Descriptor PDF
... 25. Immune system of animals 26. Evolutionary processes, including evolution by natural selection and speciation 27. Phylogenies and the history of life 28. The diversity of life, including viruses, bacteria, archaea, protists, green plants, fungi, protostome and the history of life 29. Population a ...
... 25. Immune system of animals 26. Evolutionary processes, including evolution by natural selection and speciation 27. Phylogenies and the history of life 28. The diversity of life, including viruses, bacteria, archaea, protists, green plants, fungi, protostome and the history of life 29. Population a ...
Development and Apoptosis
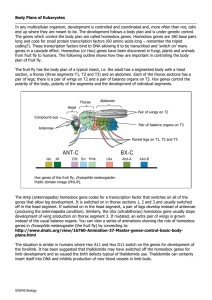
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
Coevolution (read and know!)
... Process of one species giving rise to many species that live in different ways (niches) AKA: divergent evolution ...
... Process of one species giving rise to many species that live in different ways (niches) AKA: divergent evolution ...
Protist and Fungi
... Biotechnology- use of living organisms to produce products for human use. Products can be such as genetically altered food such as milk, corn, and tomatoes Piggybacked viruses, using a harmless virus to produce capsid of a more harmful one. Idea is that harmless virus will makes “protein coat” of ha ...
... Biotechnology- use of living organisms to produce products for human use. Products can be such as genetically altered food such as milk, corn, and tomatoes Piggybacked viruses, using a harmless virus to produce capsid of a more harmful one. Idea is that harmless virus will makes “protein coat” of ha ...
A1983RC02000002
... the citations are reports of experiments that optimistically purported to have proved King and Jukes wrong at last. Selectionists felt that natural populations had enormous amounts of phenotypic variation of adaptive significance, due to polymor’ihism; neutralists felt that patterns of molccular cha ...
... the citations are reports of experiments that optimistically purported to have proved King and Jukes wrong at last. Selectionists felt that natural populations had enormous amounts of phenotypic variation of adaptive significance, due to polymor’ihism; neutralists felt that patterns of molccular cha ...
MAIN IDEAS
... 2. What is the genetic makeup of the parents? AA and aa 3. Why will Aa plants have a straight hairline rather than a peaked one? Straight hairline is dominant. ...
... 2. What is the genetic makeup of the parents? AA and aa 3. Why will Aa plants have a straight hairline rather than a peaked one? Straight hairline is dominant. ...
AB Biology Summer Assignment (Word)
... 43) Name the two types of vascular tissue found in plants, as well as what they transport. ...
... 43) Name the two types of vascular tissue found in plants, as well as what they transport. ...
Cell Processes
... 3. The nucleus is the control center of cellular activities. DNA is the “boss” of the cell and is passed down from one generation to another. PROKARYOTIC cells such as bacteria have no nucleus but still possess DNA to direct cellular functions. EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus which housed the DNA. E ...
... 3. The nucleus is the control center of cellular activities. DNA is the “boss” of the cell and is passed down from one generation to another. PROKARYOTIC cells such as bacteria have no nucleus but still possess DNA to direct cellular functions. EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus which housed the DNA. E ...
Outline - Science in the News
... Phenotype - The physical manifestation, or observable traits, of the genotype. This happens by making either proteins or functional RNA from the genes encoded by the DNA. These functional proteins or RNA then achieve some work on the living organism and therefore produce the phenotype. Natural Selec ...
... Phenotype - The physical manifestation, or observable traits, of the genotype. This happens by making either proteins or functional RNA from the genes encoded by the DNA. These functional proteins or RNA then achieve some work on the living organism and therefore produce the phenotype. Natural Selec ...
Protists
... Why Africa so bad for malaria? - mosquitos developed with humans as their main prey. ...
... Why Africa so bad for malaria? - mosquitos developed with humans as their main prey. ...
File
... 13. CHO, carbs are sugars; are simple sugars = monosaccharides, two sugars = disaccharides, many sugars = polysaccharides; examples are glucose, fructose 14. CHO; fats, cholesterol; made up of fatty acids 15. CHON; made up of amino acids; are enzymes 16. DNA, RNA 17. want Surface Area to be small so ...
... 13. CHO, carbs are sugars; are simple sugars = monosaccharides, two sugars = disaccharides, many sugars = polysaccharides; examples are glucose, fructose 14. CHO; fats, cholesterol; made up of fatty acids 15. CHON; made up of amino acids; are enzymes 16. DNA, RNA 17. want Surface Area to be small so ...
History of Evolution Jelly Bean Review
... Charles Darwin writes ‘On the Origin of Species’. Lamarck writes about evolution through acquired traits, using a giraffe as his model. DNA sequencing is developed, allowing the comparison of the genes of different organisms Malthus, an economist, writes about the inevitability that people will exha ...
... Charles Darwin writes ‘On the Origin of Species’. Lamarck writes about evolution through acquired traits, using a giraffe as his model. DNA sequencing is developed, allowing the comparison of the genes of different organisms Malthus, an economist, writes about the inevitability that people will exha ...
class01-m
... • Proteins are polypeptides of 703000 amino-acids • This structure is (mostly) determined by the sequence of amino-acids that make up the protein ...
... • Proteins are polypeptides of 703000 amino-acids • This structure is (mostly) determined by the sequence of amino-acids that make up the protein ...
Evolution Concepts
... Concept – Organisms with a given adaptation are more likely to survive and reproduce, their genes will be passed on to the next generation. -- This increases the frequency of the gene that caused the adaptation. In this way, species change over time or evolve. -- ORGANISMS THEMSELVES DO NOT EVOLVE ...
... Concept – Organisms with a given adaptation are more likely to survive and reproduce, their genes will be passed on to the next generation. -- This increases the frequency of the gene that caused the adaptation. In this way, species change over time or evolve. -- ORGANISMS THEMSELVES DO NOT EVOLVE ...
lecture0
... The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. ...
... The various genome projects have yielded the complete DNA sequences of many organisms. ...
Regents Review Sheet 1
... Mutation: Alteration of DNA resulting in a misshapen protein (chemicals & radiation.) Gel Electrophoresis: A restriction enzyme cuts the DNA at a specific base sequence. The fragments migrate towards the positive end of the gel (DNA is negatively charged). The smaller fragments move faster. Species ...
... Mutation: Alteration of DNA resulting in a misshapen protein (chemicals & radiation.) Gel Electrophoresis: A restriction enzyme cuts the DNA at a specific base sequence. The fragments migrate towards the positive end of the gel (DNA is negatively charged). The smaller fragments move faster. Species ...
Algorithms in Computational Biology
... Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino-acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. ...
... Decodes the mRNA molecules to amino-acids. It connects to the mRNA with one side and holds the appropriate amino acid on its other side. ...
Ch 1 PPT - Ludlow Independent Schools
... • Analyzing a biological structure gives us clues about what it does and how it works ...
... • Analyzing a biological structure gives us clues about what it does and how it works ...
CHAPTER 9 DNA: The Genetic Material ACROSS
... that enables a bacterium to build the proteins needed for lactose metabolism only when lactose is present. Some of the genes determine whether or not other genes will be expressed; the other genes code for enzymes that break down lactose. 37. Eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells. ...
... that enables a bacterium to build the proteins needed for lactose metabolism only when lactose is present. Some of the genes determine whether or not other genes will be expressed; the other genes code for enzymes that break down lactose. 37. Eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells. ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).