Metabolism of lactate and sugars by dairy propionibacteria: A
... cheese, for the biological production of propionate and vitamin 812 and have probiotic properties. In ail the se applications, their metabolic activities play a critical role. A complete understanding of propionate fermentation and of the metabolic routes used is therefore necessary. Dairy propionib ...
... cheese, for the biological production of propionate and vitamin 812 and have probiotic properties. In ail the se applications, their metabolic activities play a critical role. A complete understanding of propionate fermentation and of the metabolic routes used is therefore necessary. Dairy propionib ...
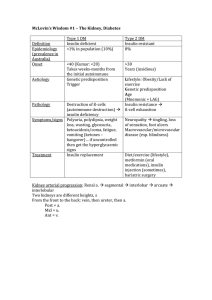
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
MUSCLE PROTEINS
... Recall that vigorous exercise can lead to a buildup of lactate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH Liver provide ...
... Recall that vigorous exercise can lead to a buildup of lactate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH Liver provide ...
SL respiration presentation
... Which process produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose? A. Anaerobic respiration in a yeast cell B. Aerobic respiration in a bacterial cell C. Glycolysis in a human liver cell D. The formation of lactic acid in a human muscle cell ...
... Which process produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose? A. Anaerobic respiration in a yeast cell B. Aerobic respiration in a bacterial cell C. Glycolysis in a human liver cell D. The formation of lactic acid in a human muscle cell ...
Practice Cellular Respiration Test
... c) It produces ADP for the electron transport chain d) It replenishes pyruvate so that the Krebs cycle can occur e) It replenishes NAD+ so that glycolysis can produce ATP _____ 18. What is the purpose of oxygen (O2) in aerobic respiration? a) Oxygen accepts electrons at the end of the electron trans ...
... c) It produces ADP for the electron transport chain d) It replenishes pyruvate so that the Krebs cycle can occur e) It replenishes NAD+ so that glycolysis can produce ATP _____ 18. What is the purpose of oxygen (O2) in aerobic respiration? a) Oxygen accepts electrons at the end of the electron trans ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... by the body. Hydrolysis is the main reaction involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. The _-amylase is produced by the salivary glands to begin the hydrolysis of the _-glycosidic bonds in the polysaccharide amylose. The hydrolysis of the smaller sections of amylose (dextrins) continues in the sma ...
... by the body. Hydrolysis is the main reaction involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. The _-amylase is produced by the salivary glands to begin the hydrolysis of the _-glycosidic bonds in the polysaccharide amylose. The hydrolysis of the smaller sections of amylose (dextrins) continues in the sma ...
Key area 2 * Cellular respiration
... only glycolysis can take place and pyruvate follows a fermentation pathway. • For both plants and animals complete the flow chart using the words; pyruvate, lactate, glucose and ethanol + CO2. ...
... only glycolysis can take place and pyruvate follows a fermentation pathway. • For both plants and animals complete the flow chart using the words; pyruvate, lactate, glucose and ethanol + CO2. ...
Unfinished business from April 4!
... Flux – where to measure, how and what is the most important “link”? Metabolites – intermediates in pathways to end-products (starch, cellulose, proteins, fats, lipids, second. products) Enzyme activity changes: steady-state of intermediates or flux? What is affected? yeast metabolomics (mutants) met ...
... Flux – where to measure, how and what is the most important “link”? Metabolites – intermediates in pathways to end-products (starch, cellulose, proteins, fats, lipids, second. products) Enzyme activity changes: steady-state of intermediates or flux? What is affected? yeast metabolomics (mutants) met ...
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration Using the
... – Many microorganisms use glycolysis to make ATP and fermentation to regenerate NAD+ – Yeast switches to alcoholic fermentation if O2 is not available • Wine and beer ...
... – Many microorganisms use glycolysis to make ATP and fermentation to regenerate NAD+ – Yeast switches to alcoholic fermentation if O2 is not available • Wine and beer ...
