Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
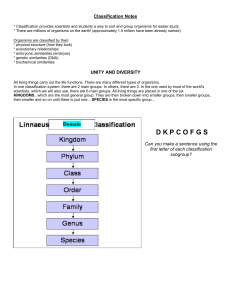
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
carson and gavy doc
... a way by using its DNA to command where it needs to go and “help”. So in a way the cell will control the whole organism because the organs control the organism and the cell controls the organ. There are different organisms ran by their own individual organ system, some of these organisms are animal, ...
... a way by using its DNA to command where it needs to go and “help”. So in a way the cell will control the whole organism because the organs control the organism and the cell controls the organ. There are different organisms ran by their own individual organ system, some of these organisms are animal, ...
What`s in a Cell?
... You know how there are organs in your body that do “things?” Well, organelles do similar things in cells. Like…your brain controls what your body does…right? There’s an organelle in a cell that controls this stuff. How? Well…it’s biochemical…but…you’ll get there Anyway, that’s an ANALOGY, which ...
... You know how there are organs in your body that do “things?” Well, organelles do similar things in cells. Like…your brain controls what your body does…right? There’s an organelle in a cell that controls this stuff. How? Well…it’s biochemical…but…you’ll get there Anyway, that’s an ANALOGY, which ...
AP Bio Evolution Study Guide (Ch 22-25)
... Fossil Record Comparative Anatomy Comparative Embryology Molecular Biology Which type of evidence provides the strongest support for evolution? ...
... Fossil Record Comparative Anatomy Comparative Embryology Molecular Biology Which type of evidence provides the strongest support for evolution? ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... good experiment? (there are 7) 1. can be repeated by others with same results. 2. Does not have to agree with your hypothesis 3. Large sample to test ...
... good experiment? (there are 7) 1. can be repeated by others with same results. 2. Does not have to agree with your hypothesis 3. Large sample to test ...
Why is life on Earth so diverse???
... fuss about?! = “a scientific explanation of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence” ...
... fuss about?! = “a scientific explanation of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence” ...
Keystone Countdown
... 2. Identify the four parts of the experiment in the space below. Miss Schantz loves to drink cold Diet Coke, but somehow it’s always warm by the time she gets a chance to drink it. She knows that if she is able to insulate the Diet Coke bottle, the soda might remain cold for a longer period of time. ...
... 2. Identify the four parts of the experiment in the space below. Miss Schantz loves to drink cold Diet Coke, but somehow it’s always warm by the time she gets a chance to drink it. She knows that if she is able to insulate the Diet Coke bottle, the soda might remain cold for a longer period of time. ...
Review for BCT
... etc.) substantiates the anatomical evidence for evolution and provides additional detail about the sequence in which various lines of descent branched 3. The principles of evolution (including natural selection and common descent) provide a scientific explanation for the history of life on Earth a ...
... etc.) substantiates the anatomical evidence for evolution and provides additional detail about the sequence in which various lines of descent branched 3. The principles of evolution (including natural selection and common descent) provide a scientific explanation for the history of life on Earth a ...
Exam 1 Review - Iowa State University
... 5. The oldest group of organisms on earth are ______ and are the common ancestor of all animals. a) plants b) prokayotes c) protists d) Euglenazoa e) dinosaurs 6. An “endosymbiont” is ___________________. The primary plastids of ___________ are thought to have originated this way. a) a chimera, red ...
... 5. The oldest group of organisms on earth are ______ and are the common ancestor of all animals. a) plants b) prokayotes c) protists d) Euglenazoa e) dinosaurs 6. An “endosymbiont” is ___________________. The primary plastids of ___________ are thought to have originated this way. a) a chimera, red ...
biology sol review sheet
... 3. ________________________- the attraction between the positive end of one water molecule and the negative end of another water molecule. ...
... 3. ________________________- the attraction between the positive end of one water molecule and the negative end of another water molecule. ...
Photosynthesis means synthesis in presence of light
... Some of the chemical processes occur in a living organisms body are these will be reactions such as oxidation-reduction reactions, photosynthesis and respiration explained earlier. This reaction is also known as electron transfer reactions. Some more processes that identify living things are dehydr ...
... Some of the chemical processes occur in a living organisms body are these will be reactions such as oxidation-reduction reactions, photosynthesis and respiration explained earlier. This reaction is also known as electron transfer reactions. Some more processes that identify living things are dehydr ...
organisation of living beings2016
... macromolecules, these can join together to form the parts of a cell: cell membrane, nucleus (contains the genetic material) and cytoplasm with organelles, each organelle performs a specific function, for example mitochondrias produce energy, ribosomes synthesize proteins and chloroplasts (only in pl ...
