Ch. 3 Cells
... Cells develop into different types of cells with specialized functions via cell differentiation; shows genetic control of nucleus as some genes are turned on while others are turned off ...
... Cells develop into different types of cells with specialized functions via cell differentiation; shows genetic control of nucleus as some genes are turned on while others are turned off ...
Unit 1 – Chemical Basis of Life
... What is the main difference between the way negative feedback and positive feedback mechanisms regulate change in the body. - Negative feedback loops counteract change to return to a set ...
... What is the main difference between the way negative feedback and positive feedback mechanisms regulate change in the body. - Negative feedback loops counteract change to return to a set ...
Slide 1 - Granbury ISD
... Cell Theory Rudolph Virchow: German doctor. Developed one of the central ideas of cell theory, cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... Cell Theory Rudolph Virchow: German doctor. Developed one of the central ideas of cell theory, cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
APh/BE161: Physical Biology of the Cell Lecture 1: The Size of
... A Single Molecule Census of the Cell The Standard Cell: “Not everyone is mindful of it, but cell biologists have two cells of interest; the one they are studying and Escherichia coli.” – Schaechter et al. 20-40% of the protein stockpile consists of integral membrane proteins. An estimate: roughly 5 ...
... A Single Molecule Census of the Cell The Standard Cell: “Not everyone is mindful of it, but cell biologists have two cells of interest; the one they are studying and Escherichia coli.” – Schaechter et al. 20-40% of the protein stockpile consists of integral membrane proteins. An estimate: roughly 5 ...
Cells & Tissues
... Animal Tissues are groups of similar cells which work together. Epithelium - Tissues composed of layers of cells that cover organ surfaces such as surface of the skin and inner lining of digestive tract: the tissues that serve for protection, secretion, and absorption. Connective tissue - As the na ...
... Animal Tissues are groups of similar cells which work together. Epithelium - Tissues composed of layers of cells that cover organ surfaces such as surface of the skin and inner lining of digestive tract: the tissues that serve for protection, secretion, and absorption. Connective tissue - As the na ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Key
... 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? Unicellular-si ...
... 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? Unicellular-si ...
organisation of living beings2016
... All our body cells have the same genetic information (ADN) because all of the cells derive from an initial cell, the cell embryo or zygote (the zygote starts dividing into cells that in turn divide again. Millions of divisions then we will have developed a body composed of millions of cells that hav ...
... All our body cells have the same genetic information (ADN) because all of the cells derive from an initial cell, the cell embryo or zygote (the zygote starts dividing into cells that in turn divide again. Millions of divisions then we will have developed a body composed of millions of cells that hav ...
Nervous MusclesSkeleton
... • Muscles do their work when the contract—that’s why each muscle in your body has two sets, one to contract your arm or leg in one direction, and another muscle to contract and move it back. • But, in order for the muscle to contract, special steps have to happen inside each cell. ...
... • Muscles do their work when the contract—that’s why each muscle in your body has two sets, one to contract your arm or leg in one direction, and another muscle to contract and move it back. • But, in order for the muscle to contract, special steps have to happen inside each cell. ...
Cells and Organs
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
Summer Review Package: `16-`17 1. Vocabulary
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
APh/BE161: Physical Biology of the Cell
... A Single Molecule Census of the Cell The Standard Cell: “Not everyone is mindful of it, but cell biologists have two cells of interest; the one they are studying and Escherichia coli.” – Schaechter et al. 20-40% of the protein stockpile consists of integral membrane proteins. An estimate: roughly 5 ...
... A Single Molecule Census of the Cell The Standard Cell: “Not everyone is mindful of it, but cell biologists have two cells of interest; the one they are studying and Escherichia coli.” – Schaechter et al. 20-40% of the protein stockpile consists of integral membrane proteins. An estimate: roughly 5 ...
B cells
... consequence of memory Two basic strategies humoral immunity – extracellular antigens cellular immunity – intracellular antigens ...
... consequence of memory Two basic strategies humoral immunity – extracellular antigens cellular immunity – intracellular antigens ...
Science Chapter 1 Unit A
... Cell division: new cells form when old cells divide in two, and cells need energy for this process Transportation: cells transport water, glucose, oxygen, waste, and minerals in the body – Ex: Diffusion & osmosis are two forms of transportation ...
