End of Semester Exam Review Guide and Answers
... 36. A virus needs a host to replicate or reproduce. A virus transfers genetic material. 37. Bacteria can be good or bad for your body. Bacteria in cheese and yogurt are good bacteria and aid in digestion. Food left unrefrigerated, or undercooked, are examples of bad bacteria and can make you sick. 3 ...
... 36. A virus needs a host to replicate or reproduce. A virus transfers genetic material. 37. Bacteria can be good or bad for your body. Bacteria in cheese and yogurt are good bacteria and aid in digestion. Food left unrefrigerated, or undercooked, are examples of bad bacteria and can make you sick. 3 ...
TOPIC 1: CELLS 1.Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to
... 5. Organelles are the small parts that make up a cell (each has at least one specific function) a. Vacuoles-- store waste and water (large in plant cells, small in animal cells) b. Ribosome – (very small and is often represented by a dot) located on the ER or in cytoplasm. Ribosomes are where protei ...
... 5. Organelles are the small parts that make up a cell (each has at least one specific function) a. Vacuoles-- store waste and water (large in plant cells, small in animal cells) b. Ribosome – (very small and is often represented by a dot) located on the ER or in cytoplasm. Ribosomes are where protei ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
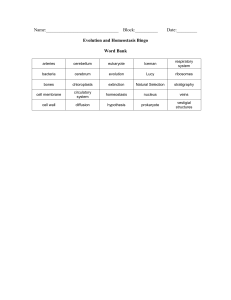
Bingo definitions
... 4. The part of an organism that becomes a fossil. 5. The first life on earth. 6. The oldest preserved human found. 7. The first hominid fossil found. 8. Organisms change over time. 9. All members of a species die forever. 10. Structures that have no function such as an appendix in humans. 11. Techni ...
... 4. The part of an organism that becomes a fossil. 5. The first life on earth. 6. The oldest preserved human found. 7. The first hominid fossil found. 8. Organisms change over time. 9. All members of a species die forever. 10. Structures that have no function such as an appendix in humans. 11. Techni ...
R 28.1
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
No Slide Title
... Natural Selection In the evolutionary struggle for existence, entire organisms, not individual genes, either survive and reproduce or do not. Natural selection can operate only on the phenotypic variation among individuals. An organism's phenotype includes all the physical and behavioral characteris ...
... Natural Selection In the evolutionary struggle for existence, entire organisms, not individual genes, either survive and reproduce or do not. Natural selection can operate only on the phenotypic variation among individuals. An organism's phenotype includes all the physical and behavioral characteris ...
found in all eukaryotes
... respiration: C6 H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP • Ribosomes – where proteins are made • Endoplasmic reticulum – path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another • Golgi apparatus – processes and packages substances produced by the cell ...
... respiration: C6 H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP • Ribosomes – where proteins are made • Endoplasmic reticulum – path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another • Golgi apparatus – processes and packages substances produced by the cell ...
1-3 Studying Life: Read pages 16-22 carefully
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
1-3 Studying Life
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
1-3_studying_life
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
... b. A multicellular organism may contain trillions of cells. c. A living thing that consists of a single cell is a multicellular organism. d. Organisms are made up of cells. 4. A type of asexual reproduction where a portion of the organism splits off to form a new organism is called _________________ ...
28.1 Reinforcement
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
Results in new DNA
... a. Ensuring that only organisms that are fittest and best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. b. Ensuring that only organisms that show no variation from other members of their population survive and reproduce. c. Acting only on mutations that are not carried in an organism’s genes. ...
... a. Ensuring that only organisms that are fittest and best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. b. Ensuring that only organisms that show no variation from other members of their population survive and reproduce. c. Acting only on mutations that are not carried in an organism’s genes. ...
CS 8.1 - 8.4 Assessment Event
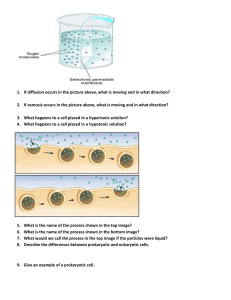
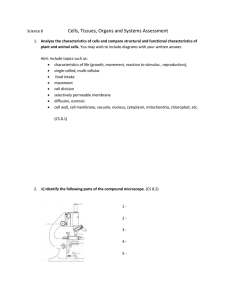
... Hint: Include topics such as: characteristics of life (growth, movement, reaction to stimulus , reproduction), single-celled, multi-cellular food intake movement cell division selectively permeable membrane diffusion, osmosis cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, nucleus, cytoplasm, mit ...
... Hint: Include topics such as: characteristics of life (growth, movement, reaction to stimulus , reproduction), single-celled, multi-cellular food intake movement cell division selectively permeable membrane diffusion, osmosis cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, nucleus, cytoplasm, mit ...
Evolution
... Genetic drift - the effect of chance events on the gene pool of small populations. Gene flow - the introduction of new alleles from nearby populations. ...
... Genetic drift - the effect of chance events on the gene pool of small populations. Gene flow - the introduction of new alleles from nearby populations. ...
28.1
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
... together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which divides to form embryonic stem cells. Stem cells can become any one of more than 200 different types of cells. Cell specialization involves determination and differentiation. Determination occurs when stem cells commit to become only ...
CHAPTER 10 Cell Growth and Division Learning objectives Read
... Learning objectives Read pages 272-290 of “Biology” Miller & Levine to make your Cornell notes and understand the following learning objectives below. Supplementary reading can be from the Cliff Notes AP Biology. Remember the following are NOT questions but guidelines for your note taking. Reading f ...
... Learning objectives Read pages 272-290 of “Biology” Miller & Levine to make your Cornell notes and understand the following learning objectives below. Supplementary reading can be from the Cliff Notes AP Biology. Remember the following are NOT questions but guidelines for your note taking. Reading f ...
Bio 112
... a. The wind is a significant factor in pollination especially because of the large petals. b. Such plants are usually self-pollinators and do not rely on external factors for pollination. c. In general, these are aquatic plants and water aids in pollination, irrespective of color and odor. d. These ...
... a. The wind is a significant factor in pollination especially because of the large petals. b. Such plants are usually self-pollinators and do not rely on external factors for pollination. c. In general, these are aquatic plants and water aids in pollination, irrespective of color and odor. d. These ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
Lecture Questions
... b. phenotypes of individuals. c. genotypes of populations. d. phenotypes of populations. ...
... b. phenotypes of individuals. c. genotypes of populations. d. phenotypes of populations. ...
Biology - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Organisms must regulate their internal environment, made up of extracellular fluids. Maintenance of the narrow range of conditions that support survival is known as homeostasis. ...
... Organisms must regulate their internal environment, made up of extracellular fluids. Maintenance of the narrow range of conditions that support survival is known as homeostasis. ...
Cell Theory
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by the work of Louis Pasteur, specifically his wor ...
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by the work of Louis Pasteur, specifically his wor ...
Chapter 4 – Structure + Function of the Cell
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...