Bio07_TR_U03_CH09.QXD
... The Krebs Cycle (pages 226-227) 3. In the presence of oxygen, how is the pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis used? ...
... The Krebs Cycle (pages 226-227) 3. In the presence of oxygen, how is the pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis used? ...
Amino Acids - UniMAP Portal
... Therefore can form ionic bonds with acidic amino acids. Lys contain amine R group which accepts a proton from water to form conjugate acid (-NH3+) His is a weak base because it partially ionized at pH 7. His act as buffer. Important role in catalytic activity of enzymes. ...
... Therefore can form ionic bonds with acidic amino acids. Lys contain amine R group which accepts a proton from water to form conjugate acid (-NH3+) His is a weak base because it partially ionized at pH 7. His act as buffer. Important role in catalytic activity of enzymes. ...
Metabolic Diversity
... In contrast to aerobic organisms, no single anaerobe is able to take glucose to CO2 Need an anaerobic food chain that takes each compound part of the way. Various organisms participate in the degradation of a polymeric sugar such as cellulose ...
... In contrast to aerobic organisms, no single anaerobe is able to take glucose to CO2 Need an anaerobic food chain that takes each compound part of the way. Various organisms participate in the degradation of a polymeric sugar such as cellulose ...
S1 Block 1 KU Test Revision
... b) Voltmeters are connected in parallel across the components in a circuit. c) Voltage is measured in Volts. d) The Voltage across each of the components in a parallel circuit will add up to the Battery Voltage (or Supply Voltage). 15) a) The Electric Current from the battery will split up between e ...
... b) Voltmeters are connected in parallel across the components in a circuit. c) Voltage is measured in Volts. d) The Voltage across each of the components in a parallel circuit will add up to the Battery Voltage (or Supply Voltage). 15) a) The Electric Current from the battery will split up between e ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... RNA is a second type of nucleic acid. RNA differs from DNA in that it has the base Uracil instead of the base Thymine (U pairs with A during base pairing); the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose, and in that the RNA is usually a single stranded molecule rather than a double helix like DNA. There ar ...
... RNA is a second type of nucleic acid. RNA differs from DNA in that it has the base Uracil instead of the base Thymine (U pairs with A during base pairing); the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose, and in that the RNA is usually a single stranded molecule rather than a double helix like DNA. There ar ...
Exam 3 Review
... For each substituent on the chain, we indicate the position in the chain (by an Arabic numeric prefix) and the kind of substituent (by its name). The position of a substituent on the chain is indicated by the lowest number possible. The number precedes the name of the substituent. When there are t ...
... For each substituent on the chain, we indicate the position in the chain (by an Arabic numeric prefix) and the kind of substituent (by its name). The position of a substituent on the chain is indicated by the lowest number possible. The number precedes the name of the substituent. When there are t ...
Nutrisi & Pertumbuhan Mikrobia
... Passive diffusion is the process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation. A few substances, such as glycerol, can cross the plasma membrane by passive diffusion. ...
... Passive diffusion is the process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation. A few substances, such as glycerol, can cross the plasma membrane by passive diffusion. ...
cellular respiration quiz review guide
... Define cellular respiration. What is the equation for cellular respiration? In what organelle does cellular respiration occur in? What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration? Define glycolysis. Why does glycolysis have to happen? Briefly describe the steps of glycolysis. What are the products of g ...
... Define cellular respiration. What is the equation for cellular respiration? In what organelle does cellular respiration occur in? What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration? Define glycolysis. Why does glycolysis have to happen? Briefly describe the steps of glycolysis. What are the products of g ...
Chem 101 notes review
... The Nucleus: Hund’s Rule states that each orbital will be filled singly Build by adding the required number of protons before pairing begins. The singly filled orbitals will have (the atomic number) and neutrons (the mass of the atom) ...
... The Nucleus: Hund’s Rule states that each orbital will be filled singly Build by adding the required number of protons before pairing begins. The singly filled orbitals will have (the atomic number) and neutrons (the mass of the atom) ...
Mutation Reading--How the Gene for Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
... …result in differences in the nucleotide sequence in mRNA… …result in differences in the amino acid sequence in the protein… …result in differences in the structure and function of the protein… …result in differences in a person's characteristics. For example, if a person has an allele that codes fo ...
... …result in differences in the nucleotide sequence in mRNA… …result in differences in the amino acid sequence in the protein… …result in differences in the structure and function of the protein… …result in differences in a person's characteristics. For example, if a person has an allele that codes fo ...
class title - Palomar College
... equations, chemical reactions, and mole; electonegativity, valence shells, and bonding. 4) Biochemistry—Important Inorganics Organic vs. inorganic molecules; monomers and polymers; dehydration synthesis; important organic groups; characteristics of water, acids, bases and pH; buffers. 5) Biochemistr ...
... equations, chemical reactions, and mole; electonegativity, valence shells, and bonding. 4) Biochemistry—Important Inorganics Organic vs. inorganic molecules; monomers and polymers; dehydration synthesis; important organic groups; characteristics of water, acids, bases and pH; buffers. 5) Biochemistr ...