A 3-month old female infant seemed normal until she developed
... to form oxaloacetate. This conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is called an anaplerotic process because of its role in restoring oxaloacetate to the TCA cycle (Gropper & Smith, 2013). In other words, pyruvate carboxylase supplies oxaloacetate to keep the TCA cycle running. ...
... to form oxaloacetate. This conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate by pyruvate carboxylase is called an anaplerotic process because of its role in restoring oxaloacetate to the TCA cycle (Gropper & Smith, 2013). In other words, pyruvate carboxylase supplies oxaloacetate to keep the TCA cycle running. ...
103 Lecture Ch21a
... • Isoenzymes are different forms of an enzyme that catalyze the same reaction in different tissues in the body - they have slight variations in the amino acid sequences of the subunits of their quaternary structure • For example, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which converts lactate to pyruvate, consi ...
... • Isoenzymes are different forms of an enzyme that catalyze the same reaction in different tissues in the body - they have slight variations in the amino acid sequences of the subunits of their quaternary structure • For example, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), which converts lactate to pyruvate, consi ...
Gibbs Free Energy Changes for the Glycolytic Enzymes
... GAP (unfavorable reaction with a ΔG° of about +47 kJ/mole). The reaction can be viewed as the sum of two processes: the oxidation of the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid by NAD+, and the joining of the carboxylic acid and inorganic phosphate to form the acyl-phosphate product. The key to this reaction ...
... GAP (unfavorable reaction with a ΔG° of about +47 kJ/mole). The reaction can be viewed as the sum of two processes: the oxidation of the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid by NAD+, and the joining of the carboxylic acid and inorganic phosphate to form the acyl-phosphate product. The key to this reaction ...
References - The University of New Mexico
... releasing, regardless of lactate production, which consumes 1 H+. For glycolysis fueled by glycogen and ending in either pyruvate or lactate, H+ coefficients for pH 6.0 and 7.0 are -3.97 and -2.01, and -1.96 and -0.01, respectively. When starting with glucose, the same conditions result in H+ coeffi ...
... releasing, regardless of lactate production, which consumes 1 H+. For glycolysis fueled by glycogen and ending in either pyruvate or lactate, H+ coefficients for pH 6.0 and 7.0 are -3.97 and -2.01, and -1.96 and -0.01, respectively. When starting with glucose, the same conditions result in H+ coeffi ...
1 - Medical Mastermind Community
... within the mitochondrial matrix. Three carbon units are added as malonyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis, while two carbon units are liberated as acetyl-CoA in fatty acid degradation. NADPH is the electron donor in fatty acid synthesis, while FAD and NAD+ are electron acceptors in fatty acid degradation ...
... within the mitochondrial matrix. Three carbon units are added as malonyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis, while two carbon units are liberated as acetyl-CoA in fatty acid degradation. NADPH is the electron donor in fatty acid synthesis, while FAD and NAD+ are electron acceptors in fatty acid degradation ...
b-Oxidation of fatty acids
... remained virtually unchanged throughout all cytochrome c regardless of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invariant arginine and lysine clusters can be found on the surface of the molecule. Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause o ...
... remained virtually unchanged throughout all cytochrome c regardless of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invariant arginine and lysine clusters can be found on the surface of the molecule. Cytochrome c has a dual function in the cell. Electron transport for ATP production AND the major cause o ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Why is gluconeogenesis not just the reverse of glycolysis? The reverse of glycolysis is 2 Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H20 a glucose +2ADP +2Pi + 2 NAD + (DG = +74 kJ/mol) This is thermodynamically unfavorable, so energetically unfavorable steps in the reverse glyolysis reaction are replaced a ...
... Why is gluconeogenesis not just the reverse of glycolysis? The reverse of glycolysis is 2 Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H20 a glucose +2ADP +2Pi + 2 NAD + (DG = +74 kJ/mol) This is thermodynamically unfavorable, so energetically unfavorable steps in the reverse glyolysis reaction are replaced a ...
Kinetic Rate Reaction
... UNIT: Enzymes II (Kinetic/Rate Reaction) (continued) -naphthylphosphate are such substrates. The second technique is to measure the ACP activity before and after adding tartrate to the mixture. Tartrate greatly inhibits the ACP from prostate, but is much less inhibitory for the ACP from erythrocyt ...
