Receptors & Transmitters
... disease (epilepsy, ALS, Parkinson’s) drug abuse (cocaine, amphetamine) treatment (depression, OCD) ...
... disease (epilepsy, ALS, Parkinson’s) drug abuse (cocaine, amphetamine) treatment (depression, OCD) ...
Psychoactive Drugs
... The Varying Effects of Drugs Substance abuse is the self-administration of drugs in ways that deviate from either medical or social norms. Psychological dependence occurs when a person continues to use the drug to gain a sense of well-being even when the drug produces adverse consequences. Physical ...
... The Varying Effects of Drugs Substance abuse is the self-administration of drugs in ways that deviate from either medical or social norms. Psychological dependence occurs when a person continues to use the drug to gain a sense of well-being even when the drug produces adverse consequences. Physical ...
Addiction
... Addictive Drugs • Characteristics of Addictive drugs – voluntarily self administered – enhance (directly or indirectly) dopaminergic synaptic function in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) – stimulate the functioning of brain reward circuitry (producing the “high” that drug users seek – functionally these ...
... Addictive Drugs • Characteristics of Addictive drugs – voluntarily self administered – enhance (directly or indirectly) dopaminergic synaptic function in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) – stimulate the functioning of brain reward circuitry (producing the “high” that drug users seek – functionally these ...
A1987L059000002
... at the right moment. The suitable author is someone who did a lot of original work in the field, causing subsequent authors to cite (or read) all the literature that was published earlier. The right moment is when a new field has reached a certain profile but isstill expanding or leading into anothe ...
... at the right moment. The suitable author is someone who did a lot of original work in the field, causing subsequent authors to cite (or read) all the literature that was published earlier. The right moment is when a new field has reached a certain profile but isstill expanding or leading into anothe ...
PPT - CBE Project Server
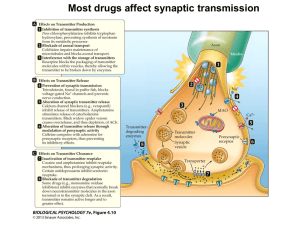
... Inhibitory neurotransmitters Inhibitory neurotransmitters cause neurons to become unable to fire – K+ channels open causing K+ to rush out to the outside of the membrane causing it to become even more positive. • At this point the membrane is said to be ...
... Inhibitory neurotransmitters Inhibitory neurotransmitters cause neurons to become unable to fire – K+ channels open causing K+ to rush out to the outside of the membrane causing it to become even more positive. • At this point the membrane is said to be ...
Psychopharmacology
... type of neurotransmitter and its corresponding enzyme • When the action potential reaches the terminal button, the vesicles migrate to the cell’s surface and drop the neurotransmitters into the synapse and triggers the next neuron • Psychoactive drugs influence one step of this process to increase o ...
... type of neurotransmitter and its corresponding enzyme • When the action potential reaches the terminal button, the vesicles migrate to the cell’s surface and drop the neurotransmitters into the synapse and triggers the next neuron • Psychoactive drugs influence one step of this process to increase o ...
Origins of Biopsychology - Shoreline Community College
... – Given equal initial doses, more heroin gets to the brain than morphine ...
... – Given equal initial doses, more heroin gets to the brain than morphine ...
Fig 4.9a Synaptic Transmission
... Addictive Drugs • Characteristics of Addictive drugs – voluntarily self administered – enhance (directly or indirectly) dopaminergic synaptic function in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) – stimulate the functioning of brain reward circuitry (producing the “high” that drug users seek – functionally these ...
... Addictive Drugs • Characteristics of Addictive drugs – voluntarily self administered – enhance (directly or indirectly) dopaminergic synaptic function in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) – stimulate the functioning of brain reward circuitry (producing the “high” that drug users seek – functionally these ...
Biopsychology
... A method for its deactivation should exist. Its application to the postsynaptic membrane should work. Following stimulation of the presynaptic cell, it should be present in the synapse. Acetylcholine - Deactivation ...
... A method for its deactivation should exist. Its application to the postsynaptic membrane should work. Following stimulation of the presynaptic cell, it should be present in the synapse. Acetylcholine - Deactivation ...
Chapter 5 Quantitative and Thought Questions 5.1 Patient A`s drug
... 5.1 Patient A’s drug very likely acts to block phospholipase A 2 , whereas patient B’s drug blocks lipoxygenase (see Figure 5.12). 5.2 The chronic loss of exposure of the heart’s receptors to norepinephrine causes an up-regulation of this receptor type (i.e., more receptors in the heart for norepine ...