Cellular Respiration Note Packet
... C. There is much _____________ stored in this molecule of _______________. This energy must be released in ___________________________ steps. If all the energy from glucose were released at once, most of it would be lost as ______________________. The energy stored in glucose will be released bit by ...
... C. There is much _____________ stored in this molecule of _______________. This energy must be released in ___________________________ steps. If all the energy from glucose were released at once, most of it would be lost as ______________________. The energy stored in glucose will be released bit by ...
Study Guide
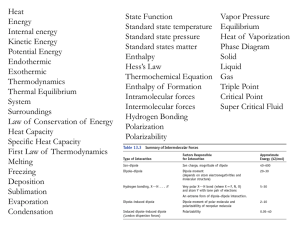
... Exam Content: The exam will cover chapters 1-6. All material covered in classnotes, book, and homework could be on the exam. Details from case studies will not be included, but problems of that sort are on the exam. Some major topics include: Solubility, free energy/enthalpy/entropy, coupled reactio ...
... Exam Content: The exam will cover chapters 1-6. All material covered in classnotes, book, and homework could be on the exam. Details from case studies will not be included, but problems of that sort are on the exam. Some major topics include: Solubility, free energy/enthalpy/entropy, coupled reactio ...
BIO 322_Rec_4part2_Spring 2013
... • In cytosol of hepatocytes, alanine amino transferase transfers the amino group of alanine to α ketoglutarate forming pyruvate and glutamate. • Glutamate goes to mitochondria releases ammonia or can undergo transamination with oxaloacetate to form aspartate, another nitrogen donor in urea synthesis ...
... • In cytosol of hepatocytes, alanine amino transferase transfers the amino group of alanine to α ketoglutarate forming pyruvate and glutamate. • Glutamate goes to mitochondria releases ammonia or can undergo transamination with oxaloacetate to form aspartate, another nitrogen donor in urea synthesis ...
Lipids WORD 1000 KB - Science Learning Hub
... Activity: Lipids Linoleic and linolenic fatty acids, since they have more than one carbon–carbon double bond present, are known as polyunsaturated. The position of the double bond is also important. Linoleic’s near-terminal double bond is at 6 (omega 6) whereas linolenic’s is at 3 (omega ...
... Activity: Lipids Linoleic and linolenic fatty acids, since they have more than one carbon–carbon double bond present, are known as polyunsaturated. The position of the double bond is also important. Linoleic’s near-terminal double bond is at 6 (omega 6) whereas linolenic’s is at 3 (omega ...
Ch 3 Cells - Review Cell theory The cell is the smallest unit of life
... Examples of transcription factors in our physiology include: hormones chemicals from adjacent cells growth factors other genes developmental chemicals proteins and cell specialization The body is made of many different cells with different functions. A cell’s structure and function is based on its ...
... Examples of transcription factors in our physiology include: hormones chemicals from adjacent cells growth factors other genes developmental chemicals proteins and cell specialization The body is made of many different cells with different functions. A cell’s structure and function is based on its ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). No stimulates guanylate cyclase forming cGMP (5), which results in a physiological response (6) No can diffuse out: a) to the presynaptic terminal (7) prolonging effect and b) into adjacent neurons (8) and glial cells (9) stimu ...
... NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). No stimulates guanylate cyclase forming cGMP (5), which results in a physiological response (6) No can diffuse out: a) to the presynaptic terminal (7) prolonging effect and b) into adjacent neurons (8) and glial cells (9) stimu ...
Structure of an Atom
... together via dehydration synthesis (like simple sugars). fl However, fats can be created through glycerol. fl Ex: Triglyceride: 3 fatty acid chains brought together via glycerol. fl Fats provide energy, protection of organs. fl Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature (unsaturated fats a ...
... together via dehydration synthesis (like simple sugars). fl However, fats can be created through glycerol. fl Ex: Triglyceride: 3 fatty acid chains brought together via glycerol. fl Fats provide energy, protection of organs. fl Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature (unsaturated fats a ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2 - Bi-YOLO-gy
... Part E. Which food molecule (monosaccharide, polysaccharide, lipid, protein) would you eat if… 68. …you needed a quick boost of energy? ...
... Part E. Which food molecule (monosaccharide, polysaccharide, lipid, protein) would you eat if… 68. …you needed a quick boost of energy? ...
Nutrition/Digestion/Excretion PPT
... Process of taking materials from environment and changing ...
... Process of taking materials from environment and changing ...
Exam 4
... 5. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 6. The tertiary structure of a protein is the A) bonding together of several different ...
... 5. Which type of interaction stabilizes the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet structures of proteins? A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 6. The tertiary structure of a protein is the A) bonding together of several different ...
Protein Synthesis Paper Lab
... Every now and then errors may occur in the process of forming proteins from the DNA coded instructions. An error is a mutation, which will result in a different amino acid sequence. The protein may be different in a good way or (more frequently) a bad way. Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cell ...
... Every now and then errors may occur in the process of forming proteins from the DNA coded instructions. An error is a mutation, which will result in a different amino acid sequence. The protein may be different in a good way or (more frequently) a bad way. Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cell ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.