Mutations
... Speciation is the formation of new species. Allopatric speciation occurs as a result of populations being reproductively isolated from each other. This is a three step process. 1. A physical barrier separates a single interbreeding population. 2. Natural selection works on the separate groups indep ...
... Speciation is the formation of new species. Allopatric speciation occurs as a result of populations being reproductively isolated from each other. This is a three step process. 1. A physical barrier separates a single interbreeding population. 2. Natural selection works on the separate groups indep ...
Bingo definitions
... 4. The part of an organism that becomes a fossil. 5. The first life on earth. 6. The oldest preserved human found. 7. The first hominid fossil found. 8. Organisms change over time. 9. All members of a species die forever. 10. Structures that have no function such as an appendix in humans. 11. Techni ...
... 4. The part of an organism that becomes a fossil. 5. The first life on earth. 6. The oldest preserved human found. 7. The first hominid fossil found. 8. Organisms change over time. 9. All members of a species die forever. 10. Structures that have no function such as an appendix in humans. 11. Techni ...
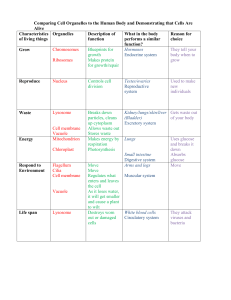
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
... Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
... Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
Evolutuion II
... b. Variation caused by large genetic switchboards. 2. Epigenetic inheritance systems, a few examples (from Earth!) a. Gene activity of generations past can be passed through generations. b. Structural inheritance can ...
... b. Variation caused by large genetic switchboards. 2. Epigenetic inheritance systems, a few examples (from Earth!) a. Gene activity of generations past can be passed through generations. b. Structural inheritance can ...
Facts to Remember to help you pass the NYS Science Assessment
... 28.) A biome is a large area with similar plant and animal communities. 29.) Renewable resources can be re-used or replaced. 30.) Non-renewable resources cannot be replaced. 31.) A Punnett Square shows the possible outcomes of a genetic cross, expressed as probabilities. 32.) Structures found only ...
... 28.) A biome is a large area with similar plant and animal communities. 29.) Renewable resources can be re-used or replaced. 30.) Non-renewable resources cannot be replaced. 31.) A Punnett Square shows the possible outcomes of a genetic cross, expressed as probabilities. 32.) Structures found only ...
Agents of Evolutionary Change
... • A change in the sequence of DNA • Mutations can occur when – There are errors when DNA is copied – There is exposure to mutagens (chemicals or radiation) ...
... • A change in the sequence of DNA • Mutations can occur when – There are errors when DNA is copied – There is exposure to mutagens (chemicals or radiation) ...
Evolution
... How can we prove that natural selection exists? Can you think of any examples? Turn to the person next ...
... How can we prove that natural selection exists? Can you think of any examples? Turn to the person next ...
CHAPTER 11: Gene Expression
... Recall that gene information codes for the proteins a cell needs for structure & function. **But not all proteins are needed all the time. ...
... Recall that gene information codes for the proteins a cell needs for structure & function. **But not all proteins are needed all the time. ...
On Evolution…
... Small changes in the DNA of living organisms (which occurs through genetic mutations when cells make copies of themselves) is the main driving force behind the large changes seen over billions of years of life on Earth. This is evolution! ...
... Small changes in the DNA of living organisms (which occurs through genetic mutations when cells make copies of themselves) is the main driving force behind the large changes seen over billions of years of life on Earth. This is evolution! ...
Biology Final Semester 1 Study Guide
... 46. food chain 47. ecological model 48. energy not used is given off as _____ 49. cell theory 50. prokaryotes ...
... 46. food chain 47. ecological model 48. energy not used is given off as _____ 49. cell theory 50. prokaryotes ...
Review Sheet
... Charles Darwin- species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, proposed the scientific theory of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection. ...
... Charles Darwin- species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, proposed the scientific theory of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection. ...
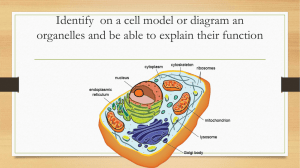
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... • Helps cell maintain shape and assisted with various movements for example in muscle movement ...
... • Helps cell maintain shape and assisted with various movements for example in muscle movement ...
sci 7 study guide
... 2 types of cells: Prokaryotes (bacteria), Eukaryotes (plants & animals) Mammals: breathe air, give birth to live young Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organi ...
... 2 types of cells: Prokaryotes (bacteria), Eukaryotes (plants & animals) Mammals: breathe air, give birth to live young Genus-group of species; when a scientist discovers a new species, it is placed with the species with which it shares the most characteristics Structure and Function of Living Organi ...
01 - Homework Now
... 1. A molecular system that controls the expression of a specific gene is called a genetic ______________________. 2. A group of related genes that lie close together and that work together as a unit is called a(n) ______________________. 3. To break down lactose, Escherichia coli need three differen ...
... 1. A molecular system that controls the expression of a specific gene is called a genetic ______________________. 2. A group of related genes that lie close together and that work together as a unit is called a(n) ______________________. 3. To break down lactose, Escherichia coli need three differen ...
Emerging Methods in Molecular Biology and Genetics
... variety of problems in neuropsychopharmacology. For example, measurements of the levels of expression of large numbers of genes in various brain regions and nerve cells are providing information about the molecular basis of normal brain functions, and the effects of drugs on these functions. The sam ...
... variety of problems in neuropsychopharmacology. For example, measurements of the levels of expression of large numbers of genes in various brain regions and nerve cells are providing information about the molecular basis of normal brain functions, and the effects of drugs on these functions. The sam ...
GENETICS
... We Can Manipulate DNA •Recombinant DNA: •Cutting the DNA from one organism and joining it with the DNA from another •Human gene for insulin into bacteria: bacteria multiply and make insulin for diabetics Insulin gene ...
... We Can Manipulate DNA •Recombinant DNA: •Cutting the DNA from one organism and joining it with the DNA from another •Human gene for insulin into bacteria: bacteria multiply and make insulin for diabetics Insulin gene ...
*Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment
... *Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment. *Membrane bound structures in cells are called organelles. *Ribosomes make protein. *Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides which include a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base. *Carbohydrates are the main energy source for organisms ...
... *Homeostasis is maintaining a stable internal environment. *Membrane bound structures in cells are called organelles. *Ribosomes make protein. *Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides which include a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogen base. *Carbohydrates are the main energy source for organisms ...
1-2.02 test study guide
... 14.What are the functions of proteins? 15.Who was the first person to see the cell? 16.What did schleiden and Schwann tell us? 17.What are the 3 principals of the cell theory 18.What does the cell theory apply to? 19.What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes 20.Eukaryotes do not only ...
... 14.What are the functions of proteins? 15.Who was the first person to see the cell? 16.What did schleiden and Schwann tell us? 17.What are the 3 principals of the cell theory 18.What does the cell theory apply to? 19.What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes 20.Eukaryotes do not only ...
Study of the evolution of animal parasite bacteria and plant symbionts
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
01 - HomeworkNOW.com
... 8. Regulatory genes that control development include [homeotic genes / telomeres]. In the space provided, explain how the terms in each pair differ in meaning. ...
... 8. Regulatory genes that control development include [homeotic genes / telomeres]. In the space provided, explain how the terms in each pair differ in meaning. ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).