Neurotransmitters
... 3. Serotonin: affects mood, hunger, temp regulation and sleep. Inhibitory or excitatory Located in the brain stem, cerebellum, pineal gland, and the spinal cord. Undersupply may lead to depression, sleeping and eating disorders. Oversupply linked to OCD ...
... 3. Serotonin: affects mood, hunger, temp regulation and sleep. Inhibitory or excitatory Located in the brain stem, cerebellum, pineal gland, and the spinal cord. Undersupply may lead to depression, sleeping and eating disorders. Oversupply linked to OCD ...
Neuronal function
... B) Myelin: saltatory conduction for fast signals 3. Synapses: Communication between neurons A)electrical synapses B) chemical synapses 4. Post-synaptic potentials A) EPSP & IPSP B) Neuronal decisions via summation C) Ionic vs metabolic synapses 5. Presynaptic potentials A) Autoreceptors and pre-syna ...
... B) Myelin: saltatory conduction for fast signals 3. Synapses: Communication between neurons A)electrical synapses B) chemical synapses 4. Post-synaptic potentials A) EPSP & IPSP B) Neuronal decisions via summation C) Ionic vs metabolic synapses 5. Presynaptic potentials A) Autoreceptors and pre-syna ...
Neurotransmission in the CNS
... • ↓ of dopamine levels is a contributing factor in parkinson,s disease . Treatment by increasing dopamine content. ...
... • ↓ of dopamine levels is a contributing factor in parkinson,s disease . Treatment by increasing dopamine content. ...
Week Three Slides
... increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
... increase number of action potentials Also binds to receptors on axon terminals in nucleus accumbens to release more dopamine with each action potential ...
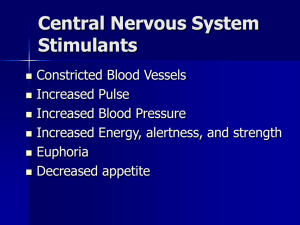
Psychoactive drugs • Drugs which affect mental processes • May be
... • A 4th way in which psychoactive drugs can affect brain functioning: involves disruption of the mechanisms by which neurotransmitters are deactivated • Neurotransmitters normally have only limited period of time to bind to receptors • Shortly after being released • will either be broken down by en ...
... • A 4th way in which psychoactive drugs can affect brain functioning: involves disruption of the mechanisms by which neurotransmitters are deactivated • Neurotransmitters normally have only limited period of time to bind to receptors • Shortly after being released • will either be broken down by en ...
File
... The preserved sheep brains we used in class were missing this tough exterior membrane (meninges) ...
... The preserved sheep brains we used in class were missing this tough exterior membrane (meninges) ...
Lecture 3 - personal.kent.edu
... VI. Tolerance A. Cross tolerance B. Tolerance develops to some chars (effects) but not others C. Types of tolerance 1. decreased drug binding (sequestering) 2. binding has less effect 3. membrane loses permeability 4. tolerance due to learning -conditioned compensatory responses VII. Withdrawal and ...
... VI. Tolerance A. Cross tolerance B. Tolerance develops to some chars (effects) but not others C. Types of tolerance 1. decreased drug binding (sequestering) 2. binding has less effect 3. membrane loses permeability 4. tolerance due to learning -conditioned compensatory responses VII. Withdrawal and ...