* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous MusclesSkeleton
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal self-avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
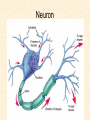
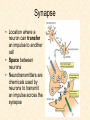
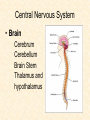
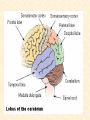
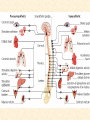
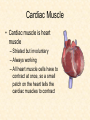
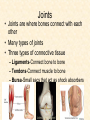
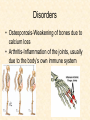
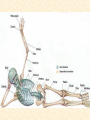
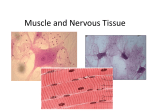
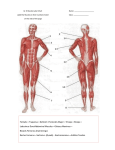
Human Body Systems Nervous /Muscles/Skeleton Systems Human Body Systems • Humans have complex systems • Cells are grouped for efficiency • Dynamic equilibrium Levels of Organization In a multicellular organism levels are: cells tissues organs organ systems tissues: group of similar cells that perform same function organ: group of tissues that work together to perform complex function (ex: sight) organ system: group of organs that perform closely related functions Human Organ Systems • • • • • • • Nervous System Respiratory System Digestive System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Excretory System • Endocrine System • Lymphatic/Immune System • Reproductive System Body Systems Functions • Although each of the 10 organ systems has a different set of functions, they all work together, as a whole, to maintain homeostasis. Nervous System • The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli • Nearly all multicellular organisms have communication systems – Specialized cells carry messages from one cell to another – Smooth and efficient communication through the body Nervous System • • Messages carried by nervous system are electrical signals called impulses Cells that transmit these impulses are called neurons (basic units of nervous system) – 3 types of neurons 1. Sensory 2. Motor 3. Interneurons Neurons • Sensory: Carry impulses from sense organs (eyes, ears, etc) to the spinal cord and brain • Motor: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands • Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them Parts of a Neuron • Cell Body – Largest part; contains nucleus and most of cytoplasm – Most metabolic activities occur here • Dendrites – Short, branched extensions – Carry impulses from environment or other neuron toward cell body – Neurons can have several dendrites • Axon – Long fiber which carries impulses away from cell body – Ends in axon terminals, located a distance away from cell body – Neurons only have one axon • Myelin Sheath – Insulating membrane surrounding axon Neuron Nerve Impulse • An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or the environment Synapse • Location where a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell • Space between neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by neurons to transmit an impulse across the synapse Human Nervous System • Divided into two major divisions: – Central Nervous System (CNS) • Relays messages, processes info and analyzes info – Peripheral Nervous System • Receives information from the environment and relays commands from the CNS to organs and glands Central Nervous System • Brain Cerebrum Cerebellum Brain Stem Thalamus and hypothalamus Brain • Made of 50-100 billion neurons • 4 lobes or regions – Frontal Lobe- memory, judgment, inhibitions, personality – Temporal Lobe- Long term memory, auditory processing – Occipital Lobe- Vision processing – Parietal Lobe- Sensory integration Spinal Cord • Main communications link between the brain and the rest of the body • Certain kinds of info (reflexes) are processed in spinal cord • Reflex is a quick, automatic response to a stimulus – Sneezing and blinking – Allows your body to respond to danger immediately without thinking Peripheral Nervous System • Lies outside of CNS • Consists of all the nerves and cells that are not a part of the brain or spinal cord – Cranial nerves – Divided into 2 divisions: • Sensory • Motor Peripheral Nervous System Sensory division: transmits impulses from sense organs to the CNS Motor division: transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 1. somatic nervous system- regulates conscious controlled activities 2. autonomic nervous system- regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary ~Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system Muscles • Nerves act on muscles to move the body and control bodily functions • Types of muscles – Skeletal- Usually attached to bones; cause voluntary movement. – Smooth-Found in hollow organs; causes involuntary movement – Cardiac: Found only in the heart; causes the heart to beat. Smooth Muscle Tissue • Not under voluntary control • Found in stomach, intestines, blood vessels, etc. • Also, your diaphragm-the muscles which causes your lungs to expand and contract. Skeletal Muscles • Skeletal muscles are called striated, because they are collections of muscle fibers, or cells. • Skeletal muscle cells are very large and complex – From 1mm to 30 cm long! – Have many nuclei How do Skeletal Muscles Work? • Muscles do their work when the contract—that’s why each muscle in your body has two sets, one to contract your arm or leg in one direction, and another muscle to contract and move it back. • But, in order for the muscle to contract, special steps have to happen inside each cell. Inside a Muscle Cell • Inside a muscle cell, there filaments, thin and thick made of protein. • The thin filament is called actin. • The thick filament is called myosin. • Myosin grips the actin and pulls it when the muscle contracts Cardiac Muscle • Cardiac muscle is heart muscle – Striated but involuntary – Always working – All heart muscle cells have to contract at once, so a small patch on the heart tells the cardiac muscles to contract Skeletal System • Muscles can’t cause movement without something to PULL on • Functions of the Skeletal System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Supports the body Protects internal organs Provides for movement Stores mineral reserves Provides site for blood cell formation Bones • Bones are protein fibers and calcium deposits. – 206 bones in an adult, 215 in an infant – Bone cells are called osteocytes – Compact bone is solid – Spongy bone is like a network of girders, strong but light Bone Marrow • Bone marrow- found within cavities of bones – 2 types: yellow primarily fat cells red produces RBC’s, some WBC’s and platelets Joints • Joints are where bones connect with each other • Many types of joints • Three types of connective tissue – Ligaments-Connect bone to bone – Tendons-Connect muscle to bone – Bursa-Small sacs that act as shock absorbers Disorders • Osteoporosis-Weakening of bones due to calcium loss • Arthritis-Inflammation of the joints, usually due to the body’s own immune system