Lecture 5
... •Concept adapted from the studies of Ptashne •Modular nature of proteins. •Companies now make kits for this ...
... •Concept adapted from the studies of Ptashne •Modular nature of proteins. •Companies now make kits for this ...
Recombinant Human Activin-A active (rh Activin-A)
... future use below -18° C. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA). Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. Purity: Greater than 97.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Amino Acid Sequence: HHHHHHGLECDGKVNICCKKQFFVSFKDIGWNDWIIAPSG YHANYCEGECPSHIAGTSGSSLSFHSTVINHYRMRGHSPF ...
... future use below -18° C. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA). Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. Purity: Greater than 97.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Amino Acid Sequence: HHHHHHGLECDGKVNICCKKQFFVSFKDIGWNDWIIAPSG YHANYCEGECPSHIAGTSGSSLSFHSTVINHYRMRGHSPF ...
Cellular Respiration - Jackson School District
... Fuel molecules in food store solar energy in chemical bonds Animals depend on plants to convert solar energy to chemical energy This chemical energy is in the form of sugars and other organic molecules ...
... Fuel molecules in food store solar energy in chemical bonds Animals depend on plants to convert solar energy to chemical energy This chemical energy is in the form of sugars and other organic molecules ...
Biological monomers and polymers (1)
... Enzymes lower the energy barrier between reactants and products, thus increasing the rate of the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. A catalyst is a species that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction whilst remaining unchanged at the end of the reaction. Catalysis is achieved by reduci ...
... Enzymes lower the energy barrier between reactants and products, thus increasing the rate of the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. A catalyst is a species that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction whilst remaining unchanged at the end of the reaction. Catalysis is achieved by reduci ...
Protein catabolism in metabolic acidosis: inhibition of glycolysis by
... the expression of ubiquitin, of subunits of the proteasome [l] and of branched-chain keto-acid dehydrogenase, the enzyme thought to regulate branched chain amino-acid catabolism in skeletal muscle. The net effect is degradation of protein, accompanied by increased oxidation of the amino acids libera ...
... the expression of ubiquitin, of subunits of the proteasome [l] and of branched-chain keto-acid dehydrogenase, the enzyme thought to regulate branched chain amino-acid catabolism in skeletal muscle. The net effect is degradation of protein, accompanied by increased oxidation of the amino acids libera ...
Proteins and amino acids
... a donor: donates a hydrogen (N-H or O-H) an acceptor: accepts the donated hydrogen (N or O) Example ...
... a donor: donates a hydrogen (N-H or O-H) an acceptor: accepts the donated hydrogen (N or O) Example ...
Chem331 Lect 5 Amino acids peptides
... Amino acids are zwitterions - a molecule with both a pos and neg charge All naturally occurring amino acids are optically active isomers, except glycine. L amino acids R-groups determine the functionality of the amino acids. All amino acids can be based on one of three basic groups, non-polar, uncha ...
... Amino acids are zwitterions - a molecule with both a pos and neg charge All naturally occurring amino acids are optically active isomers, except glycine. L amino acids R-groups determine the functionality of the amino acids. All amino acids can be based on one of three basic groups, non-polar, uncha ...
course contents 160 - drseemaljelani
... Innovative Assignments will be designed not just to test what they know, but to help them develop their knowledge, skills and confidence. Tutorials and personal supervision comprise skills from problem solving to preparing a talk to give in the tutorial. This will be done in groups. Power point Chem ...
... Innovative Assignments will be designed not just to test what they know, but to help them develop their knowledge, skills and confidence. Tutorials and personal supervision comprise skills from problem solving to preparing a talk to give in the tutorial. This will be done in groups. Power point Chem ...
Richards, F.M. The Protein Folding Problem. Scientific American, pp
... bonds foundin alI native proteins. First pathways, although only two possibilities are shown. First the chain forms renormal hydrogen atoms bound to the gions o€unstable structure (uncoZored CyIinders).By associating,certain regions nitrogen involved in peptide bondsare become stabilized (color).The ...
... bonds foundin alI native proteins. First pathways, although only two possibilities are shown. First the chain forms renormal hydrogen atoms bound to the gions o€unstable structure (uncoZored CyIinders).By associating,certain regions nitrogen involved in peptide bondsare become stabilized (color).The ...
Objective 11 Notes Tuesday Jan 17
... contain mitochondrial DNA in which 4 of the 64 words have different meanings from the “standard” code. In most organisms, these differences are so slight as to be trivial. • In common molds, for example, the sequence “UGA” is translated into the amino acid tryptophan. In the standard code, it's a “s ...
... contain mitochondrial DNA in which 4 of the 64 words have different meanings from the “standard” code. In most organisms, these differences are so slight as to be trivial. • In common molds, for example, the sequence “UGA” is translated into the amino acid tryptophan. In the standard code, it's a “s ...
QUIZ #4 LIPID STRUCTURES AND METABOLISM
... Which of the following statements is (are) TRUE? a. HMG~CoA --> mevalonate is the regulatory step in cholesterol biosynthesis b. Synthesis of cholesterol begins with the condensation of two acetyl~CoA's in the cytosol c. Glucagon ultimately leads to decreased HMG~CoA reductase activity d. Cytosolic ...
