c5. definitive course document and course file
... which are used to reinforce and assess the concepts and skills acquired by the students; and to let them know the level of understanding that they are expected to reach. At least one test would be administered during the course of the subject as a means of timely checking of learning progress by ref ...
... which are used to reinforce and assess the concepts and skills acquired by the students; and to let them know the level of understanding that they are expected to reach. At least one test would be administered during the course of the subject as a means of timely checking of learning progress by ref ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
- Lexington JHS
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
... • Energy is the ability to do work…. – And that work causes an object to move in the direction of the force. ...
What is a mineral - group items
... occurring elements. Earth’s crust is composed of 3000 different minerals. Minerals may be metallic, like gold, or nonmetallic, like talc. Most have to be compounds or there couldn’t be that many. ...
... occurring elements. Earth’s crust is composed of 3000 different minerals. Minerals may be metallic, like gold, or nonmetallic, like talc. Most have to be compounds or there couldn’t be that many. ...
Chemical Bonds
... Opposite electric forces (protons and electrons) attract each other. These forces pull atoms together to form compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... Opposite electric forces (protons and electrons) attract each other. These forces pull atoms together to form compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
What Determines the Physical Properties of a Mineral?
... Metallic bonding (not chemical bonding) Metallic bonding (not chemical bonding) Valence electrons are free to migrate among atoms The migrating electron creates a “glue” Weaker and less common than ionic or covalent bonds Ex: Cu, Au, Al as a result have high electrical conductivity ...
... Metallic bonding (not chemical bonding) Metallic bonding (not chemical bonding) Valence electrons are free to migrate among atoms The migrating electron creates a “glue” Weaker and less common than ionic or covalent bonds Ex: Cu, Au, Al as a result have high electrical conductivity ...
Week 6 Review 2014-15
... Pure Substances vs. Mixtures • Pure substance: matter that has a fixed (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...
... Pure Substances vs. Mixtures • Pure substance: matter that has a fixed (constant) composition and unique properties. Contains only 1 type element or compound; homogeneous ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Change
... • Distillation - a liquid is boiled to produce a vapor which is condensed into a liquid Other ways? distillation • How to perform simple distillation in the chemistry lab | Wonder How To ...
... • Distillation - a liquid is boiled to produce a vapor which is condensed into a liquid Other ways? distillation • How to perform simple distillation in the chemistry lab | Wonder How To ...
classification of matter - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... Physical Change- change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter • Substance does not change identity when it undergoes a physical change • Distillation is a process for separating a mixture by evaporating a liquid and condensing its vapor. ...
... Physical Change- change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter • Substance does not change identity when it undergoes a physical change • Distillation is a process for separating a mixture by evaporating a liquid and condensing its vapor. ...
Minerals: Naturally occurring solid with a crystal structure and a
... Naturally occurring solid with a crystal structure and a unique set of properties Crystal structure is made of molecules arranged in a regular repeating pattern Ex: Topaz, Quartz, Diamond Physical Properties: o Hardness o Luster o Color o Streak (the color left on a streak plate from rubbing) o Dens ...
... Naturally occurring solid with a crystal structure and a unique set of properties Crystal structure is made of molecules arranged in a regular repeating pattern Ex: Topaz, Quartz, Diamond Physical Properties: o Hardness o Luster o Color o Streak (the color left on a streak plate from rubbing) o Dens ...
7R CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEW
... 2. If an element is divided into smaller and smaller parts, the smallest particle obtained would be a (an) A) molecule. B) compound. C) mixture. D) atom. 3. The fact that iron cannot be changed into a simpler form indicates that iron is a (an) A) compound. B) molecule. C) element. ...
... 2. If an element is divided into smaller and smaller parts, the smallest particle obtained would be a (an) A) molecule. B) compound. C) mixture. D) atom. 3. The fact that iron cannot be changed into a simpler form indicates that iron is a (an) A) compound. B) molecule. C) element. ...
