PS 1 answers
... (decrease in order) because clumping hydrophobic molecules together with each other reduces the number of water molecules in total that must order themselves around the hydrophobic molecules. (d) …the atoms in a single 6 carbon sugar? Covalent bonds. Carbon has 4 unpaired electrons and thus forms 4 ...
... (decrease in order) because clumping hydrophobic molecules together with each other reduces the number of water molecules in total that must order themselves around the hydrophobic molecules. (d) …the atoms in a single 6 carbon sugar? Covalent bonds. Carbon has 4 unpaired electrons and thus forms 4 ...
Making basic science clinically relevant for learners: the biochemistry example Eric Niederhoffer
... acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How is skeletal muscle phosphofructokinase-1 regulated? • What are the key Ca2+ regulated steps? • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glia ...
... acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How is skeletal muscle phosphofructokinase-1 regulated? • What are the key Ca2+ regulated steps? • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glia ...
Protein Chemistry
... increasing the rates of final stage in folding process. Many proteins contain chaperons “signals” (specific a.a. sequence). ...
... increasing the rates of final stage in folding process. Many proteins contain chaperons “signals” (specific a.a. sequence). ...
Chapter 2 Outline 6TH PERIOD
... either solid or liquid. Triglycerides help keep the body warm and protect body tissues. *phospholipids are very much like triglycerides except that they have 2 fatty acids instead of 3. The “head” of a phospholipid has an electrical charge, while the “tail” does not. *steroids are flat molecules for ...
... either solid or liquid. Triglycerides help keep the body warm and protect body tissues. *phospholipids are very much like triglycerides except that they have 2 fatty acids instead of 3. The “head” of a phospholipid has an electrical charge, while the “tail” does not. *steroids are flat molecules for ...
Section 2 - Introduction to Molecular Biology
... • A protein is a linear polymer of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. • The average protein is c. 200 amino acids long, but some can contain thousands of amino acids. • Proteins are the main functional chemicals in the cell, carrying out many functions, for example catalysis of the reacti ...
... • A protein is a linear polymer of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. • The average protein is c. 200 amino acids long, but some can contain thousands of amino acids. • Proteins are the main functional chemicals in the cell, carrying out many functions, for example catalysis of the reacti ...
Lecture PPT
... proteins to be analysed are isolated from cell lysate or tissues by biochemical fractionation or affinity selection. This often includes a final step of onedimensional gel electrophoresis, and defines the 'sub-proteome' to be analysed. MS of whole proteins is less sensitive than peptide MS and the m ...
... proteins to be analysed are isolated from cell lysate or tissues by biochemical fractionation or affinity selection. This often includes a final step of onedimensional gel electrophoresis, and defines the 'sub-proteome' to be analysed. MS of whole proteins is less sensitive than peptide MS and the m ...
Enzymes Recap
... • Explain why glucose acts as a fuel of choice for the genera=on of ATP. • Detail how dietary carbohydrate is digested and the general mechanisms of glucose uptake in the gut and beyond. • List ...
... • Explain why glucose acts as a fuel of choice for the genera=on of ATP. • Detail how dietary carbohydrate is digested and the general mechanisms of glucose uptake in the gut and beyond. • List ...
Compare and Contrast table for Photosynthesis and Cellular
... 6.) Inorganic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. ____________ 7.) The type of pathway body builders are interested in maximizing. ________________ 8.) The free energy of a non-spontaneous reaction. ____________________ 9.) Energy can neither be created nor destro ...
... 6.) Inorganic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. ____________ 7.) The type of pathway body builders are interested in maximizing. ________________ 8.) The free energy of a non-spontaneous reaction. ____________________ 9.) Energy can neither be created nor destro ...
Compare and Contrast table for Photosynthesis and Cellular
... 6.) Inorganic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. ____________ 7.) The type of pathway body builders are interested in maximizing. ________________ 8.) The free energy of a non-spontaneous reaction. ____________________ 9.) Energy can neither be created nor destro ...
... 6.) Inorganic molecules that bind to enzymes and are necessary for their functioning. ____________ 7.) The type of pathway body builders are interested in maximizing. ________________ 8.) The free energy of a non-spontaneous reaction. ____________________ 9.) Energy can neither be created nor destro ...
