Lecture 5
... We start as a single fertilized egg which divides into identical cells So why aren’t we born as blobs of identical cells? Why do we stop growing? Every cell has identical DNA, so what makes cells different? Genes are not operating in the same places in the same manner Certain genes are turned on, ot ...
... We start as a single fertilized egg which divides into identical cells So why aren’t we born as blobs of identical cells? Why do we stop growing? Every cell has identical DNA, so what makes cells different? Genes are not operating in the same places in the same manner Certain genes are turned on, ot ...
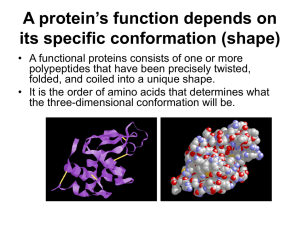
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... protein’s conformation and ability to function. • In individuals with sickle cell disease, abnormal hemoglobins, oxygen-carrying proteins, develop because of a single amino acid substitution. – These abnormal hemoglobins crystallize, deforming the red blood cells and leading to clogs in tiny blood v ...
... protein’s conformation and ability to function. • In individuals with sickle cell disease, abnormal hemoglobins, oxygen-carrying proteins, develop because of a single amino acid substitution. – These abnormal hemoglobins crystallize, deforming the red blood cells and leading to clogs in tiny blood v ...
Exam Review two KEY
... B. Light is captured in the head region of the chlorophyll C. Chlorophyll absorbs light at all wavelengths of the visible spectrum D. The tail region of chlorophyll has no known function 43. Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A. Thylakoid membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Stroma D. Granum 44. The replic ...
... B. Light is captured in the head region of the chlorophyll C. Chlorophyll absorbs light at all wavelengths of the visible spectrum D. The tail region of chlorophyll has no known function 43. Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A. Thylakoid membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Stroma D. Granum 44. The replic ...
UTACCEL 2010
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
... By understanding the function of a gene in one organism, scientists can get an idea of what function that gene may perform in a more complex organism such as humans. The knowledge gained can then be applied to various fields such as medicine, biological engineering and forensics. ...
B2 Topic 1 The Components of Life
... • Genetic Issues • Enzymes and conditions affecting them Organisms have adapted to live in extreme environments, what are two examples of these? ...
... • Genetic Issues • Enzymes and conditions affecting them Organisms have adapted to live in extreme environments, what are two examples of these? ...
3.13 Amino acids, proteins and DNA
... They are the building blocks for proteins which are held together by peptide links. The body has 20 naturally occurring amino acids which join to form proteins, polypeptides, dipeptides, tripeptides and enzymes etc. The R is an organic side group and can contain OH, SH, COOH or NH2 groups. Glycine i ...
... They are the building blocks for proteins which are held together by peptide links. The body has 20 naturally occurring amino acids which join to form proteins, polypeptides, dipeptides, tripeptides and enzymes etc. The R is an organic side group and can contain OH, SH, COOH or NH2 groups. Glycine i ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Duplin County Schools
... • Enzymes regulate many chemical reactions such as: – Photosynthesis – Cellular respiration – Digestion ...
... • Enzymes regulate many chemical reactions such as: – Photosynthesis – Cellular respiration – Digestion ...
Chapt. 3-Proteins - University of New England
... response to heat shock into irregular foci that disappear upon recovery at optimal temperatures. We have tagged Hsp104 with a fluorescent protein (GFP) so that its subcellular responses to various physiological conditions can be observed. ...
... response to heat shock into irregular foci that disappear upon recovery at optimal temperatures. We have tagged Hsp104 with a fluorescent protein (GFP) so that its subcellular responses to various physiological conditions can be observed. ...
The Body`s Fundamental Building Blocks
... The 40 urine amino acid analysis is best used for discriminating the metabolic effects of short-term (24-48 hour) dietary changes. Urine analysis requires more rigorous dietary control than plasma analysis in order to give an accurate picture of the patient’s steady state amino acid sufficiency and ...
... The 40 urine amino acid analysis is best used for discriminating the metabolic effects of short-term (24-48 hour) dietary changes. Urine analysis requires more rigorous dietary control than plasma analysis in order to give an accurate picture of the patient’s steady state amino acid sufficiency and ...
The Body`s Fundamental Building Blocks
... The 40 urine amino acid analysis is best used for discriminating the metabolic effects of short-term (24-48 hour) dietary changes. Urine analysis requires more rigorous dietary control than plasma analysis in order to give an accurate picture of the patient’s steady state amino acid sufficiency and ...
... The 40 urine amino acid analysis is best used for discriminating the metabolic effects of short-term (24-48 hour) dietary changes. Urine analysis requires more rigorous dietary control than plasma analysis in order to give an accurate picture of the patient’s steady state amino acid sufficiency and ...
I. LIFE FUNCTIONS (Processes)
... - doesn’t require O2 Not as efficient as aerobic - doesn’t yield as much ATP ...
... - doesn’t require O2 Not as efficient as aerobic - doesn’t yield as much ATP ...
video slide
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
Chapter 5 The Structure & Function of Molecules
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
Self-Replication
... • Viruses infect all three branches of “life”. • The overwhelming number of viruses are not harmful to their hosts and peacefully co-exist – We have more viral genes than human genes in us, if you take a whole body and process it for genes. • Viruses may have been a step in the sequence of evolution ...
... • Viruses infect all three branches of “life”. • The overwhelming number of viruses are not harmful to their hosts and peacefully co-exist – We have more viral genes than human genes in us, if you take a whole body and process it for genes. • Viruses may have been a step in the sequence of evolution ...
lecture 47 slides no animations
... These amino acids participate in the more common, right-handed form of helices ...
... These amino acids participate in the more common, right-handed form of helices ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life
... • sources of necessary ions (Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, etc.) • play important roles in metabolism ...
... • sources of necessary ions (Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, etc.) • play important roles in metabolism ...
The Origin and Early Evolution of Life
... RNA World DNA is genetic material now DNA-to-RNA-to-protein system is complicated RNA may have been first genetic material ...
... RNA World DNA is genetic material now DNA-to-RNA-to-protein system is complicated RNA may have been first genetic material ...
Protein Synthesis
... Once DNA is replicated, the cell now needs to make proteins. How does DNA’s message travel OUT of the nucleus and INTO THE CELL, where the message gets expressed as a protein??? This is known as… ...
... Once DNA is replicated, the cell now needs to make proteins. How does DNA’s message travel OUT of the nucleus and INTO THE CELL, where the message gets expressed as a protein??? This is known as… ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
Bioknowlodgy worksheet 2.4
... 2.4.U1 Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. AND 2.4.S1 Drawing molecular diagrams to show the formation of a peptide bond. 1. Condensation of amino acids is a polymerisation reaction. A chain of amino acids joined together is called a polypeptide. These building reac ...
... 2.4.U1 Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. AND 2.4.S1 Drawing molecular diagrams to show the formation of a peptide bond. 1. Condensation of amino acids is a polymerisation reaction. A chain of amino acids joined together is called a polypeptide. These building reac ...
1 1) What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most
... A) Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. B) Enzymes display specificity for certain molecules with which they interact. C) Enzymes raise the activation energy for the reactions they catalyze. D) An enzyme may be used many times over for a specific reaction. ...
... A) Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. B) Enzymes display specificity for certain molecules with which they interact. C) Enzymes raise the activation energy for the reactions they catalyze. D) An enzyme may be used many times over for a specific reaction. ...
Chapter 3
... the active sites, enabling the great variety of proteins to interact with all different kinds of molecules. ...
... the active sites, enabling the great variety of proteins to interact with all different kinds of molecules. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.