Y8_Cells_Summary - Ralph Thoresby School
... A group of cells that are the same, all doing the same job, is called a tissue (e.g. muscle tissue). A group of different tissues working together to do an important job makes an organ. For example the heart is an organ and is made of muscle tissue and nerve tissue. Organs have very important jobs: ...
... A group of cells that are the same, all doing the same job, is called a tissue (e.g. muscle tissue). A group of different tissues working together to do an important job makes an organ. For example the heart is an organ and is made of muscle tissue and nerve tissue. Organs have very important jobs: ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF LIVING ORGANISMS
... trachea in the neck, then into the 2 bronchi and finally into the 2 bronchioles. Gas is exchanged in the lungs in capillary sacs called alveoli. The diaphragm keeps the lungs open to fill with gases. Oxygen is transferred into the blood stream through capillaries and veins and then carbon dioxide is ...
... trachea in the neck, then into the 2 bronchi and finally into the 2 bronchioles. Gas is exchanged in the lungs in capillary sacs called alveoli. The diaphragm keeps the lungs open to fill with gases. Oxygen is transferred into the blood stream through capillaries and veins and then carbon dioxide is ...
Immunity WS # 1/Living Environment Name Multiple Choice Section
... are called (1.) antigens (2.) antibodies (3.) platelets (4.) red blood cells 4. Some white blood cells recognize _____ as foreign molecules. (1.) antibodies (2.) antigens (3.) allergies (4.) platelets 5. ______ are proteins formed by some white blood cells to destroy antigens. (1.) Antibodies (2.) A ...
... are called (1.) antigens (2.) antibodies (3.) platelets (4.) red blood cells 4. Some white blood cells recognize _____ as foreign molecules. (1.) antibodies (2.) antigens (3.) allergies (4.) platelets 5. ______ are proteins formed by some white blood cells to destroy antigens. (1.) Antibodies (2.) A ...
The neuron - Ms Lindstrom`s Blog
... Biological level of analysis Nervous system: structure and function By Ms Lindstrom ...
... Biological level of analysis Nervous system: structure and function By Ms Lindstrom ...
Multicellular Organisms - Thomas A. Stewart Secondary School
... begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, stem cells simply divide to pro ...
... begin as stem cells. These are unspecialized cells capable of developing into many different types of cell. Stem cells found in embryos are called embryonic stem cells and develop into all the different types of cell in the body. In the earliest stages of development, stem cells simply divide to pro ...
Use for Nov. 20,12 Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... A plant cell has a thick outer layer called the cell _____. This is made of _____. The cytoplasm of a plant cell contains many _____ that are used in the process of photosynthesis. The large permanent _____ is full of _____ and this helps to maintain the shape of the cell. ...
... A plant cell has a thick outer layer called the cell _____. This is made of _____. The cytoplasm of a plant cell contains many _____ that are used in the process of photosynthesis. The large permanent _____ is full of _____ and this helps to maintain the shape of the cell. ...
Cells Study Guide
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
Red Blood Cells Red blood cells main job, or function, is to take in
... Can easily pass through small blood vessels ...
... Can easily pass through small blood vessels ...
HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM Cells
... Heredity- passing of physical traits from parents to offspring. Genetics- study of heredity. Gregor Mendel- father of genetics. did pea plants study. factors that control traits are called genes. different forms of a gene are called alleles. 2 alleles for each trait. one from each parent. 2 alleles ...
... Heredity- passing of physical traits from parents to offspring. Genetics- study of heredity. Gregor Mendel- father of genetics. did pea plants study. factors that control traits are called genes. different forms of a gene are called alleles. 2 alleles for each trait. one from each parent. 2 alleles ...
NOTES: Simple Invertebrates
... “stomach”, cells that dissolve prey for-the-good-of-the-organism STINGING CELLS, part of a NERVE “NET” (a primitive nervous system, a de-centralized nerve cord), NO BRAIN but sensors TWO LAYERS of cells (epidermis & gastrodermis)…no body cavity ...
... “stomach”, cells that dissolve prey for-the-good-of-the-organism STINGING CELLS, part of a NERVE “NET” (a primitive nervous system, a de-centralized nerve cord), NO BRAIN but sensors TWO LAYERS of cells (epidermis & gastrodermis)…no body cavity ...
CELL
... constant component of plant cells. Next, the nuclei were also observed and recognized as such in some animal cells. •Finally, a living substance called PROTOPLASM was ...
... constant component of plant cells. Next, the nuclei were also observed and recognized as such in some animal cells. •Finally, a living substance called PROTOPLASM was ...
nervous-system-structure-and-function
... organs. The autonomic division controls involuntary functions such as those of the heart, blood vessels and lungs. The autonomic division is further divided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The former prepares the body in emergency situations and the latter helps the body retu ...
... organs. The autonomic division controls involuntary functions such as those of the heart, blood vessels and lungs. The autonomic division is further divided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The former prepares the body in emergency situations and the latter helps the body retu ...
From cell to an organism
... Fat cells (heat production, insullation and energy storage) You have two different types of fat cells: 1. ________ fat cells: used to _________ ______ for the body, especially when you’re cold (shivering). 2. ________ fat cells: used to ________ ________ in the form of _____. Think of these cells ...
... Fat cells (heat production, insullation and energy storage) You have two different types of fat cells: 1. ________ fat cells: used to _________ ______ for the body, especially when you’re cold (shivering). 2. ________ fat cells: used to ________ ________ in the form of _____. Think of these cells ...
)151t€\f-
... 8. The levels of organization for structure and tunction in the human body from least complex to most complex are (1) systems -> organs *> tissues -> cells (2) cells -> organs -> tissues -> systems ...
