anaerobic (2) rearranges the bonds in glucose molecules, releasing free energy to form ATP from ADP through substrate-level phosphorylation resulting in the production of pyruvate. c. Kreb’s cycle (1) occurs in mitochondrial matrix (2) also called the citric acid cycle (3) o ...
Subject Description Form
... Lectures are designed to provide students with the basic concepts of structurefunction relationship of common biolmolecules and the principles of metabolism and enzymology. To enhance their learning and knowledge, problem-based learning approach will be adopted. Students will be given assignments in ...
... Lectures are designed to provide students with the basic concepts of structurefunction relationship of common biolmolecules and the principles of metabolism and enzymology. To enhance their learning and knowledge, problem-based learning approach will be adopted. Students will be given assignments in ...
Do Now - Montville.net
... Name some examples of foods containing carbohydrates. What are lipids used in our bodies for? Name examples of foods that contain both saturated and unsaturated fats. ...
... Name some examples of foods containing carbohydrates. What are lipids used in our bodies for? Name examples of foods that contain both saturated and unsaturated fats. ...
Chlorella CGF
... DESCRIPTION Planktonic algae, microscopic size of a chlorophyll cell (green), usually spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
... DESCRIPTION Planktonic algae, microscopic size of a chlorophyll cell (green), usually spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
Biology 4974/5974, Evolution
... Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon association arose by chance and perhaps several times. In a successful group of protocells, any major change would produce nonfunctional proteins. ...
... Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon association arose by chance and perhaps several times. In a successful group of protocells, any major change would produce nonfunctional proteins. ...
Metabolism
... as compounds other than primary compounds. A compound is classified as a secondary metabolite if it does not seem to directly function in the processes of growth and development. Even though secondary compounds are a normal part of the metabolism of an organism, they are often produced in specialize ...
... as compounds other than primary compounds. A compound is classified as a secondary metabolite if it does not seem to directly function in the processes of growth and development. Even though secondary compounds are a normal part of the metabolism of an organism, they are often produced in specialize ...
Student PPT Notes
... unique bonding properties of carbon are key to the complexity of organic molecules 1. ________ 4 valence electrons (room for 8) can form up to __ bonds with other atoms or itself capable of making ______________, and ____________ bonds hydrogen carbon nitrogen oxygen ...
... unique bonding properties of carbon are key to the complexity of organic molecules 1. ________ 4 valence electrons (room for 8) can form up to __ bonds with other atoms or itself capable of making ______________, and ____________ bonds hydrogen carbon nitrogen oxygen ...
File - Ms. Kuiper`s Website
... body, they serve as _______________-term energy storage molecules. Lipids include fats, _______________, and _______________. 27. The 3 most important classes of lipids are neutral fats, _______________, and _______________. 28. Oil, fat, butter are all composed of lipid molecules called ___________ ...
... body, they serve as _______________-term energy storage molecules. Lipids include fats, _______________, and _______________. 27. The 3 most important classes of lipids are neutral fats, _______________, and _______________. 28. Oil, fat, butter are all composed of lipid molecules called ___________ ...
Review Questions
... and still others that form hydrogen bonds. For example, cysteine is an amino acid that has a sulfadryl group (-SH) for its R group. If a cysteine gets in close proximity with another cysteine down the chain, they will form a covalent bond between the two sulfurs (called a disulfide bridge). The tert ...
... and still others that form hydrogen bonds. For example, cysteine is an amino acid that has a sulfadryl group (-SH) for its R group. If a cysteine gets in close proximity with another cysteine down the chain, they will form a covalent bond between the two sulfurs (called a disulfide bridge). The tert ...
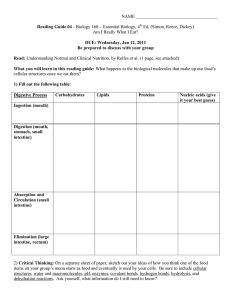
Reading Guide 04- Digestion
... 2) Critical Thinking: On a separate sheet of paper, sketch out your ideas of how you think one of the food items on your group’s menu starts as food and eventually is used by your cells. Be sure to include cellular structures, water and macromolecules, pH, enzymes, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, hy ...
... 2) Critical Thinking: On a separate sheet of paper, sketch out your ideas of how you think one of the food items on your group’s menu starts as food and eventually is used by your cells. Be sure to include cellular structures, water and macromolecules, pH, enzymes, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, hy ...
Chapter 17 - Amino Acid Metabolism
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
Slide 1
... DNA is a “twisted ladder”…alternating sugar and phosphate groups make up the uprights of the ladder and the rungs are nitrogen bases hydrogen bonded together (recall hydrogen bonds are weak bonds and can come apart easily). The rungs are always one purine bonded to one pyrimidine…A always to T and ...
... DNA is a “twisted ladder”…alternating sugar and phosphate groups make up the uprights of the ladder and the rungs are nitrogen bases hydrogen bonded together (recall hydrogen bonds are weak bonds and can come apart easily). The rungs are always one purine bonded to one pyrimidine…A always to T and ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.