Donald C. Cox Seminar Series in Microbiology Presents:
... remain uncultivated and the diversity of organisms and enzymes that participate in the carbon cycle is staggeringly complex. We are developing a new toolbox for exploring the carbon cycle and the metabolic and ecological characteristics of uncultivated microorganisms. We have employed high-resolutio ...
... remain uncultivated and the diversity of organisms and enzymes that participate in the carbon cycle is staggeringly complex. We are developing a new toolbox for exploring the carbon cycle and the metabolic and ecological characteristics of uncultivated microorganisms. We have employed high-resolutio ...
How Cells Obtain and Use Glucose Modeled with AgentSheets
... This Lesson Plan is brought to you for free and open access by the CMST Institute at Digital Commons @Brockport. It has been accepted for inclusion in Lesson Plans by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @Brockport. For more information, please contact [email protected]. ...
... This Lesson Plan is brought to you for free and open access by the CMST Institute at Digital Commons @Brockport. It has been accepted for inclusion in Lesson Plans by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @Brockport. For more information, please contact [email protected]. ...
Nova Southeastern University
... Attend lab sessions and submit timely and well-written lab reports. Every student must write their own lab reports even though they have worked with a lab partner. Contact the instructor if you are having problem. Attend help sessions if required by the instructor. Study in groups and review the cou ...
... Attend lab sessions and submit timely and well-written lab reports. Every student must write their own lab reports even though they have worked with a lab partner. Contact the instructor if you are having problem. Attend help sessions if required by the instructor. Study in groups and review the cou ...
Workshop: Protein Structure Introduction Learning Objectives
... • Be able to use rules that you develop in the workshop to categorize the 20 naturally occurring amino acids according to chemical character (nonpolar, polar, acidic, or basic) if shown their structures. • Be able to identify a peptide bond in a series of linked amino acids or draw two amino acids j ...
... • Be able to use rules that you develop in the workshop to categorize the 20 naturally occurring amino acids according to chemical character (nonpolar, polar, acidic, or basic) if shown their structures. • Be able to identify a peptide bond in a series of linked amino acids or draw two amino acids j ...
HB_Cell_Resp_KEYS_and_Review_Notes_12_BH
... Oxidation of Pyruvate - Pyruvate loses a carbon (leaves as CO2) - The broken bond is used to reduce NAD+ to NADH (charges up the molecule with two high energy electrons) - The remaining two carbons from the pyruvate bond to coenzyme A ...
... Oxidation of Pyruvate - Pyruvate loses a carbon (leaves as CO2) - The broken bond is used to reduce NAD+ to NADH (charges up the molecule with two high energy electrons) - The remaining two carbons from the pyruvate bond to coenzyme A ...
4.2 Cellular Respiration - Dr Rob's A
... organic molecules and the creation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) ...
... organic molecules and the creation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living
... 41.___________ _____________ is a form of technology that scientists use to alter the genetic instructions in organisms. 43.______________ _______________ a process that produces domestic animals and new varieties of plants with traits that are desired. 44.Gene splicing: ____________________________ ...
... 41.___________ _____________ is a form of technology that scientists use to alter the genetic instructions in organisms. 43.______________ _______________ a process that produces domestic animals and new varieties of plants with traits that are desired. 44.Gene splicing: ____________________________ ...
Are You suprised ?
... Note: answers will not be posted. You should be able to answer all of these questions by studying your notes and/or text. Please see me if you have trouble with a question(s). Multiple choice. Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. If you isolate mitochondria and place them in buffer with a l ...
... Note: answers will not be posted. You should be able to answer all of these questions by studying your notes and/or text. Please see me if you have trouble with a question(s). Multiple choice. Circle the letter next to the best answer. 1. If you isolate mitochondria and place them in buffer with a l ...
1. A Draw the structure of glucose using either a ring or straight
... C. Ferredoxin (Fd) is an iron containing protein present in the photosynthetic apparatus; during photosynthesis the iron undergoes a 1-electron redox reaction with an Eo' = -0.42v. Similarly cytochrome b5 is an iron-protein present in the microsomes with an Eo' = 0.0 v. For the reaction at pH = 7 ...
