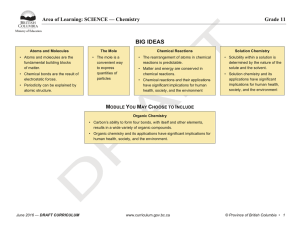
matter
... • One material disperses evenly into another material so the first one seems to disappear Example: stirring sugar in tea ...
... • One material disperses evenly into another material so the first one seems to disappear Example: stirring sugar in tea ...
Rocks and Minerals - ACMS Bullpup Science
... pieces. No chemical change. ex. Wind, Water, Roots Chemical – Chemical properties that make up that rock change ex. Acid Rain Erosion – Movement of sediment from place to place by wind, water, and glaciers. ...
... pieces. No chemical change. ex. Wind, Water, Roots Chemical – Chemical properties that make up that rock change ex. Acid Rain Erosion – Movement of sediment from place to place by wind, water, and glaciers. ...
Chapter One Powerpoint - Geneva Area City Schools
... maintains the chemical identity of that element. • Fundamental building block of matter • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, more stable substances and is made of one type of atom. • A compound is a substance that is composed of 2 or more elements that are chemic ...
... maintains the chemical identity of that element. • Fundamental building block of matter • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, more stable substances and is made of one type of atom. • A compound is a substance that is composed of 2 or more elements that are chemic ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: Matter and Measurement
... Chemistry is concerned with matter and energy and how the two interact with each other. ...
... Chemistry is concerned with matter and energy and how the two interact with each other. ...
673 lab three
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - Proteins – molecules that contain _____________, carbon, ____________, & ___________ - ____________ are made up of ________ of __________ __________ - Amino acids - ________________ with an __________ group on one end & a ___________ group on the other end, there are more than ____ in ___________ ...
... - Proteins – molecules that contain _____________, carbon, ____________, & ___________ - ____________ are made up of ________ of __________ __________ - Amino acids - ________________ with an __________ group on one end & a ___________ group on the other end, there are more than ____ in ___________ ...
File
... Its a molecule made of a metal and one or more non-metals. In this type of compounds, there is a transfer of e-→ The metal loses e- and the non-metals gains e- to form an ionic bond. Physical Properties ...
... Its a molecule made of a metal and one or more non-metals. In this type of compounds, there is a transfer of e-→ The metal loses e- and the non-metals gains e- to form an ionic bond. Physical Properties ...
Minerals
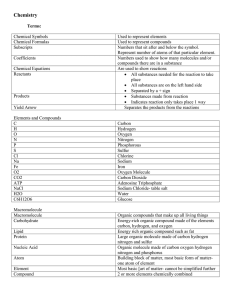
... Elements and Compounds • Element – Most fundamental substance into which matter can be separated by chemical means ...
... Elements and Compounds • Element – Most fundamental substance into which matter can be separated by chemical means ...
Chem A Week 2 Matter Notes
... and bounce away, so they do not _________ stay in contact with each other. ...
... and bounce away, so they do not _________ stay in contact with each other. ...
Minerals
... Which rocks are made from sediment? Which rocks are made from magma? Which rock type can make metamorphic rock? What are rocks made of? ...
... Which rocks are made from sediment? Which rocks are made from magma? Which rock type can make metamorphic rock? What are rocks made of? ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipole 33. Which of the following compounds contains polar bonds, yet the molecule itself is nonpolar? B. ...
... 32. Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide all exhibit which type of intermolecular force? a. metallic b. network covalent c. ionic d. hydrogen e. dipole-dipole 33. Which of the following compounds contains polar bonds, yet the molecule itself is nonpolar? B. ...
Mineral definition and classification
... referred to as the 14 "Bravais lattices". Each of these lattices can be classified into one of the six crystal systems, and all crystal structures currently recognized fit in one Bravais lattice and one crystal system. This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement t ...
... referred to as the 14 "Bravais lattices". Each of these lattices can be classified into one of the six crystal systems, and all crystal structures currently recognized fit in one Bravais lattice and one crystal system. This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement t ...
Elements, Compounds and Chemical Reactions
... • Add in the Hydrogen from water, and that’s only 5 elements out of 118 that make up most of what we know! ...
... • Add in the Hydrogen from water, and that’s only 5 elements out of 118 that make up most of what we know! ...
Name: ______ Aim 36: Elements, atoms, compounds and miztures
... New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
... New properties are formed. Only metals retain their original properties. New elements are formed. ...
Supersaturating drug delivery systems: effect of
... out of 14 drug systems while the SBEbCD generated 11 hits (<25% precipitation) and two addition compounds that gave extents of precipitation of 27% and 36% during the 2 h time course of the experiment. An interesting observation is also available by comparing Tables 1 and 3. Specifically, those comp ...
... out of 14 drug systems while the SBEbCD generated 11 hits (<25% precipitation) and two addition compounds that gave extents of precipitation of 27% and 36% during the 2 h time course of the experiment. An interesting observation is also available by comparing Tables 1 and 3. Specifically, those comp ...
the properties and structure of matter
... • Atoms move rapidly enough to slide over one another i.e. ability to flow ...
... • Atoms move rapidly enough to slide over one another i.e. ability to flow ...
Chapter 5 Minerals - Pepperell Middle School
... Rocks and minerals are not the same thing. A mineral is a solid, naturally formed inorganic substance that always has the same composition and the same properties. A mineral compares to a rock as a tree compares to a forest. A forest is made up of trees; most rocks are made up of minerals. ...
... Rocks and minerals are not the same thing. A mineral is a solid, naturally formed inorganic substance that always has the same composition and the same properties. A mineral compares to a rock as a tree compares to a forest. A forest is made up of trees; most rocks are made up of minerals. ...
Chapter 2 - Cloudfront.net
... Weigh mass before and after change. Mass before and after is always the same. ...
... Weigh mass before and after change. Mass before and after is always the same. ...
Chemistry Standard Outline
... SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical processes. SC6a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. SC6c. Analyzing (both conceptual ...
... SC1b. Identify substances based on chemical and physical properties. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical processes. SC6a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. SC6c. Analyzing (both conceptual ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Matter can be classified as either a gas, liquid, or solid Generally, as you add energy, particles move faster and farther apart As you remove energy, particles move closer and become attracted to each other ...
... Matter can be classified as either a gas, liquid, or solid Generally, as you add energy, particles move faster and farther apart As you remove energy, particles move closer and become attracted to each other ...