... UNIT: Enzymes II (Kinetic/Rate Reaction) (continued) -naphthylphosphate are such substrates. The second technique is to measure the ACP activity before and after adding tartrate to the mixture. Tartrate greatly inhibits the ACP from prostate, but is much less inhibitory for the ACP from erythrocyt ...
Cell Respiration Key
... 2. Fermentation enables cells to make ATP in the absence of Oxygen. 3. For every molecule of glucose consumed, glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and NADH. 4. The products of alcoholic fermentation are alcohol and CO2. 5. Lactic Acid ...
... 2. Fermentation enables cells to make ATP in the absence of Oxygen. 3. For every molecule of glucose consumed, glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and NADH. 4. The products of alcoholic fermentation are alcohol and CO2. 5. Lactic Acid ...
Oxidation
... A key to understanding the biochemical logic behind two of these reactions of pyruvate is to recognize that glycolysis needs a continuing supply of NAD+. • if no oxygen is present to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, then another way must be found to reoxidize. ...
... A key to understanding the biochemical logic behind two of these reactions of pyruvate is to recognize that glycolysis needs a continuing supply of NAD+. • if no oxygen is present to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, then another way must be found to reoxidize. ...
Module 3- Bioenergetics - Bangen Athletic Development
... mitochondrial content. This shift allows athletes to perform more work before fatigue sets in. Oxygen deficit is the anaerobic contribution to the total energy cost during the start of exercise. This phenomenon occurs because of the time it takes for the aerobic energy systems to “kick in” to supply ...
... mitochondrial content. This shift allows athletes to perform more work before fatigue sets in. Oxygen deficit is the anaerobic contribution to the total energy cost during the start of exercise. This phenomenon occurs because of the time it takes for the aerobic energy systems to “kick in” to supply ...
Enzymes
... Inhibitors must be lacking The temperature should be constant within ±0.1°C throughout the assay at a temperature at which the enzyme is active M. Zaharna Clin. Chem. 2015 ...
... Inhibitors must be lacking The temperature should be constant within ±0.1°C throughout the assay at a temperature at which the enzyme is active M. Zaharna Clin. Chem. 2015 ...
Enzymes lII: Clinical Applications
... patterns (Table 8-2) that may be reflected in the relative serum concentrations of the respective enzymes in disease. The diseased tissue can be further identified by determination of the isoenzyme pattern of one of these enzymes (e.g., lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase) in the serum, since man ...
... patterns (Table 8-2) that may be reflected in the relative serum concentrations of the respective enzymes in disease. The diseased tissue can be further identified by determination of the isoenzyme pattern of one of these enzymes (e.g., lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase) in the serum, since man ...
Krebs cycle
... atoms leave the cycle in four oxidation reactions (three molecules of NAD+ one molecule of FAD are reduced). One molecule of GTP, is formed. Two molecules of water are consumed. 9 ATP (2.5 ATP per NADH, and 1.5 ATP per FADH2) are produced during oxidative phosphorylation. 1 ATP is directly f ...
... atoms leave the cycle in four oxidation reactions (three molecules of NAD+ one molecule of FAD are reduced). One molecule of GTP, is formed. Two molecules of water are consumed. 9 ATP (2.5 ATP per NADH, and 1.5 ATP per FADH2) are produced during oxidative phosphorylation. 1 ATP is directly f ...
RBC Enzymopathies
... • What if the patient had a history of eating paint which had lead in it and his serum lead levels were elevated? • Would pyrimidine 5’ nucleotidase be low? ...
... • What if the patient had a history of eating paint which had lead in it and his serum lead levels were elevated? • Would pyrimidine 5’ nucleotidase be low? ...
pentose phosphate pathway
... The phosphopentose isomerase reaction converts a ketose to an aldose. The reaction ...
... The phosphopentose isomerase reaction converts a ketose to an aldose. The reaction ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.