Krebs cycle
... Fatty Acids The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules — amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. ...
... Fatty Acids The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules — amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. ...
Pyruvate Glucose - School of Medicine
... • Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. • Glucose stores are depleted during periods of starvation or fasting beyond a day. • Since the brain relies on glucose (120g/d) as a source of energy, glucose must be synthesized from molecules other than carbohydrates. ...
... • Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. • Glucose stores are depleted during periods of starvation or fasting beyond a day. • Since the brain relies on glucose (120g/d) as a source of energy, glucose must be synthesized from molecules other than carbohydrates. ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life
... o Its importance in accounting for the ability of some enzymes to bind to several substrates should be mentioned. o Scientific truths are often pragmatic. We accept them as true because they give us predictive power, that is, they work. The German scientist Emil Fischer introduced the lock-and-key m ...
... o Its importance in accounting for the ability of some enzymes to bind to several substrates should be mentioned. o Scientific truths are often pragmatic. We accept them as true because they give us predictive power, that is, they work. The German scientist Emil Fischer introduced the lock-and-key m ...
8 Cellular Respiration-An Overview
... uncontrolled. An organism would not be able to handle all that energy at once to do the work of the cell. Cellular respiration is essentially the same reaction as combustion, but the oxidation of glucose occurs in several controlled steps. The same amount of energy is ultimately released, but it is ...
... uncontrolled. An organism would not be able to handle all that energy at once to do the work of the cell. Cellular respiration is essentially the same reaction as combustion, but the oxidation of glucose occurs in several controlled steps. The same amount of energy is ultimately released, but it is ...
HUBS1406 Summary Notes
... 1g carbs = 1g protein (4kJ) All chemical reactions occurring in all cells of the body Anabolism: building up of substances from simple to more 1g fat = 38kJ complex o Require energy input Catabolism: breaking down of complex substances into simpler ones o Release energy Energy to power growth + repa ...
... 1g carbs = 1g protein (4kJ) All chemical reactions occurring in all cells of the body Anabolism: building up of substances from simple to more 1g fat = 38kJ complex o Require energy input Catabolism: breaking down of complex substances into simpler ones o Release energy Energy to power growth + repa ...
Amino Acid Metabolism - Breakdown Other metabolic
... NADPH - used in fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis (found most in mammary gland, adrenal cortex, liver and adipose tissue) Ribose 5-phosphate - used to synthesize nucleic acids (occurs at high rates in growing and regenerating tissues and in tumors) ...
... NADPH - used in fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis (found most in mammary gland, adrenal cortex, liver and adipose tissue) Ribose 5-phosphate - used to synthesize nucleic acids (occurs at high rates in growing and regenerating tissues and in tumors) ...
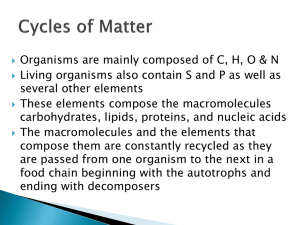
Cycles in Nature PowerPoint
... After plants have taken up nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate ions, the nitrogen is passed along the food chain. When those plants and animals dies, bacteria and fungi take up and use some of the nitrogen from the plant/animal protein and other nitrogen containing molecules. The remaining ...
... After plants have taken up nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrate ions, the nitrogen is passed along the food chain. When those plants and animals dies, bacteria and fungi take up and use some of the nitrogen from the plant/animal protein and other nitrogen containing molecules. The remaining ...
File
... • This also happens naturally in the brown fat tissue of new-born babies and hibernating mammals: • Respiration takes place, but no ATP is made, with the energy being turned into heat instead ...
... • This also happens naturally in the brown fat tissue of new-born babies and hibernating mammals: • Respiration takes place, but no ATP is made, with the energy being turned into heat instead ...
the PDF for the Organix Test
... secondary ammonia detoxification pathway Orotate is sensitive to anything that increases ammonia, including a high protein diet, intestinal dysbiosis, urea cycle overloads cause increased orotate synthesis and spillage as a secondary ammonia detoxification pathway. Orotate is sensitive to anything t ...
... secondary ammonia detoxification pathway Orotate is sensitive to anything that increases ammonia, including a high protein diet, intestinal dysbiosis, urea cycle overloads cause increased orotate synthesis and spillage as a secondary ammonia detoxification pathway. Orotate is sensitive to anything t ...
6.4 RNA - Part 2 - Translation rna_2_s12
... What does a protein do? “Machinery” of the cell: pumps, enzymes, contraction, cytoskeleton... Sure...but what are they? ...
... What does a protein do? “Machinery” of the cell: pumps, enzymes, contraction, cytoskeleton... Sure...but what are they? ...
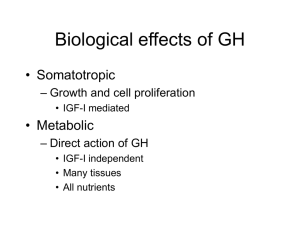
Biological effects of GH
... • Required for normal growth and development • Only hormone that can lower blood glucose level – Dominant metabolic regulator • Unregulated glucose level if absent • Hypoglycemia if too high – Cause neural shock ...