GEOS 306 Mineralogy — Lecture Summary for Final Exam
... Crystal chemistry — Pauling's rules and application Optical mineralogy — nature of light, modes of interaction with solids, principal features and origin, relationship to crystallography Reflected light — phenomena observed Mineral stability — principles Mineral stability in different environm ...
... Crystal chemistry — Pauling's rules and application Optical mineralogy — nature of light, modes of interaction with solids, principal features and origin, relationship to crystallography Reflected light — phenomena observed Mineral stability — principles Mineral stability in different environm ...
What is Chemistry
... – Contains ions rather than atoms • Attraction of ionic charges pull molecules closer together than in gas ...
... – Contains ions rather than atoms • Attraction of ionic charges pull molecules closer together than in gas ...
CHAPTER 1, MATTER AND CHANGE Section 1, Chemistry Is a
... ! A compound is a substance that can be broken down into simple stable substances. Each compound is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. (Example: hydrogen peroxide, H2O2) Properties and changes in matter: ! Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter that ...
... ! A compound is a substance that can be broken down into simple stable substances. Each compound is made from the atoms of two or more elements that are chemically bonded. (Example: hydrogen peroxide, H2O2) Properties and changes in matter: ! Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter that ...
Cosmetology Learning Module 12
... composition, structures, and properties of matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
... composition, structures, and properties of matter and how matter changes under different chemical conditions Organic Chemistry – is the study of substances that contain carbon All living things are made up of compounds that contain carbon Organic compounds will burn ...
Oppgave 5.
... you expect to see in the 13C-NMR spectrum of the following compounds: a) Cyclopropane b) Methyl-cyclopropane c) Cis dimethyl-cyclopropane d) Trans dimethyl-cyclopropane e) Cyclobutene f) 1-methyl-cyclobutene g) 1-ethyl-cyclohexane ...
... you expect to see in the 13C-NMR spectrum of the following compounds: a) Cyclopropane b) Methyl-cyclopropane c) Cis dimethyl-cyclopropane d) Trans dimethyl-cyclopropane e) Cyclobutene f) 1-methyl-cyclobutene g) 1-ethyl-cyclohexane ...
Why do scientists grow crystals? - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web
... X-ray crystallography is a method for determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal. ...
... X-ray crystallography is a method for determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal. ...
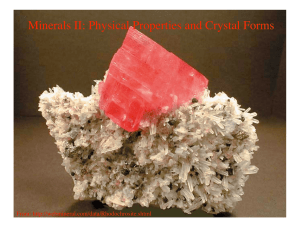
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms
... composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment discussed above, will also be manifested in macroscopic physical and chemical properties. This is indeed the case. ...
... composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment discussed above, will also be manifested in macroscopic physical and chemical properties. This is indeed the case. ...
Physical properties of minerals
... composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment discussed above, will also be manifested in macroscopic physical and chemical properties. This is indeed the case. ...
... composed of atoms, arranged in a specific order, with a well defined chemical composition. We might expect then that the microscopic variations in bond environment discussed above, will also be manifested in macroscopic physical and chemical properties. This is indeed the case. ...
Chemistry: the study of composition, structure, and properties of
... Change of State: physical change from one state to another. • Solid Liquid (Melting) Liquid Solid (Freezing) • Solid Gas (Subliming) Gas Solid (Deposition) • Liquid Gas (Evap./Boil) Gas Liquid (Condensing) SOLID - LIQUID - GAS ...
... Change of State: physical change from one state to another. • Solid Liquid (Melting) Liquid Solid (Freezing) • Solid Gas (Subliming) Gas Solid (Deposition) • Liquid Gas (Evap./Boil) Gas Liquid (Condensing) SOLID - LIQUID - GAS ...
PwrPt
... C = the number of components: the minimum number of chemical constituents required to specify every phase in the system F = the number of degrees of freedom: the number of independently variable intensive parameters of state (such as temperature, pressure, the composition of each phase, etc.) ...
... C = the number of components: the minimum number of chemical constituents required to specify every phase in the system F = the number of degrees of freedom: the number of independently variable intensive parameters of state (such as temperature, pressure, the composition of each phase, etc.) ...