... 8. The levels of organization for structure and tunction in the human body from least complex to most complex are (1) systems -> organs *> tissues -> cells (2) cells -> organs -> tissues -> systems ...
Cell Specialization and Levels of Organization
... • Embryonic stem cells are found in embryos that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
... • Embryonic stem cells are found in embryos that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
Tissues and Organs - sciencelanguagegallery
... Cells, Tissues LO: to define and identify and Organs different tissues, organs and organ systems TASK: With your partner list as many organs as you can think of, again there will be a merit for the pair that think of the most. Use the pictures to help you ...
... Cells, Tissues LO: to define and identify and Organs different tissues, organs and organ systems TASK: With your partner list as many organs as you can think of, again there will be a merit for the pair that think of the most. Use the pictures to help you ...
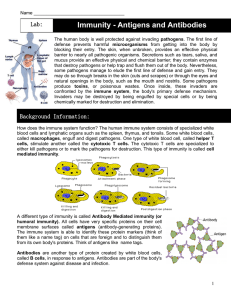
Antigens and Antibodies
... humoral immunity). All cells have very specific proteins on their cell membrane surfaces called antigens (antibody-generating proteins). The immune system is able to identify these protein markers (think of them like a name tag) on cells that are foreign and to distinguish them from its own body's p ...
... humoral immunity). All cells have very specific proteins on their cell membrane surfaces called antigens (antibody-generating proteins). The immune system is able to identify these protein markers (think of them like a name tag) on cells that are foreign and to distinguish them from its own body's p ...
Animal Form and Function (Ch. 40)
... connected to muscles with tendons used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from thr ...
... connected to muscles with tendons used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from thr ...
Document
... 53 The table shows a comparison of some amino acids found in cytochrome c. The two organisms in the table that are most closely related are — A Q and T B R and S C Q and R D Q and S ...
... 53 The table shows a comparison of some amino acids found in cytochrome c. The two organisms in the table that are most closely related are — A Q and T B R and S C Q and R D Q and S ...
File
... About 60 percent of the adult human body is fluid, mainly a water solution of ions and other substances. Although most of this fluid is inside the cells and is called intracellular fluid, about one third is in the spaces outside the cells and is called extracellular fluid. In the extracellular flui ...
... About 60 percent of the adult human body is fluid, mainly a water solution of ions and other substances. Although most of this fluid is inside the cells and is called intracellular fluid, about one third is in the spaces outside the cells and is called extracellular fluid. In the extracellular flui ...
Chapter 1 Review and Test Preparation Vocabulary Review Use the
... 17. How do vascular plants compare with nonvascular plants? 18. You discover a fossil organism that had gills instead of lungs. What can you infer about where the organism lived? ...
... 17. How do vascular plants compare with nonvascular plants? 18. You discover a fossil organism that had gills instead of lungs. What can you infer about where the organism lived? ...
Producing new cells - Clydebank High School
... 5. New nuclear membrance forms round chromosomes and cytoplasm divides ...
... 5. New nuclear membrance forms round chromosomes and cytoplasm divides ...
CELL PROCESSES A selectively permeable cell membrane allows
... (head) and spinal nerves, which travel to all parts of the body. ...
... (head) and spinal nerves, which travel to all parts of the body. ...
Histology
... • connected to muscles with tendons • used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function • most differentiate early in development from thr ...
... • connected to muscles with tendons • used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function • most differentiate early in development from thr ...
Immunity - 1st and 2nd lines of defense
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
Neuronal lineage marker

A Neuronal lineage marker is an endogenous tag that is expressed in different cells along neurogenesis and differentiated cells as neurons. It allows detection and identification of cells by using different techniques. A neuronal lineage marker can be either DNA, mRNA or RNA expressed in a cell of interest. It can also be a protein tag, as a partial protein, a protein or a epitope that discriminates between different cell types or different states of a common cell. An ideal marker is specific to a given cell type in normal conditions and/or during injury. Cell markers are very valuable tools for examining the function of cells in normal conditions as well as during disease. The discovery of various proteins specific to certain cells led to the production of cell-type-specific antibodies that have been used to identify cells.The techniques used for its detection can be immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, methods that utilize transcriptional modulators and site-specific recombinases to label specific neuronal population, in situ hybridization or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A neuronal lineage marker can be a neuronal antigen that is recognized by an autoantibody for example Hu, which is highly restricted to neuronal nuclei. By immunohistochemistry, anti-Hu stains the nuclei of neurons. To localize mRNA in brain tissue, one can use a fragment of DNA or RNA as a neuronal lineage marker, a hybridization probe that detects the presence of nucleotide sequences that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. This technique is known as in situ hybridization. Its application have been carried out in all different tissues, but particularly useful in neuroscience. Using this technique, it is possible to locate gene expression to specific cell types in specific regions and observe how changes in this distribution occur throughout the development and correlate with the behavioral manipulations.Although immunohistochemistry is the staple methodology for identifying neuronal cell types, since it is relatively low in cost and a wide range of immunohistochemical markers are available to help distinguish the phenotype of cells in the brain, sometimes it is time-consuming to produce a good antibody. Therefore, one of the most convenient methods for the rapid assessment of the expression of a cloned ion channel could be in situ hybridization histochemistry.After cells are isolated from tissue or differentiated from pluripotent precursors, the resulting population needs to be characterized to confirm whether the target population has been obtained. Depending on the goal of a particular study, one can use neural stem cells markers, neural progenitor cell markers, neuron markers or PNS neuronal markers.