... Which of the following statements is (are) TRUE? a. HMG~CoA --> mevalonate is the regulatory step in cholesterol biosynthesis b. Synthesis of cholesterol begins with the condensation of two acetyl~CoA's in the cytosol c. Glucagon ultimately leads to decreased HMG~CoA reductase activity d. Cytosolic ...
Answers to end of chapter questions
... (B) Inner mitochondrial membrane 15. The model for membrane structure proposed by Singer and Nicholson in 1972 is called what? (A) Fluid mosaic model 16. Which one of the following statements is correct with regard to an integral membrane protein? (D) All of the above statements are correct ...
... (B) Inner mitochondrial membrane 15. The model for membrane structure proposed by Singer and Nicholson in 1972 is called what? (A) Fluid mosaic model 16. Which one of the following statements is correct with regard to an integral membrane protein? (D) All of the above statements are correct ...
Q1. (a) An enzyme catalyses only one reaction. Explain why
... its grains. This protein is unusual because it has two functions. It acts as both an enzyme inhibitor and as an enzyme. As an inhibitor, the protein reduces the activity of starch-digesting enzymes. The protein acts as an enzyme by breaking down chitin, a polysaccharide found in the walls of many fu ...
... its grains. This protein is unusual because it has two functions. It acts as both an enzyme inhibitor and as an enzyme. As an inhibitor, the protein reduces the activity of starch-digesting enzymes. The protein acts as an enzyme by breaking down chitin, a polysaccharide found in the walls of many fu ...
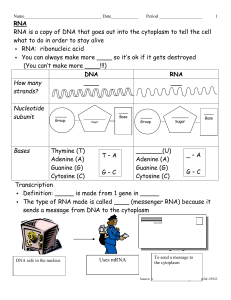
amino acid
... separate strands by the enzyme DNA helicase. DNA helicase “unzips” the DNA by breaking the bonds between the nitrogen base pairs. 2. Next, free floating nucleotides are matched to their complementary nucleotides through base pairing. 3. Another enzyme called DNA polymerase bonds these new nucleotide ...
... separate strands by the enzyme DNA helicase. DNA helicase “unzips” the DNA by breaking the bonds between the nitrogen base pairs. 2. Next, free floating nucleotides are matched to their complementary nucleotides through base pairing. 3. Another enzyme called DNA polymerase bonds these new nucleotide ...
Biology 2 - All Hallows Catholic High School
... Enzymes are protein molecules made up of long chains of amino acids. Enzymes have an active site that the substrate (food substance) fits into. High temperatures destroy this special shape (DENATURE). Different enzymes work best at different pH values. Enzymes inside living cells catalyse processes ...
... Enzymes are protein molecules made up of long chains of amino acids. Enzymes have an active site that the substrate (food substance) fits into. High temperatures destroy this special shape (DENATURE). Different enzymes work best at different pH values. Enzymes inside living cells catalyse processes ...
Eukaryotes - Alice Pevyhouse
... • RNA can duplicate itself • Catalyze reactions that produce subunits of RNA (more building blocks!) • Catalyze chains of amino acids which can be used to produce proteins! ...
... • RNA can duplicate itself • Catalyze reactions that produce subunits of RNA (more building blocks!) • Catalyze chains of amino acids which can be used to produce proteins! ...
Slide 1
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
2 HI
... All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) ...
... All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS does not break covalent bonds (i.e., disulfides) ...
NUCLEOTIDES AND NUCLEIC ACIDS 2
... • 3. HISTONES: are small proteins and are positively charged at physiological pH due to their high content of lysine and arginine. • There are 5 major classes of histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. • These histones are arranged in structural octamer units called nucleosomes. • 4. GENE:can be defined ...
... • 3. HISTONES: are small proteins and are positively charged at physiological pH due to their high content of lysine and arginine. • There are 5 major classes of histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. • These histones are arranged in structural octamer units called nucleosomes. • 4. GENE:can be defined ...
CHAPTER 7 – COENZYMES AND VITAMINS CHAPTER SUMMARY
... 35. Ubiquinone (coenzyme ___) is lipid soluble and synthesized by almost all species. Its long hydrophobic chain allows it to dissolve into _______________, and its function is the transport of _______________ between membrane-embedded enzyme complexes. 36. Coenzyme Q is responsible for moving _____ ...
... 35. Ubiquinone (coenzyme ___) is lipid soluble and synthesized by almost all species. Its long hydrophobic chain allows it to dissolve into _______________, and its function is the transport of _______________ between membrane-embedded enzyme complexes. 36. Coenzyme Q is responsible for moving _____ ...
UNIT 7 Metabolism and generation of ATP
... intermediates; stage 2, the interconversion of monomeric sugars, amino acids and lipids with still simpler organic compounds and stage 3, the ultimate degradation to, or synthesis from inorganic compounds such as CO2, H2O and NH3. These stages of complexity are shown below. ...
... intermediates; stage 2, the interconversion of monomeric sugars, amino acids and lipids with still simpler organic compounds and stage 3, the ultimate degradation to, or synthesis from inorganic compounds such as CO2, H2O and NH3. These stages of complexity are shown below. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.