... macromolecules, these can join together to form the parts of a cell: cell membrane, nucleus (contains the genetic material) and cytoplasm with organelles, each organelle performs a specific function, for example mitochondrias produce energy, ribosomes synthesize proteins and chloroplasts (only in pl ...
CRCT Review PPT
... back through the body. Before it can be reused, which organ must the blood pass through before it is returned to the rest of the body? A. the stomach, because it must receive nutrients B. the lungs, because it must be re-oxygenated ...
... back through the body. Before it can be reused, which organ must the blood pass through before it is returned to the rest of the body? A. the stomach, because it must receive nutrients B. the lungs, because it must be re-oxygenated ...
Module A-1 (Principles of Biology)
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...
2016-2017 Biology Spring Final Study Guide
... Biology Spring Final Study Guide The final will cover all information since the beginning of the school year, but the emphasis will be second semester (approx 30% 1st semester, 70% 2nd semester information). *Study guides are intended to aide in preparation for tests. They may not list every item th ...
... Biology Spring Final Study Guide The final will cover all information since the beginning of the school year, but the emphasis will be second semester (approx 30% 1st semester, 70% 2nd semester information). *Study guides are intended to aide in preparation for tests. They may not list every item th ...
Which is the odd one out and why?
... protein. • Your body uses the protein you eat to make lots of specialised protein molecules that have specific jobs. • Proteins are sometimes described as long necklaces with differently shaped heads. Each bead is a small amino acid. • Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They make thous ...
... protein. • Your body uses the protein you eat to make lots of specialised protein molecules that have specific jobs. • Proteins are sometimes described as long necklaces with differently shaped heads. Each bead is a small amino acid. • Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They make thous ...
NoB1ch02QUICKcheck-ed
... Consider a cell with cilia beating on its surface. Identify one other organelle that would be expected to assist in the action of these cilia. Because the beating of cilia is an energy-requiring process of a cell, it is reasonable to suggest that mitochondria would be present to assist the action of ...
... Consider a cell with cilia beating on its surface. Identify one other organelle that would be expected to assist in the action of these cilia. Because the beating of cilia is an energy-requiring process of a cell, it is reasonable to suggest that mitochondria would be present to assist the action of ...
EOC review packet answers Biology EOC
... 62. What is DNA fingerprinting? What are some useful applications of DNA fingerprinting? DNA fingerprinting involves cutting different DNA samples with restriction enzymes and running them through a gel. Differences in mass, charge and size of the DNA fragments will identify differences between indi ...
... 62. What is DNA fingerprinting? What are some useful applications of DNA fingerprinting? DNA fingerprinting involves cutting different DNA samples with restriction enzymes and running them through a gel. Differences in mass, charge and size of the DNA fragments will identify differences between indi ...
Historical Overview of Evolutionary Biology
... established by observation or experiment, and is propounded or accepted as accounting for the known facts. • Because theory is a set of statements, it usually does not stand or fall on the basis of a single critical test, as simple hypotheses do. Rather, theories evolve as they are confronted with n ...
... established by observation or experiment, and is propounded or accepted as accounting for the known facts. • Because theory is a set of statements, it usually does not stand or fall on the basis of a single critical test, as simple hypotheses do. Rather, theories evolve as they are confronted with n ...
./ ` . `.`4 Body Tissues 13. Figure 3-6: A. Simple squamous epLthelium
... water and (free) oxygen gas ...
... water and (free) oxygen gas ...
Unit 7 Test with answers
... 22. If you color your hair blue, this trait will NOT be passed on to your offspring. Why? Because only traits in your DNA are passed on through your genes to your offspring. 23. What are gametes? Reproductive cells (sperm or egg) 24. Which type of reproduction, sexual or asexual, provides more genet ...
... 22. If you color your hair blue, this trait will NOT be passed on to your offspring. Why? Because only traits in your DNA are passed on through your genes to your offspring. 23. What are gametes? Reproductive cells (sperm or egg) 24. Which type of reproduction, sexual or asexual, provides more genet ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... Nerve cells which carry out-going impulses to their effectors, either glands or muscles A propagated action potential In animals, the egg-producing gonad of the female. In flowering plants, the enlarged base of the pistil. In which seeds develop Single celled protists- animal- like characteristics- ...
... Nerve cells which carry out-going impulses to their effectors, either glands or muscles A propagated action potential In animals, the egg-producing gonad of the female. In flowering plants, the enlarged base of the pistil. In which seeds develop Single celled protists- animal- like characteristics- ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).