Memantine and Neuroprotection
... background noise long lasting alteration in synaptic strength. NMDA receptors plays central role in such alterations and an endogenous “noise suppressant” is magnesium. ...
... background noise long lasting alteration in synaptic strength. NMDA receptors plays central role in such alterations and an endogenous “noise suppressant” is magnesium. ...
Autacoid Drugs Major autacoids
... Aminophylline is a bronchodilator. It is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate. Aminophylline is a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor which rais ...
... Aminophylline is a bronchodilator. It is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate. Aminophylline is a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor which rais ...
Lecture 19
... -They work at two receptors (α,β) -α receptor are excitatory (constriction effect) -β receptor inhibitory on smooth muscle -β1 found in the heart -β2 found in the lung this not from the lecture it can help you to understand the receptors : -α1 : mainly effect is constriction -α2: mainly has feedback ...
... -They work at two receptors (α,β) -α receptor are excitatory (constriction effect) -β receptor inhibitory on smooth muscle -β1 found in the heart -β2 found in the lung this not from the lecture it can help you to understand the receptors : -α1 : mainly effect is constriction -α2: mainly has feedback ...
Psychopharmacology and Other Biologic Treatments
... reactions within cells and are targets for some drugs. • Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that breaks down most bioamine neurotransmitters (NE, DA, 5-HT). • Enzymes may be inhibited to produce greater neurotransmitter effect. ...
... reactions within cells and are targets for some drugs. • Monoamine oxidase is an enzyme that breaks down most bioamine neurotransmitters (NE, DA, 5-HT). • Enzymes may be inhibited to produce greater neurotransmitter effect. ...
NTs
... Golgi apparatus in cell body • Precursors, enzymes, and vesicles are transported from cell body down axon to terminal • At terminal, NTs are synthesized and packaged into vesicles • Filled vesicles dock onto proteins in terminal ...
... Golgi apparatus in cell body • Precursors, enzymes, and vesicles are transported from cell body down axon to terminal • At terminal, NTs are synthesized and packaged into vesicles • Filled vesicles dock onto proteins in terminal ...
Drugs and Drug Abuse
... ◦ intravenous - reaches brain in ~ 10 secs quick response but also most dangerous ...
... ◦ intravenous - reaches brain in ~ 10 secs quick response but also most dangerous ...
5-Mechanism of drug action2015-10-14 05:152.0 MB
... but with low intrinsic activity (<1) e.g. pindolol Antagonist having full affinity to the receptor but ...
... but with low intrinsic activity (<1) e.g. pindolol Antagonist having full affinity to the receptor but ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases
... Memantine acts by blocking the NMDA receptor–associated ion channel, but, at therapeutic doses, only a fraction of these channels are actually blocked. This partial blockade may allow memantine to limit Ca2+ influx into the neuron, such that toxic intracellular levels are not achieved during NMDA-r ...
... Memantine acts by blocking the NMDA receptor–associated ion channel, but, at therapeutic doses, only a fraction of these channels are actually blocked. This partial blockade may allow memantine to limit Ca2+ influx into the neuron, such that toxic intracellular levels are not achieved during NMDA-r ...
Slide 1
... related epigenetic mechanisms. D1 receptors signal via PKA as well as other cascades, including ERK and the phosphoinositide-3-kinase pathway. Some effects are mediated indirectly by DARPP-32, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 that is involved in many aspects of addiction (see Ch. 24). The ...
... related epigenetic mechanisms. D1 receptors signal via PKA as well as other cascades, including ERK and the phosphoinositide-3-kinase pathway. Some effects are mediated indirectly by DARPP-32, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 that is involved in many aspects of addiction (see Ch. 24). The ...
File
... 3n) Neurotransmitters, mood & behaviour Endorphins are neurotransmitters that stimulate neurons involved in reducing the intensity of pain – they act as natural painkillers Increased levels of endorphins are also connected with euphoric feelings, appetite modulation and release of sex hormones Endo ...
... 3n) Neurotransmitters, mood & behaviour Endorphins are neurotransmitters that stimulate neurons involved in reducing the intensity of pain – they act as natural painkillers Increased levels of endorphins are also connected with euphoric feelings, appetite modulation and release of sex hormones Endo ...
Problems with synapses File
... • How is Schizophrenia treated? • It can be treated by drugs which block the binding of dopamine in the post-synaptic neurons- less action potentials are fired. • How is the treatment for schizophrenia similar/different to the dopamine agonists used in treatment of Parkinson’s? • They have a similar ...
... • How is Schizophrenia treated? • It can be treated by drugs which block the binding of dopamine in the post-synaptic neurons- less action potentials are fired. • How is the treatment for schizophrenia similar/different to the dopamine agonists used in treatment of Parkinson’s? • They have a similar ...
AnatomyTestNervousSystem1
... 3. After a neuron depolarizes, it must undergo ______________ to return the neuron to its polarized state. 4. What are the three major parts of a neuron? 5. Name a neurotransmitter and the enzyme that breaks down that neurotransmitter. 6. What is the ion that is involved in causing the presynaptic v ...
... 3. After a neuron depolarizes, it must undergo ______________ to return the neuron to its polarized state. 4. What are the three major parts of a neuron? 5. Name a neurotransmitter and the enzyme that breaks down that neurotransmitter. 6. What is the ion that is involved in causing the presynaptic v ...
Drugs of Abuse II - London Metropolitan University
... dopaminergic neurons and induces release of dopamine from nerve terminals Interacts with dopaminecontaining synaptic vesicles and provokes release into cytoplasm of the terminal Binds to DAT (dopamine ...
