Animal body systems
... transported throughout the body •Circulation may be OPEN or CLOSED system •Open Circulatory System – two main blood vessels (dorsal and ventral); heart pumps blood out into vessels that open into the body cavity for gas and nutrient exchange ...
... transported throughout the body •Circulation may be OPEN or CLOSED system •Open Circulatory System – two main blood vessels (dorsal and ventral); heart pumps blood out into vessels that open into the body cavity for gas and nutrient exchange ...
Unit Test Review
... Sensory neuron: convey information to spinal cord Interneurons: information integration Motor neurons: convey signals to effector cell (muscle or gland) Reflex: simple response; sensory to motor neurons Ganglion (ganglia): cluster of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Supporting cells/glia: nonconductiong ...
... Sensory neuron: convey information to spinal cord Interneurons: information integration Motor neurons: convey signals to effector cell (muscle or gland) Reflex: simple response; sensory to motor neurons Ganglion (ganglia): cluster of nerve cell bodies in the PNS Supporting cells/glia: nonconductiong ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
Unit A: Chapter 1: Comparing Living Things Lesson 1: Is It Living or
... In many living things, life processes are carried out at a very small level, usually by cells. In the human body, for example, cells use energy, get rid of waste, reproduce, grow, and help people respond to change. Viruses are not living things and therefore cannot carry out life processes Bacteria ...
... In many living things, life processes are carried out at a very small level, usually by cells. In the human body, for example, cells use energy, get rid of waste, reproduce, grow, and help people respond to change. Viruses are not living things and therefore cannot carry out life processes Bacteria ...
Chapter 28 How Plants and Animals Work Introduction Barheaded
... ____________________________ in some cells can change a hormone’s level in plant tissues The _________________________ for flowering describes three genes that are the master switches for floral development –_______________________________, and other structures Communication in the Animal Body _____ ...
... ____________________________ in some cells can change a hormone’s level in plant tissues The _________________________ for flowering describes three genes that are the master switches for floral development –_______________________________, and other structures Communication in the Animal Body _____ ...
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
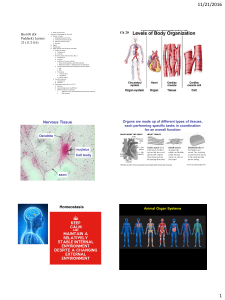
... Ch 2 Lesson 3: How do organs work together? I. Organ Systems- group of organs working together ...
... Ch 2 Lesson 3: How do organs work together? I. Organ Systems- group of organs working together ...
CELLS
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
video summaries: cells
... The%movement%of%water from%an%area%of% high%concentra2on%to%low%concentra2on% ...
... The%movement%of%water from%an%area%of% high%concentra2on%to%low%concentra2on% ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... 2. controls the cell and contains instructions to make more cells – nucleus 3. the jelly-like part of the cell where chemical reactions take place – cytoplasm 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant c ...
... 2. controls the cell and contains instructions to make more cells – nucleus 3. the jelly-like part of the cell where chemical reactions take place – cytoplasm 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant c ...
Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells and viruses differ
... Key Learning(s): Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells and viruses differ in complexity and general structure Structure and function of cell membranes Roles of Golgi and ER in the production and secretion of proteins ...
... Key Learning(s): Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells and viruses differ in complexity and general structure Structure and function of cell membranes Roles of Golgi and ER in the production and secretion of proteins ...
Cells and Systems Notes Topic 1 1. What are five characteristics that
... 11. When an organism gets bigger, do its cells get bigger or does it add more cells? Explain why you gave the answer you gave. ...
... 11. When an organism gets bigger, do its cells get bigger or does it add more cells? Explain why you gave the answer you gave. ...
Chapter 1: Cells
... Breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals and returning materials from dead organisms back to the environment, where new organisms can use them. 18. Cilia- small hairs that sweep food particles into a paramecium’s oral groove. 19. Diffusion- the movement of particles from an area of highe ...
... Breaking down the remains of dead plants and animals and returning materials from dead organisms back to the environment, where new organisms can use them. 18. Cilia- small hairs that sweep food particles into a paramecium’s oral groove. 19. Diffusion- the movement of particles from an area of highe ...
22/18 INVESTIGATOR Name Jeremy P. Brockes Address Ludwig
... 50-100 g of protein for priming and for several boosts before sacrificing i.p. none ...
... 50-100 g of protein for priming and for several boosts before sacrificing i.p. none ...
The Nervous System
... are NOT included in the spinal cord – Sensory Division: Transmits impulses from sense organs to the CNS – Motor Division: Transmits impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands ...
... are NOT included in the spinal cord – Sensory Division: Transmits impulses from sense organs to the CNS – Motor Division: Transmits impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands ...
Genetics Review
... • EEG - uses electrical impulses produced by the brain to show brain activity • CAT scan - produces a 3-D image using X - rays and a computer. This can be used to reveal disorders like tumors, broken blood vessels and other brain problems (reduces the need to open up people's heads!) ...
... • EEG - uses electrical impulses produced by the brain to show brain activity • CAT scan - produces a 3-D image using X - rays and a computer. This can be used to reveal disorders like tumors, broken blood vessels and other brain problems (reduces the need to open up people's heads!) ...
HA4 c19 INVESTIGATOR Name Dr. Ann Hubbard
... stains a membrane protein in the bile canalicular domain of hepatocytes (and other epithelial cells) PUBLICATIONS : Hubbard, A.L., Bartels, J.R., and Braiterman, L.T. (1985). Identification of rat hepatocyte plasma membrane proteins using monoclonal antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 100, 1115-1125. Young, H ...
... stains a membrane protein in the bile canalicular domain of hepatocytes (and other epithelial cells) PUBLICATIONS : Hubbard, A.L., Bartels, J.R., and Braiterman, L.T. (1985). Identification of rat hepatocyte plasma membrane proteins using monoclonal antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 100, 1115-1125. Young, H ...
Cell Unit Test Study Guide
... a. The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Chapter 3 1. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? a. All organisms are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. c. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... a. The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Chapter 3 1. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? a. All organisms are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. c. All cells come from existing cells. ...
Cells
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
... • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such as roots and leaves. ...
File
... 78. What is a feedback loop and how is it similar to a thermostat in your house? It operates by doing the opposite (negative) of what it senses. If senses it is to hot, it tries to cool down, to cold, tries to warm up. ...
... 78. What is a feedback loop and how is it similar to a thermostat in your house? It operates by doing the opposite (negative) of what it senses. If senses it is to hot, it tries to cool down, to cold, tries to warm up. ...
Levels of Organization
... • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
... • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
Tissue Types - wwhsanatomy
... receive information from the environment and long AXONS that carry or relay information to other nerve cells. At the end of the axon is an intercellular junction called a SYNAPSE The cell body or SOMA contains the nucleus. ...
... receive information from the environment and long AXONS that carry or relay information to other nerve cells. At the end of the axon is an intercellular junction called a SYNAPSE The cell body or SOMA contains the nucleus. ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.