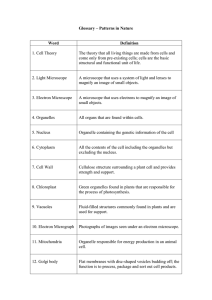
CELL SPECIALIZATION - Biology with Miss Amy
... What size or surfaces is/are best then? large surface area to volume ratio – that is – small cells or cells with folds or projections from the ...
... What size or surfaces is/are best then? large surface area to volume ratio – that is – small cells or cells with folds or projections from the ...
Document
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
... 2. Micro – small changes in genes, chromosome, and allele frequencies in a population II. Natural Selection A. Differences in survival and reproduction among individuals in a population that differ in heritable traits B. Individuals with higher fitness (superior phenotypes) will survive, reproduce, ...
Immunity - 1st and 2nd lines of defense
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
... Destroying cells gone bad! Natural Killer Cells perforate cells release perforin protein insert into membrane of target cell forms pore allowing fluid to flow in & out of cell natural killer cell cell ruptures (lysis) ...
Packet 9 Evolution(1).
... due to genetic drift (chance). After a long period of time even if the two groups were to meet back up the organisms may refuse to mate. At this point they would be considered separate species. When one species becomes 2 separate species this is called SPECIATION ...
... due to genetic drift (chance). After a long period of time even if the two groups were to meet back up the organisms may refuse to mate. At this point they would be considered separate species. When one species becomes 2 separate species this is called SPECIATION ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living
... Hormone therapy Ultrasound In vitro-fertilization 53.____________is the process by which organisms have changed overtime simple, single-celled: complex-single-celled : complex, multicellular 54.Geologic time is based on the ______________ Record. 55. Define natural selection: ...
... Hormone therapy Ultrasound In vitro-fertilization 53.____________is the process by which organisms have changed overtime simple, single-celled: complex-single-celled : complex, multicellular 54.Geologic time is based on the ______________ Record. 55. Define natural selection: ...
Evolution Questions
... Tortoises that long necks and legs lived in areas with tall plants while tortoises with short legs lived in mossy areas with short plants. The finches with thick beaks lived in areas with large, hard shelled nuts while finches with smaller beaks were found where fruit and insects were more prevalent ...
... Tortoises that long necks and legs lived in areas with tall plants while tortoises with short legs lived in mossy areas with short plants. The finches with thick beaks lived in areas with large, hard shelled nuts while finches with smaller beaks were found where fruit and insects were more prevalent ...
Cells and Microbes
... make food. 6 Sugar is a type of food for the plant. Page 42–43 1 1 diatom 2 amoeba 3 bacteria 4 slime mold 2 1 There are a few many different types of microbe. 2 Microbes live in a few many different places. 3 An amoeba is bigger smaller than a grain of salt. 4 Amoebas eat microbes that are bigger ...
... make food. 6 Sugar is a type of food for the plant. Page 42–43 1 1 diatom 2 amoeba 3 bacteria 4 slime mold 2 1 There are a few many different types of microbe. 2 Microbes live in a few many different places. 3 An amoeba is bigger smaller than a grain of salt. 4 Amoebas eat microbes that are bigger ...
Evolution: How Change Occurs
... • Today we define evolutionary fitness as the success an organism has in passing on its genes to the next generation • An adaptation is any genetically controlled trait that increases an organism’s fitness • Think about the weight lifter- big muscles won’t be inherited but gene for the potential to ...
... • Today we define evolutionary fitness as the success an organism has in passing on its genes to the next generation • An adaptation is any genetically controlled trait that increases an organism’s fitness • Think about the weight lifter- big muscles won’t be inherited but gene for the potential to ...
Dev Biol L1
... tissues into organs, organs into organ systems, & organ systems into whole organism. ...
... tissues into organs, organs into organ systems, & organ systems into whole organism. ...
Investigation 1 “Living Cells”
... 2. Oxygen: an atmospheric gas needed by most living cells. 3. Carbon Dioxide: a waste gas product by living cells. 4. Heart: a muscular organ that contracts rhythmically, producing a pulse with each contraction. a. The human heart has four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, an ...
... 2. Oxygen: an atmospheric gas needed by most living cells. 3. Carbon Dioxide: a waste gas product by living cells. 4. Heart: a muscular organ that contracts rhythmically, producing a pulse with each contraction. a. The human heart has four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, an ...