... dopaminergic neurons and induces release of dopamine from nerve terminals Interacts with dopaminecontaining synaptic vesicles and provokes release into cytoplasm of the terminal Binds to DAT (dopamine ...
Legend
... motor interface is apparent. Dashed lines indicate limbic glutamatergic afferent inputs to the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Purple lines represent efferent signals from the NAc believed to be involved in drug reward. Bold blue lines indicate projections of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system, which ar ...
... motor interface is apparent. Dashed lines indicate limbic glutamatergic afferent inputs to the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Purple lines represent efferent signals from the NAc believed to be involved in drug reward. Bold blue lines indicate projections of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system, which ar ...
PSYC550 Psychopharmacology
... Psychopharmacology • Psychopharmacology is the study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and on behavior • The term drug has many meanings: – Medication to treat a disease – A chemical that is likely to be abused – An “exogenous” chemical that significantly alters the function of certain ...
... Psychopharmacology • Psychopharmacology is the study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and on behavior • The term drug has many meanings: – Medication to treat a disease – A chemical that is likely to be abused – An “exogenous” chemical that significantly alters the function of certain ...
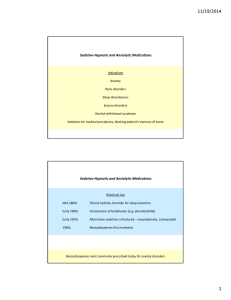
11/19/2014 Sedative‐Hypnotic and Anxiolytic Medications
... GABA receptor are chloride ion (Cl‐) channels. When open, Cl‐ can diffuse into neurons with its concentration gradient (against the electrical gradient) hyperpolarizing membranes, reducing propensity for action potentials. ...
... GABA receptor are chloride ion (Cl‐) channels. When open, Cl‐ can diffuse into neurons with its concentration gradient (against the electrical gradient) hyperpolarizing membranes, reducing propensity for action potentials. ...
Drug Action - people.vcu.edu
... Example: pilocarpine was selective and potent for excitation of parasympathetic nervous system, while atropine was capable of blocking this effect! …… both interact with same component of the cell ...
... Example: pilocarpine was selective and potent for excitation of parasympathetic nervous system, while atropine was capable of blocking this effect! …… both interact with same component of the cell ...
Pharmacology 2a – Mechanisms of Drug action
... 1. Briefly explain what you understand by the term 'structure-activity relationship'. 2. Differentiate between the four principal types of drug antagonism. Give one example of each type of antagonist. 3. Name the four main families of receptors. On what basis are they distinguishable? 4. Describe th ...
... 1. Briefly explain what you understand by the term 'structure-activity relationship'. 2. Differentiate between the four principal types of drug antagonism. Give one example of each type of antagonist. 3. Name the four main families of receptors. On what basis are they distinguishable? 4. Describe th ...
Routes of Excretion
... ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified ◦ control many cellular processes ...
... ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified ◦ control many cellular processes ...
Brain changes and drug addiction
... Legal drug widely used as beverages for social and medical benefits Sedative, hypnotic, euphoric, ‘social lubricant’, anxiolytic Disinhibitory effects, stimulant At high doses it impairs: Motor coordination, reaction time, cognition, sensory processing, judgment Chronic use: Addiction (alcoholism), ...
... Legal drug widely used as beverages for social and medical benefits Sedative, hypnotic, euphoric, ‘social lubricant’, anxiolytic Disinhibitory effects, stimulant At high doses it impairs: Motor coordination, reaction time, cognition, sensory processing, judgment Chronic use: Addiction (alcoholism), ...
CNS Neurotransmitters
... • Major role is in the spinal cord • Glycine receptor is an ionotropic chloride channel analagous to the GABAA receptor. • Strychnine, a competitive antagonist of glycine, removes spinal inhibition to skeletal muscle and induces a violent motor response. ...
... • Major role is in the spinal cord • Glycine receptor is an ionotropic chloride channel analagous to the GABAA receptor. • Strychnine, a competitive antagonist of glycine, removes spinal inhibition to skeletal muscle and induces a violent motor response. ...
Document
... • Major role is in the spinal cord • Glycine receptor is an ionotropic chloride channel analagous to the GABAA receptor. • Strychnine, a competitive antagonist of glycine, removes spinal inhibition to skeletal muscle and induces a violent motor response. ...
... • Major role is in the spinal cord • Glycine receptor is an ionotropic chloride channel analagous to the GABAA receptor. • Strychnine, a competitive antagonist of glycine, removes spinal inhibition to skeletal muscle and induces a violent motor response. ...
Léčiva působící prostř. histaminu, serotoninu a dopaminu
... (historical example cimetidine) • Antagonists of H3 receptors = betahistin for Meniere disease and problems like tinnitus, hearing loss ...
... (historical example cimetidine) • Antagonists of H3 receptors = betahistin for Meniere disease and problems like tinnitus, hearing loss ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM Bachelor
... The actions of the drug on the body are termed as pharmacodynamics. The effect of a drug present at the site of action is determined by that drug’s binding with a receptor. However, at the molecular level, drug binding is only the first among a complex set of events. Types of drug – receptor interac ...
... The actions of the drug on the body are termed as pharmacodynamics. The effect of a drug present at the site of action is determined by that drug’s binding with a receptor. However, at the molecular level, drug binding is only the first among a complex set of events. Types of drug – receptor interac ...