Molecular Biology Final Exam (Set A)
... complementary, anti-parallel strand. This means that DNA has a very regular structure, typically a Watson-Crick double helix, regardless of its sequence. In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. Thi ...
... complementary, anti-parallel strand. This means that DNA has a very regular structure, typically a Watson-Crick double helix, regardless of its sequence. In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. Thi ...
Electron Transport Chain Questions
... when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxidation-reduction reaction). The other H+ ion goes into the cytosol to build up the concentration gradient that helps generate ATP in the next stage. NADH then goes on t ...
... when it is oxidized (loses electrons and H+ ion), NAD+ collects the energy in the form of electrons and becomes reduced to NADH (oxidation-reduction reaction). The other H+ ion goes into the cytosol to build up the concentration gradient that helps generate ATP in the next stage. NADH then goes on t ...
A Mad Scientist`s Chemistry Presentation
... carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • The most common element in biomolecules is carbon. • Carbon atoms can bond with one another and with other atoms easily. • Therefore, they can form many different compounds. ...
... carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • The most common element in biomolecules is carbon. • Carbon atoms can bond with one another and with other atoms easily. • Therefore, they can form many different compounds. ...
Keystone review powerpoint content only with Images
... • Dominant traits are represented by capital letters, while recessive (non-dominant traits) are represented by lower case letters. – Each parent has two copies of the gene, so they will get two letters. The different letters represent the different alleles (flower pedal color) of a trait. – Since wh ...
... • Dominant traits are represented by capital letters, while recessive (non-dominant traits) are represented by lower case letters. – Each parent has two copies of the gene, so they will get two letters. The different letters represent the different alleles (flower pedal color) of a trait. – Since wh ...
Amino acids 1
... Hydrophobicity is the most important characteristic of amino acids. It is the hydrophobic effect that drives proteins towards folding. Actually, it is all done by water. Water does not like hydrophobic surfaces. When a protein folds, exposed hydrophobic side chains get buried, and release water of i ...
... Hydrophobicity is the most important characteristic of amino acids. It is the hydrophobic effect that drives proteins towards folding. Actually, it is all done by water. Water does not like hydrophobic surfaces. When a protein folds, exposed hydrophobic side chains get buried, and release water of i ...
Ch. 5 - Macromolecules
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... – Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
Living Environment Regents Review
... Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Too much carbon dioxide chloroplasts will cause the Earth to heat up Animals can (the greenhouse effect). eat the sugar made to use as energy ...
... Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. Too much carbon dioxide chloroplasts will cause the Earth to heat up Animals can (the greenhouse effect). eat the sugar made to use as energy ...
What meaning(s) do these two photos represent? (Hint* dna,rna
... Evolution, spliced in different ways in different tissues ...
... Evolution, spliced in different ways in different tissues ...
Dan`s poster - The University of Sheffield
... None of the lines thus far reported show an easily perceived phenotype, however, it is hoped that our method will reveal transport differences within the plants. ...
... None of the lines thus far reported show an easily perceived phenotype, however, it is hoped that our method will reveal transport differences within the plants. ...
2: Chemistry Comes Alive: Objectives Part 1: Basic Chemistry
... 11. Define the three major types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, and exchange. Comment on the nature of oxidation-reduction reactions and their importance. 12. Explain why chemical reactions in the body are often irreversible. 13. Describe factors that affect chemical reaction rates ...
... 11. Define the three major types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, and exchange. Comment on the nature of oxidation-reduction reactions and their importance. 12. Explain why chemical reactions in the body are often irreversible. 13. Describe factors that affect chemical reaction rates ...
amino acid , peptide and protein metabolism
... Dipeptide , tetrapeptides, pentapeptides, etc few amino acids are joined ------ oligopeptide. many amino acids are joined----- polypeptide (protein usually >50 amino acids) ...
... Dipeptide , tetrapeptides, pentapeptides, etc few amino acids are joined ------ oligopeptide. many amino acids are joined----- polypeptide (protein usually >50 amino acids) ...
Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
... your muscles will outpace your body’s ability to deliver it Metabolism then becomes anaerobic, and your muscle cells switch to an “emergency mode” Break down glucose very inefficiently and produce lactic acid as a by-product So exergonic reactions can provide the energy to drive the formation of ATP ...
... your muscles will outpace your body’s ability to deliver it Metabolism then becomes anaerobic, and your muscle cells switch to an “emergency mode” Break down glucose very inefficiently and produce lactic acid as a by-product So exergonic reactions can provide the energy to drive the formation of ATP ...
Macromolecules Biological Molecules Macromolecules
... • There are four categories of biologically important carbohydrates: 1. Monosaccharides, simple sugars; glucose, ribose, and fructose. the monomers for the larger carbohydrates. 2. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides linked together by covalent bonds. 3. Oligosaccharides (oligo, "several") ...
... • There are four categories of biologically important carbohydrates: 1. Monosaccharides, simple sugars; glucose, ribose, and fructose. the monomers for the larger carbohydrates. 2. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides linked together by covalent bonds. 3. Oligosaccharides (oligo, "several") ...
Unit 06 Lecture Notes: Metabolism and Respiration
... b) Converts pyruvate into CO2 + acetaldehyde, acetaldehyde into ethanol c) Requires NADH, produces NAD+ d) When do yeasts go anaerobic? e) Why do you have to cover container when making beer or wine? ...
... b) Converts pyruvate into CO2 + acetaldehyde, acetaldehyde into ethanol c) Requires NADH, produces NAD+ d) When do yeasts go anaerobic? e) Why do you have to cover container when making beer or wine? ...
File - Wk 1-2
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
Lectures 1-3: Review of forces and elementary statistical
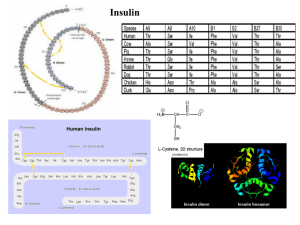
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
Chapter 5 Active Lecture Questions
... Apoenzymes are inactive by themselves and must be activated by ...
... Apoenzymes are inactive by themselves and must be activated by ...
BHS 150.1 – Course I Date: 10/18/12, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
... TEARS & ANYTHING EYE RELATED: TESTED AS NEW MATERIAL IN FULL DETAIL Amino acids and proteins: structure and function, stabilizing bonds for each structure Proteins made by 2 organelles: RER & Golgi Know tear-related proteins and their functions Enzymes: function and how they work—how can side chains ...
... TEARS & ANYTHING EYE RELATED: TESTED AS NEW MATERIAL IN FULL DETAIL Amino acids and proteins: structure and function, stabilizing bonds for each structure Proteins made by 2 organelles: RER & Golgi Know tear-related proteins and their functions Enzymes: function and how they work—how can side chains ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... (methionine) to the ribosome. • Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. • The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must complement codon for amino acid to be added to protein chain ...
... (methionine) to the ribosome. • Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. • The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must complement codon for amino acid to be added to protein chain ...
lecture5lifes_chemical_basis
... The helical content of a protein may vary anywhere between 0% to 100%. 75% of AAs in Ferritin, an iron storage protein is in alpha-helices. α-helices are usually less than 45Å long. However, two or more α-helices can entwine to form a very stable structure, which can have a length of 1000Å or more. ...
... The helical content of a protein may vary anywhere between 0% to 100%. 75% of AAs in Ferritin, an iron storage protein is in alpha-helices. α-helices are usually less than 45Å long. However, two or more α-helices can entwine to form a very stable structure, which can have a length of 1000Å or more. ...
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life
... sugar, base, phosphate group •DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, 2 strands of nucleotides that spiral around each other •RNA, ribonucleic acid, single strand ...
... sugar, base, phosphate group •DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, 2 strands of nucleotides that spiral around each other •RNA, ribonucleic acid, single strand ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.