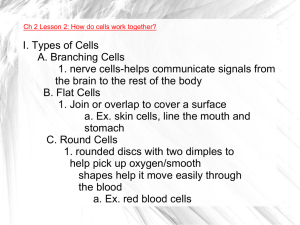
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... Ch 2 Lesson 3: How do organs work together? I. Organ Systems- group of organs working together ...
... Ch 2 Lesson 3: How do organs work together? I. Organ Systems- group of organs working together ...
Circulatory System 1
... Function of the Circulatory System • Carries material to and from the cells of the body. ...
... Function of the Circulatory System • Carries material to and from the cells of the body. ...
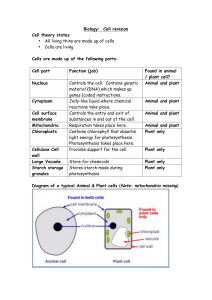
The Cell: A Review
... The nucleus is arguably the most important structure for many cells. While some single-celled organisms including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the inst ...
... The nucleus is arguably the most important structure for many cells. While some single-celled organisms including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the inst ...
New B1 B2 B3 Revision
... for e.g. growth, keeping warm etc •Only about 10% of the energy at each stage of a food chain gets passed to the next level. The rest -Escapes as heat and used for movement -Excreted or cannot be eaten and passes to decomposers (bacteria ...
... for e.g. growth, keeping warm etc •Only about 10% of the energy at each stage of a food chain gets passed to the next level. The rest -Escapes as heat and used for movement -Excreted or cannot be eaten and passes to decomposers (bacteria ...
Biology Cell revision
... • Use iodine solution for plant cells (e.g. onion cells) • Use methylene blue for animal cells (e.g. human cheek cells) 4. Lower a cover slip carefully over the cells – this helps to prevent air bubbles. 5. Place prepared slide onto microscope. 6. View the slide using the low power lens first moving ...
... • Use iodine solution for plant cells (e.g. onion cells) • Use methylene blue for animal cells (e.g. human cheek cells) 4. Lower a cover slip carefully over the cells – this helps to prevent air bubbles. 5. Place prepared slide onto microscope. 6. View the slide using the low power lens first moving ...
Cellular organisation
... Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, consist of just a single cell. Multicellular organisms consists of many cells – humans are made from an estimated 50 trillion cells! ...
... Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, consist of just a single cell. Multicellular organisms consists of many cells – humans are made from an estimated 50 trillion cells! ...
mechanisms of evolution presentation
... • sickle-cell carriers are protected from malaria •What is evolution? - a change in genes frequency in a population between generations - sickle-cell genes decline in frequency when malaria is not present ...
... • sickle-cell carriers are protected from malaria •What is evolution? - a change in genes frequency in a population between generations - sickle-cell genes decline in frequency when malaria is not present ...
100
... Galapagos Islands for many years. Since the island is small, the lineage of every bird for several generations is known. This allows a family tree of each bird to be developed. Some family groups have survived and others have died out. The groups that survive probably have ...
... Galapagos Islands for many years. Since the island is small, the lineage of every bird for several generations is known. This allows a family tree of each bird to be developed. Some family groups have survived and others have died out. The groups that survive probably have ...
Ch. 4 Cells
... • -Vacuoles: (plant) Storage of starch • -Plastids: (plant) store food and pigments • -Cilia: hair-like projection to sweep materials across and away from the cell ...
... • -Vacuoles: (plant) Storage of starch • -Plastids: (plant) store food and pigments • -Cilia: hair-like projection to sweep materials across and away from the cell ...
Fact you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------53. _____________________ -the process by which organisms have changed from one form to another over time from simple celled, to complex sing ...
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------53. _____________________ -the process by which organisms have changed from one form to another over time from simple celled, to complex sing ...
Biology: Microbiology: Bacteria I
... however their genetic material (DNA) is concentrated together in the bacterial cell. Also, most bacteria can reproduce on their own without having to invade other living cells, however, some bacteria do need to live inside another cell just as viruses do (e.g. chlamydia). ...
... however their genetic material (DNA) is concentrated together in the bacterial cell. Also, most bacteria can reproduce on their own without having to invade other living cells, however, some bacteria do need to live inside another cell just as viruses do (e.g. chlamydia). ...