... C. Ferredoxin (Fd) is an iron containing protein present in the photosynthetic apparatus; during photosynthesis the iron undergoes a 1-electron redox reaction with an Eo' = -0.42v. Similarly cytochrome b5 is an iron-protein present in the microsomes with an Eo' = 0.0 v. For the reaction at pH = 7 ...
Chapter 3 - Martini
... Fundamental Unit of Life Rudolf Virchow says: • Life as we define it consists ...
... Fundamental Unit of Life Rudolf Virchow says: • Life as we define it consists ...
Chapter 5
... • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lip ...
... • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lip ...
Unit 7
... reactions by lowering the activation energy. • Enzymes can be controlled by: -Temperature. High temperatures decrease reaction rates. -pH balance. They function best at a level of 7. -Salinity. If enzymes are dissolved in fluids that exceed the tolerance level, the hydrogen bonds will break, thus in ...
... reactions by lowering the activation energy. • Enzymes can be controlled by: -Temperature. High temperatures decrease reaction rates. -pH balance. They function best at a level of 7. -Salinity. If enzymes are dissolved in fluids that exceed the tolerance level, the hydrogen bonds will break, thus in ...
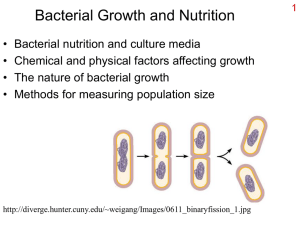
Bacterial Growth and Nutrition
... Chemical form must be appropriate • Not all bacteria can use the same things – Some molecules cannot be transported in – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences are used for identification ...
... Chemical form must be appropriate • Not all bacteria can use the same things – Some molecules cannot be transported in – Enzymes for metabolizing it might not be present – Chemical may be used, but more expensive – These differences are used for identification ...
CK12 Homework Sections 1.27 to 1.30 Section 1.27 Glycolysis 1
... Most living things use oxygen to make ATP from glucose. However, many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobi ...
... Most living things use oxygen to make ATP from glucose. However, many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobi ...
Presentation
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
Document
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
... Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates • Starches that are composed of many sugars linked together • They provide the body with long-term energy since they are digested more slowly than sugars. • Foods with LOTS of starch: rice, beans, potatoes © 2005 JupiterImages Corporation ...
Fermentation - cloudfront.net
... Name the two types of fermentation. How much ATP does glycolysis create? How much ATP does fermentation create? Which molecule is broken down during glycolysis? A buildup of which molecule causes sore muscles? Which waste molecules are created by alcoholic fermentation? 7) Is fermentation aerobic or ...
... Name the two types of fermentation. How much ATP does glycolysis create? How much ATP does fermentation create? Which molecule is broken down during glycolysis? A buildup of which molecule causes sore muscles? Which waste molecules are created by alcoholic fermentation? 7) Is fermentation aerobic or ...
NOTES: 13.1-13.2 - Protein Synthesis (powerpoint)
... • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
... • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
DOC
... The topic of Molecular Genetics deals with the DNA of the cell and the process that is used to decode its genetic code and use the information to make proteins. Genes are made of DNA. The expression of DNA is protein. The term given for making a protein is called “protein synthesis.” This requires D ...
... The topic of Molecular Genetics deals with the DNA of the cell and the process that is used to decode its genetic code and use the information to make proteins. Genes are made of DNA. The expression of DNA is protein. The term given for making a protein is called “protein synthesis.” This requires D ...
CHAP NUM="9" ID="CH
... ecosystems. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and ultimately leaves as heat, while the chemical elements essential to life are recycled. Figure 9.3 Methane combustion as an energy-yielding redox reaction. The reaction releases energy to the surroundings because the electrons lose potentia ...
... ecosystems. Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and ultimately leaves as heat, while the chemical elements essential to life are recycled. Figure 9.3 Methane combustion as an energy-yielding redox reaction. The reaction releases energy to the surroundings because the electrons lose potentia ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.