... 5.1 Patient A’s drug very likely acts to block phospholipase A 2 , whereas patient B’s drug blocks lipoxygenase (see Figure 5.12). 5.2 The chronic loss of exposure of the heart’s receptors to norepinephrine causes an up-regulation of this receptor type (i.e., more receptors in the heart for norepine ...
Neurotransmittersand drugs - New Paltz Central School District
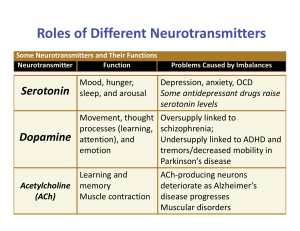
... excess serotonin so it continues to affect the receiving neurons – SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) treat many kinds of depression ...
... excess serotonin so it continues to affect the receiving neurons – SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) treat many kinds of depression ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Antagonist -chemical that block or inhibit postsynaptic effects -example: a choline reuptake blocker would prevent choline from reentering the cell thereby preventing the re-synthesis of ACh ...
... Antagonist -chemical that block or inhibit postsynaptic effects -example: a choline reuptake blocker would prevent choline from reentering the cell thereby preventing the re-synthesis of ACh ...
Chapter 3 Neurons powerpoints
... Laws and implications of action potentials All or none law: neurons either “fire” an action potential or they do not; there are no halfway responses Action potentials do not vary in intensity, either within the same neuron at different times or across different ...
... Laws and implications of action potentials All or none law: neurons either “fire” an action potential or they do not; there are no halfway responses Action potentials do not vary in intensity, either within the same neuron at different times or across different ...
Psych 260
... (With the exception of the last question, each question is worth 1 pt. Write your answers for the last questions directly on the quiz, and hand it in along with your scantron. Be sure to put your name on both the scantron and your quiz!) 1. ___________ refers to the process by which drugs are absorb ...
... (With the exception of the last question, each question is worth 1 pt. Write your answers for the last questions directly on the quiz, and hand it in along with your scantron. Be sure to put your name on both the scantron and your quiz!) 1. ___________ refers to the process by which drugs are absorb ...
Specific NT systems
... • A drug can do only two things, either: – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to ...
... • A drug can do only two things, either: – Increase the effect of neurotransmitter X (agonist) – Decrease the effect of neurotransmitter X (antagonist) Thus, in order to understand the action of a ‘drug Y’, we need to understand the neurochemical system it interacts with. In other words, we need to ...
Practice Exam Each question is worth 4 points unless otherwise
... 15. (Worth 8 points) Discuss the characteristics of temporal and spatial summation in single nerve cells. In what ways are these processes important for information processing by the nervous system? ...
... 15. (Worth 8 points) Discuss the characteristics of temporal and spatial summation in single nerve cells. In what ways are these processes important for information processing by the nervous system? ...
BLOA
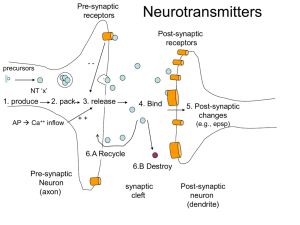
... 3. Any unused NT’s are reabsorbed back into the neuron of origin (REUPTAKE….RECYCLED to be used again) ...
... 3. Any unused NT’s are reabsorbed back into the neuron of origin (REUPTAKE….RECYCLED to be used again) ...
Document
... • When neurotransmitters are accepted by the receptors on the receiving neurons their effect may be either excitatory (making the cell more likely to fire) or inhibitory (making the cell less likely to fire). • Neurotransmitters that are not accepted by the receptor sites must be removed from the s ...
... • When neurotransmitters are accepted by the receptors on the receiving neurons their effect may be either excitatory (making the cell more likely to fire) or inhibitory (making the cell less likely to fire). • Neurotransmitters that are not accepted by the receptor sites must be removed from the s ...
The Synapse
... • On the post-synaptic side of the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters bind to chemical receptors that open chemically-gated ion channels. • Some of these ion channels are K+ channels, which allow K+ ions to leave the cell. This has the effect of hyperpolarizing the area, which inhibits the post-synap ...
... • On the post-synaptic side of the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters bind to chemical receptors that open chemically-gated ion channels. • Some of these ion channels are K+ channels, which allow K+ ions to leave the cell. This has the effect of hyperpolarizing the area, which inhibits the post-synap ...
Neurotransmission
... Antagonist • Some drugs block the production of neurotransmitter. • Dopamine receptor antagonists are used for some diseases such as Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder, nausea and vomiting. It can also control the symptoms of hyper sexuality and increased ...
... Antagonist • Some drugs block the production of neurotransmitter. • Dopamine receptor antagonists are used for some diseases such as Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder, nausea and vomiting. It can also control the symptoms of hyper sexuality and increased ...