... • Required for normal growth and development • Only hormone that can lower blood glucose level – Dominant metabolic regulator • Unregulated glucose level if absent • Hypoglycemia if too high – Cause neural shock ...
TCA Cycle Handout 1
... The Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway involving eight enzymes essential for energy production through aerobic respiration, and, like glycolysis, arose early in evolution. This pathway is also an important source of biosynthetic building blocks used in ...
... The Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway involving eight enzymes essential for energy production through aerobic respiration, and, like glycolysis, arose early in evolution. This pathway is also an important source of biosynthetic building blocks used in ...
Chapter 1: What is Biology
... Most cells have ~70% water Chemical Equations (Reactions) Hydrolysis: breaking down substances Condensation: building substances o Also called a dehydration synthesis pH Acids Bases Neutral pH scale Organic Molecules: backbone of life Have the element _____________ in it 4 types of ...
... Most cells have ~70% water Chemical Equations (Reactions) Hydrolysis: breaking down substances Condensation: building substances o Also called a dehydration synthesis pH Acids Bases Neutral pH scale Organic Molecules: backbone of life Have the element _____________ in it 4 types of ...
Scientific Process - THS Biology EOC Tutorials
... G. Water molecules and radiant energy are necessary for anaerobic respiration to take place. H. Oxygen molecules release energy in the form of heat ...
... G. Water molecules and radiant energy are necessary for anaerobic respiration to take place. H. Oxygen molecules release energy in the form of heat ...
1. The graph shows the relative levels of Cdk1 and cyclin B
... versus a linear polysaccharide like amylose? Branches give rise to multiple non-reducing chain ends per molecule. Since glucose addition occurs at the non reducing ends, this multiplies the effective susbtrate concentration of the glycogen. ...
... versus a linear polysaccharide like amylose? Branches give rise to multiple non-reducing chain ends per molecule. Since glucose addition occurs at the non reducing ends, this multiplies the effective susbtrate concentration of the glycogen. ...
Cellular Metabolism
... Step 4 – Electron Transport System use of high energy protons and electrons (from coenzymes) to power ATP synthesis ...
... Step 4 – Electron Transport System use of high energy protons and electrons (from coenzymes) to power ATP synthesis ...
Chapter 15 Cori and Alanine Cycles: Cori Cycle: Occurs between
... Clinical: Galactosemia is a hereditary disorder in one enzyme in the conversion of galactose (milk sugar) to glucose. Since galactose cannot be converted into glucose, it gets converted to galactose 1-phosphate which builds up and becomes toxic. The results are cataract formation, growth failure, me ...
... Clinical: Galactosemia is a hereditary disorder in one enzyme in the conversion of galactose (milk sugar) to glucose. Since galactose cannot be converted into glucose, it gets converted to galactose 1-phosphate which builds up and becomes toxic. The results are cataract formation, growth failure, me ...
B2 Revision - Tonypandy Community College
... more cells it contains. Plants have a special way of growing, when new cells are formed around root and stem tips, their cell walls are still soft. The cells absorb water into their vacuoles and get longer. This process is called elongation as the cells get longer the roots or shoots get longer. The ...
... more cells it contains. Plants have a special way of growing, when new cells are formed around root and stem tips, their cell walls are still soft. The cells absorb water into their vacuoles and get longer. This process is called elongation as the cells get longer the roots or shoots get longer. The ...
Bio 263/F94/T2 - millersville.edu
... I. Multiple Choice. Fill in the circle on the test form corresponding to the correct answer. For the next six questions you will need to refer to the structures of the amino acid R groups shown at the end of the multiple choice questions. 1. ________ typically forms ________ bonds between two differ ...
... I. Multiple Choice. Fill in the circle on the test form corresponding to the correct answer. For the next six questions you will need to refer to the structures of the amino acid R groups shown at the end of the multiple choice questions. 1. ________ typically forms ________ bonds between two differ ...
Chapter 8
... pull mRNA through the ribosome, reading it one codon at a time. • The large subunit has three binding sites for tRNA’s ...
... pull mRNA through the ribosome, reading it one codon at a time. • The large subunit has three binding sites for tRNA’s ...
Macromolecules of Life – Lecture 1
... structures. Chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments are located in the membranes of the thylakoids. ...
... structures. Chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments are located in the membranes of the thylakoids. ...
Photosynthesis means synthesis in presence of light
... triphosphate (ATP) molecules which are the powerhouse of energy are generated which give us energy to do our day-to-day functions. These ATPs and ADPs (adenosine diphosphates) are the phosphates, which are characterized by their curly phosphate bonds, which the chemists and biochemists have characte ...
... triphosphate (ATP) molecules which are the powerhouse of energy are generated which give us energy to do our day-to-day functions. These ATPs and ADPs (adenosine diphosphates) are the phosphates, which are characterized by their curly phosphate bonds, which the chemists and biochemists have characte ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.