Contents Unit 5- Evolution Chapter 15 I. Evolution A. Central theme
... 2. Darwin realized it more strongly applied to plants and animals. IV. Darwins Theory A. Competition- living space/ food / is limited B. Variation- not all individuals of a species are alike. C. Adaptations- characteristics that increase chance for survival. D. Natural Selection-Individuals with var ...
... 2. Darwin realized it more strongly applied to plants and animals. IV. Darwins Theory A. Competition- living space/ food / is limited B. Variation- not all individuals of a species are alike. C. Adaptations- characteristics that increase chance for survival. D. Natural Selection-Individuals with var ...
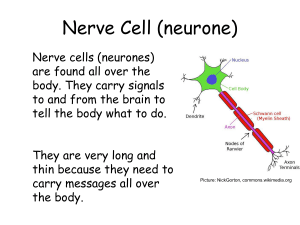
TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... All living things are made up of cells! (including you!) Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
... All living things are made up of cells! (including you!) Cells do all the life functions that we do: - grow - make energy - reproduce - get rid of wastes - need food (to make energy) - die ...
File
... : recombination of genes that occurs during production of gametes Causes most inheritable differences between relatives As a result, sexual reproduction is a major source of ...
... : recombination of genes that occurs during production of gametes Causes most inheritable differences between relatives As a result, sexual reproduction is a major source of ...
Bacteria and Viruses Notes Review: Archaebacteria • Are
... ______________________________________ – create their own energy. Photoautotrophs – gain energy from light from the sun to convert CO2 and water into energy. Chemoautotrophs – make organic carbon from CO2. Do not require light, but instead use energy from chemical reactions using Ammonia, HS, nitrat ...
... ______________________________________ – create their own energy. Photoautotrophs – gain energy from light from the sun to convert CO2 and water into energy. Chemoautotrophs – make organic carbon from CO2. Do not require light, but instead use energy from chemical reactions using Ammonia, HS, nitrat ...
15-1 The Puzzle of Life*s Diversity
... not always random • Sexual Selection – some features do not have a function that help individuals survive, but help them have more offspring ...
... not always random • Sexual Selection – some features do not have a function that help individuals survive, but help them have more offspring ...
Ch.1 Invitation to Biology - OCC
... • Experiments are tests that can simplify observation in nature, b/c conditions under which observations are made can be controlled. • Well-designed experiments test predictions about what you will find in nature when a hypothesis is correct-or won’t find if it is wrong. ...
... • Experiments are tests that can simplify observation in nature, b/c conditions under which observations are made can be controlled. • Well-designed experiments test predictions about what you will find in nature when a hypothesis is correct-or won’t find if it is wrong. ...
Document
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
Living Systems
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
L4-specialised-cells-cards
... are in our body to help us move. Muscle cells are adapted to their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
... are in our body to help us move. Muscle cells are adapted to their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
SCIENCE
... 2. Unexcused absences: If you cut you will receive zeros for all assignments on that day. 3. Excused Absences: Students will have an equal number of days to make up their work. Assignments received before an absences are due upon your return. 4. Assignments must be titled and have your name, period, ...
... 2. Unexcused absences: If you cut you will receive zeros for all assignments on that day. 3. Excused Absences: Students will have an equal number of days to make up their work. Assignments received before an absences are due upon your return. 4. Assignments must be titled and have your name, period, ...
levels of organization directed reading
... digestive endocrine excretory (urinary) immune (lymphatic) integumentary (skin) muscular nervous reproductive respiratory skeletal ...
... digestive endocrine excretory (urinary) immune (lymphatic) integumentary (skin) muscular nervous reproductive respiratory skeletal ...
115 things you should know for the living environment regents exam
... 43. The first living organisms were single celled prokaryotic organisms. 44. The rate at which evolution occurs varies from organism to organism. ...
... 43. The first living organisms were single celled prokaryotic organisms. 44. The rate at which evolution occurs varies from organism to organism. ...