Chapter 6 Proteins and Amino Acids I Introduction II The Structure of
... A. if there's NOT enough glucose available to the cell, the AA will be stripped of its (which is excreted in ...
... A. if there's NOT enough glucose available to the cell, the AA will be stripped of its (which is excreted in ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... Chemical reactions that involve the loss of hydrogen and electrons are called oxidation reactions. Chemical reactions that result in the uptake of hydrogen and electrons are called reduction reactions. In general, the breaking down of larger molecules into smaller molecules are oxidation reactions. ...
... Chemical reactions that involve the loss of hydrogen and electrons are called oxidation reactions. Chemical reactions that result in the uptake of hydrogen and electrons are called reduction reactions. In general, the breaking down of larger molecules into smaller molecules are oxidation reactions. ...
Presentation
... • Elevated levels of citrate (indicate ample substrates for citric acid cycle) also inhibit PFK-1 ...
... • Elevated levels of citrate (indicate ample substrates for citric acid cycle) also inhibit PFK-1 ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
Mechanism of Enzyme Action
... Enzyme has appropriate three dimensional structure to keep the substrates in a specific orientation, such that reactive groups come to physical apposition. Eg: Glucose + ATP = Glucose-6-P ...
... Enzyme has appropriate three dimensional structure to keep the substrates in a specific orientation, such that reactive groups come to physical apposition. Eg: Glucose + ATP = Glucose-6-P ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... 1. Describe ways ATP is used in the body. RSQ – list at least 5. V. Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs when oxygen _______________ available. a. Equation for lactic acid fermentation-b. Equation for alcoholic fermentation-2. Compare lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation by describing what p ...
... 1. Describe ways ATP is used in the body. RSQ – list at least 5. V. Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs when oxygen _______________ available. a. Equation for lactic acid fermentation-b. Equation for alcoholic fermentation-2. Compare lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation by describing what p ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... The phosphate esters that are formed are intermediates in further processes Nature uses phosphates the way chemists use tosylates (to make an OH into a leaving group) ...
... The phosphate esters that are formed are intermediates in further processes Nature uses phosphates the way chemists use tosylates (to make an OH into a leaving group) ...
Protein Structure - FAU College of Engineering
... The amino acids are linked covalently by peptide bonds. The image shows how three amino acids linked by peptide bonds into a tripeptide. ...
... The amino acids are linked covalently by peptide bonds. The image shows how three amino acids linked by peptide bonds into a tripeptide. ...
Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case
... Proteins regulate gene expression at multiple stages ranging from transcription through RNA processing and translation. At each stage, regulatory proteins overcome diverse problems of molecular recognition to associate with the target nucleic acid and respond to cellular signals. This seminar descri ...
... Proteins regulate gene expression at multiple stages ranging from transcription through RNA processing and translation. At each stage, regulatory proteins overcome diverse problems of molecular recognition to associate with the target nucleic acid and respond to cellular signals. This seminar descri ...
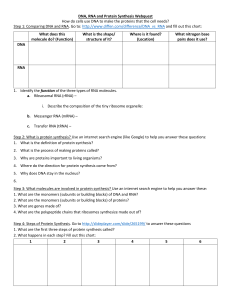
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Webquest
... Step 3: What molecules are involved in protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine to help you answer these: 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the poly ...
... Step 3: What molecules are involved in protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine to help you answer these: 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the poly ...
RESPIRATION & PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... Respiration is a catabolic process: large molecules are broken down and the energy released from bonds is used for: maintenance growth (anabolic process) reproduction The energy released is transformed into ATP ...
... Respiration is a catabolic process: large molecules are broken down and the energy released from bonds is used for: maintenance growth (anabolic process) reproduction The energy released is transformed into ATP ...
Intro Cell Physiolog..
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
Give reasons for the following: (i) Bond enthalpy of F2
... PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3 because NH3 molecule possess intermolecular hydrogen bondings which binds them strongly whereas PH3 has weaker Vander Waal’s forces. Thus, PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3. The structures of following molecules are as follows: (i) BrF3, Bent T-shape ...
... PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3 because NH3 molecule possess intermolecular hydrogen bondings which binds them strongly whereas PH3 has weaker Vander Waal’s forces. Thus, PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3. The structures of following molecules are as follows: (i) BrF3, Bent T-shape ...
Metabolism
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.