Chapter 5
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
Review for second exam:
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
... Determination of empirical formulas from experimental data Finding the molecular formula from the empirical formula and molecular mass Naming rules for simple substances (see Handout 1) Organic compounds - definition; hydrocarbons; functional groups (alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes) Ch ...
Class Notes
... A single substance material is a pure substance, while a material composed of several substances is classified as a mixture. ...
... A single substance material is a pure substance, while a material composed of several substances is classified as a mixture. ...
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... random motion unless constrained. Use Ar atom as an example. Draw diagrams of s, l, and g Ar and use them to show how this theory explains all of the observations in chart above describing properties of states of matter ...
... random motion unless constrained. Use Ar atom as an example. Draw diagrams of s, l, and g Ar and use them to show how this theory explains all of the observations in chart above describing properties of states of matter ...
Science Outline NHPS: Chemistry
... hypothesis and the design of the experiment. D INQ.4 Design and conduct appropriate types of scientific investigations to answer different questions. D INQ.5 Identify independent and dependent variables, including those that are kept constant and those used as controls. D INQ.6 Use appropriate tools ...
... hypothesis and the design of the experiment. D INQ.4 Design and conduct appropriate types of scientific investigations to answer different questions. D INQ.5 Identify independent and dependent variables, including those that are kept constant and those used as controls. D INQ.6 Use appropriate tools ...
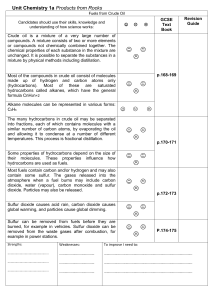
Unit_Chemistry_1a_Oil
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
... compounds. A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are unchanged. It is possible to separate the substances in a mixture by physical methods including distillation. ...
national institute
... Qualitative Organic Analysis: Functional group interconversions, structural problems using chemical reactions, identification of functional groups by chemical tests, elementary 1H NMR and IR spectroscopy as a tool for structural elucidation. Natural Products Chemistry: Introductory chemistry of alka ...
... Qualitative Organic Analysis: Functional group interconversions, structural problems using chemical reactions, identification of functional groups by chemical tests, elementary 1H NMR and IR spectroscopy as a tool for structural elucidation. Natural Products Chemistry: Introductory chemistry of alka ...
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Qualitative Organic Analysis: Functional group interconversions, structural problems using chemical reactions, identification of functional groups by chemical tests, elementary 1H NMR and IR spectroscopy as a tool for structural elucidation. Natural Products Chemistry: Introductory chemistry of alka ...
... Qualitative Organic Analysis: Functional group interconversions, structural problems using chemical reactions, identification of functional groups by chemical tests, elementary 1H NMR and IR spectroscopy as a tool for structural elucidation. Natural Products Chemistry: Introductory chemistry of alka ...
Unit 1 - Measurement Atomic Theory
... The number of DECIMAL PLACES in the result is the same as the fewest DECIMAL PLACED of any of the values used. ...
... The number of DECIMAL PLACES in the result is the same as the fewest DECIMAL PLACED of any of the values used. ...
Diapositive 1 - Aptar
... • Future guidance may be based on “PQRI Safety Thresholds and Best Practices for Extractables and Leachables in Orally Inhaled and Nasal Drug Products” (2007?) ...
... • Future guidance may be based on “PQRI Safety Thresholds and Best Practices for Extractables and Leachables in Orally Inhaled and Nasal Drug Products” (2007?) ...
Study Guide – Unit Test (9-27-13)
... Water Evaporation/condensing (physical) Dry Ice Subliming (physical) There will be other examples included on the test. (Look at notes/old quizzes and worksheets) ...
... Water Evaporation/condensing (physical) Dry Ice Subliming (physical) There will be other examples included on the test. (Look at notes/old quizzes and worksheets) ...
Student Worksheet The Chemistry of Water Quality Tests
... a. The design and/or interpretation of the results of a separation experiment (filtration, paper chromatography, column chromatography, or distillation) are in terms of the relative strength of interactions among and between the components. b. The translation of an observed chemical change into a ba ...
... a. The design and/or interpretation of the results of a separation experiment (filtration, paper chromatography, column chromatography, or distillation) are in terms of the relative strength of interactions among and between the components. b. The translation of an observed chemical change into a ba ...
are physical changes - Chemistry Information Site
... - Cannot be broken down into simpler substances using physical or chemical means - Elements are the building blocks of chemistry! They are the simple things ...
... - Cannot be broken down into simpler substances using physical or chemical means - Elements are the building blocks of chemistry! They are the simple things ...
Assignment 2 (MINERALS) Solution (1)
... Please answer practice questions 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.12 at the end of the text book. 3.4. How does the internal structure of a mineral relate to its external appearance? The unique internal arrangement of the atoms in minerals determines the shapes of crystal faces which in turn reflect to the external ...
... Please answer practice questions 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.12 at the end of the text book. 3.4. How does the internal structure of a mineral relate to its external appearance? The unique internal arrangement of the atoms in minerals determines the shapes of crystal faces which in turn reflect to the external ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
Chapter 2 Matter Study Guide
... similar throughout because substances are so evenly mixed. An example is Salt water 3. What makes up elements? A pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance 4. What makes up compounds? a substance made of two or more elements 5. What is a mixture? Made up of more than one kind ...
... similar throughout because substances are so evenly mixed. An example is Salt water 3. What makes up elements? A pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substance 4. What makes up compounds? a substance made of two or more elements 5. What is a mixture? Made up of more than one kind ...
Document
... • Physical change: • change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter • substance does not change identity when it undergoes a physical ...
... • Physical change: • change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter • substance does not change identity when it undergoes a physical ...
File
... Elements are composed of _________________ kind of atom. __________________________ are pure substances that are composed of __________________________types of elements that are chemically combined. Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements through _______________________ ...
... Elements are composed of _________________ kind of atom. __________________________ are pure substances that are composed of __________________________types of elements that are chemically combined. Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements through _______________________ ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...