File
... This concept can be used to calculate the frequency of different genotypes and to measure how fast allele frequencies are changing within a population (how fast the population is evolving). ...
... This concept can be used to calculate the frequency of different genotypes and to measure how fast allele frequencies are changing within a population (how fast the population is evolving). ...
Darwin: Who wants to live a million years
... 8. What were some of the selective pressures (limiting factors) in your environment that accented the survival of some of you population? ...
... 8. What were some of the selective pressures (limiting factors) in your environment that accented the survival of some of you population? ...
Evolution - Biology Junction
... 2. Principle or idea that allele frequency will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change 3. A situation in which the allele frequencies in a population do NOT change and the population does NOT EVOLVE 9. Type of selection in which individuals at both ends of the d ...
... 2. Principle or idea that allele frequency will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change 3. A situation in which the allele frequencies in a population do NOT change and the population does NOT EVOLVE 9. Type of selection in which individuals at both ends of the d ...
Evolution Unit Test Review
... • The fossil is actually called Sinosauropteryx • Sinosauropteryx is a compsognathid (small and carnivorous) dinosaur. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae to be found with evidence of feathers. It was covered with a coat of very simple filament-like feathers. ...
... • The fossil is actually called Sinosauropteryx • Sinosauropteryx is a compsognathid (small and carnivorous) dinosaur. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae to be found with evidence of feathers. It was covered with a coat of very simple filament-like feathers. ...
Evolution Vocabulary
... Evolutionary timing methods based on the observation that at least some regions of genomes evolve at constant rates. Pertaining to a taxon derived from a single ancestral species that gave rise to no species in any other taxa. A rare change in the DNA of a gene ultimately creating genetic diversity. ...
... Evolutionary timing methods based on the observation that at least some regions of genomes evolve at constant rates. Pertaining to a taxon derived from a single ancestral species that gave rise to no species in any other taxa. A rare change in the DNA of a gene ultimately creating genetic diversity. ...
PuzzleforSyntheticTh..
... fatal in early childhood. Eastern European Jews have an unusually high frequency of this harmful recessive allele in their population. 7. A more or less distinct group of individuals within a species who are reproductively isolated from other groups. 9. An alteration of genetic material (DNA) such t ...
... fatal in early childhood. Eastern European Jews have an unusually high frequency of this harmful recessive allele in their population. 7. A more or less distinct group of individuals within a species who are reproductively isolated from other groups. 9. An alteration of genetic material (DNA) such t ...
115 THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW FOR THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT REGENTS EXAM
... 43. The first living organisms were single celled prokaryotic organisms. 44. The rate at which evolution occurs varies from organism to organism. 45. The allele frequency in a population is the percentage of alleles for a specific characteristic. 46. When a small group of individuals is separated fr ...
... 43. The first living organisms were single celled prokaryotic organisms. 44. The rate at which evolution occurs varies from organism to organism. 45. The allele frequency in a population is the percentage of alleles for a specific characteristic. 46. When a small group of individuals is separated fr ...
NAME: : ______ DUE/DOQ
... 10. This organelle gives plant cells their shape and protects it from bursting: ______________________________________. ...
... 10. This organelle gives plant cells their shape and protects it from bursting: ______________________________________. ...
Unit A: Chapter 1: Comparing Living Things Lesson 1: Is It Living or
... Scientist classify plants as being vascular or nonvascular. Vascular have tube like cells that carry nutrients, water, and provide support. Plants are also grouped by how they reproduce and if they do or do not produce flowers. Mosses are not vascular. They are low-growing and do not have seeds or f ...
... Scientist classify plants as being vascular or nonvascular. Vascular have tube like cells that carry nutrients, water, and provide support. Plants are also grouped by how they reproduce and if they do or do not produce flowers. Mosses are not vascular. They are low-growing and do not have seeds or f ...