... Cell division: new cells form when old cells divide in two, and cells need energy for this process Transportation: cells transport water, glucose, oxygen, waste, and minerals in the body – Ex: Diffusion & osmosis are two forms of transportation ...
Summer Review Package: `14 -`15 PART I 1. Vocabulary – Please b
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
Cells and Tissues
... • Two or more tissues working together • Organs that work together make up an organ system • The body has 12 major organ systems ...
... • Two or more tissues working together • Organs that work together make up an organ system • The body has 12 major organ systems ...
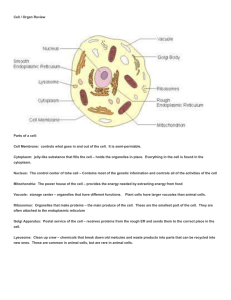
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Lysosome: Clean up crew – chemicals that break down old melcules and waste products into parts that can be recycled into new ones. These are common in animal cells, but are rare in animal cells. ...
... Lysosome: Clean up crew – chemicals that break down old melcules and waste products into parts that can be recycled into new ones. These are common in animal cells, but are rare in animal cells. ...
Regents Review
... • Pathogen- viruses, bacteria, fungi and other parasites that interfere with our normal functioning and make us seriously ill. • Cancer- genetic mutations in a cell that result in uncontrolled cell division. Immune system- body’s primary defense against disease causing pathogens • Antigen- trigger a ...
... • Pathogen- viruses, bacteria, fungi and other parasites that interfere with our normal functioning and make us seriously ill. • Cancer- genetic mutations in a cell that result in uncontrolled cell division. Immune system- body’s primary defense against disease causing pathogens • Antigen- trigger a ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The individual neuron cannot do much
... The study of the lateral in the Limulus provides a model of perception based on neuronal circuits, collections of neurons working in tandem. However, there is also the specialized neuron model for the inking in Aplysia. These and other studies have lead to a conclusion that most information processi ...
... The study of the lateral in the Limulus provides a model of perception based on neuronal circuits, collections of neurons working in tandem. However, there is also the specialized neuron model for the inking in Aplysia. These and other studies have lead to a conclusion that most information processi ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLS
... Vocabulary Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smalle ...
... Vocabulary Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smalle ...
INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN BIOLOGY pp. 907-910
... • Endocrine: controls • Nervous: regulation, conduction, and body function via chemical messengers. coordination ...
... • Endocrine: controls • Nervous: regulation, conduction, and body function via chemical messengers. coordination ...
Human Body Progress Check
... I can describe differences between plant cells and animal cells I can explain what is meant by the term ‘specialised cell.’ I can give examples of specialised cells and identify features that make them specialised. I can state that a group of similar cells is called a tissue. I can state that a grou ...
... I can describe differences between plant cells and animal cells I can explain what is meant by the term ‘specialised cell.’ I can give examples of specialised cells and identify features that make them specialised. I can state that a group of similar cells is called a tissue. I can state that a grou ...
File
... • Nervous systems are composed of nerve cells/neurons and glia (support cells). • Neurons are organized into informationprocessing neural networks • The nervous system regulates and controls body functions; they respond to stimuli and transmit electrical impulses over substantial distances within th ...
... • Nervous systems are composed of nerve cells/neurons and glia (support cells). • Neurons are organized into informationprocessing neural networks • The nervous system regulates and controls body functions; they respond to stimuli and transmit electrical impulses over substantial distances within th ...
Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... However, this year, you get to learn about the cell in great detail. We will explore how the cell is important to life and we will explore the human body to see how cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make systems and the systems make the body. ...
... However, this year, you get to learn about the cell in great detail. We will explore how the cell is important to life and we will explore the human body to see how cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make systems and the systems make the body. ...
I was here - Warren County Schools
... Carried in the blood to all parts of the body Hormones have specific functions, but only with cells with specific receptors Come from glands (pituitary, thyroid, etc.) ...
... Carried in the blood to all parts of the body Hormones have specific functions, but only with cells with specific receptors Come from glands (pituitary, thyroid, etc.) ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.