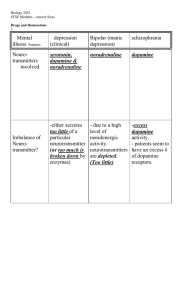
Drugs and Homeostasis STSE Answers File
... depression or suicidal tendencies - dependencies may lead to crime - difficulty in tailoring a drug treatment to a particular patient’s ...
... depression or suicidal tendencies - dependencies may lead to crime - difficulty in tailoring a drug treatment to a particular patient’s ...
L2a.a transmitter201..
... partly by neurons and partly by astrocytes, which convert it to glutamine. Astrocytes release glutamine via a transporter, and neurons take it up and synthesise glutamate. ...
... partly by neurons and partly by astrocytes, which convert it to glutamine. Astrocytes release glutamine via a transporter, and neurons take it up and synthesise glutamate. ...
The Future of Psychiatric Research: Genomes and Neural
... treatment for generalized anxiety disorder an anxioselective compound with functional selectivity for alpha2- and ...
... treatment for generalized anxiety disorder an anxioselective compound with functional selectivity for alpha2- and ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
Chemical transmission and drug action in the central nervous
... 1. Neuroleptic drugs (D receptors) antipsychotic drugs, antischizophrenic drugs Increase of dopaminergic activity in the brain is the cause of schizoprenia, 2. Antidepressive drugs – antidepressans (NA, 5HT) Depression and bipolar disorders are ...
... 1. Neuroleptic drugs (D receptors) antipsychotic drugs, antischizophrenic drugs Increase of dopaminergic activity in the brain is the cause of schizoprenia, 2. Antidepressive drugs – antidepressans (NA, 5HT) Depression and bipolar disorders are ...
mode-of-action-of-recreational
... dehydration, anxiety, panic attacks, paranoia and depression. ...
... dehydration, anxiety, panic attacks, paranoia and depression. ...
E4 Neurotransmitters and synapses trs
... •Inhibitory NTs cause hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron (makes neuron more negative), thereby inhibiting action potentials. •When inhibitory NTs bind to receptors, either K+ ions move out of the cell, or Clions move in. ...
... •Inhibitory NTs cause hyperpolarization of post synaptic neuron (makes neuron more negative), thereby inhibiting action potentials. •When inhibitory NTs bind to receptors, either K+ ions move out of the cell, or Clions move in. ...
CHEMICAL SIGNALLING IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... partly by neurons and partly by astrocytes, which convert it to glutamine. Astrocytes release glutamine via a transporter, and neurons take it up and synthesise glutamate. ...
... partly by neurons and partly by astrocytes, which convert it to glutamine. Astrocytes release glutamine via a transporter, and neurons take it up and synthesise glutamate. ...
Chapter 3 Sherringtons Reflex Work - Reflex arc (the circuit between
... - Metabotropic Effects (the neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds to a G-linked receptor on the postsynaptic terminal, i.e. dendrite, which causes an activation of a second chemical messenger inside of the cell. The signal is then propagated chemically. Response occurs within 30ms and lasts ...
... - Metabotropic Effects (the neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds to a G-linked receptor on the postsynaptic terminal, i.e. dendrite, which causes an activation of a second chemical messenger inside of the cell. The signal is then propagated chemically. Response occurs within 30ms and lasts ...
Definition of RECEPTOR: macromolecular component of the
... to the no. of occupied receptors by that specified drug. Rate theory: — The magnitude and intensity of drug effect is directly proportional to rate of drug-receptor complex formation (mostly specific to explain enzymes behavior as targeted molecules i.e. receptor. Perturbation theory: — When a drug ...
... to the no. of occupied receptors by that specified drug. Rate theory: — The magnitude and intensity of drug effect is directly proportional to rate of drug-receptor complex formation (mostly specific to explain enzymes behavior as targeted molecules i.e. receptor. Perturbation theory: — When a drug ...
Dopamin
... • At least five different major classes are recognized (D1D5), with some subtypes formed by alternative splicing. • They are membrane proteins, at least some of which are glycosylated. • Most have seven transmembrane domains with cytoplasmic loops. • Most appear to be coupled to G proteins. • Some a ...
... • At least five different major classes are recognized (D1D5), with some subtypes formed by alternative splicing. • They are membrane proteins, at least some of which are glycosylated. • Most have seven transmembrane domains with cytoplasmic loops. • Most appear to be coupled to G proteins. • Some a ...
nervous-system
... • Drug enhances amount of dopamine in the synapses • Increased dopamine results in increased feelings of pleasure • Nervous system responds by reducing the number of dopamine receptor sites • Addict must take more drug to produce the same “high” • “So while addicts begin by taking drugs to feel high ...
... • Drug enhances amount of dopamine in the synapses • Increased dopamine results in increased feelings of pleasure • Nervous system responds by reducing the number of dopamine receptor sites • Addict must take more drug to produce the same “high” • “So while addicts begin by taking drugs to feel high ...
Model Description Sheet
... Opium and its derivatives have been used for centuries to treat severe acute or chronic pain by binding to opioid receptors in the body, causing beneficial effects of analgesic and harmful effects. Their addictiveness has led to several opiates becoming recreational drugs such as opium, morphine, an ...
... Opium and its derivatives have been used for centuries to treat severe acute or chronic pain by binding to opioid receptors in the body, causing beneficial effects of analgesic and harmful effects. Their addictiveness has led to several opiates becoming recreational drugs such as opium, morphine, an ...
Dopamine Theory of Schizophrenia
... Neuroleptics take 2-3 weeks to work Parkinson’s disease (PD) side effects PD = reduced DA in striatum Schizophrenia = too much DA Cocaine/amphetamine increase DA levels and induce schizophrenia type symptoms (stereotype behavior) ...
... Neuroleptics take 2-3 weeks to work Parkinson’s disease (PD) side effects PD = reduced DA in striatum Schizophrenia = too much DA Cocaine/amphetamine increase DA levels and induce schizophrenia type symptoms (stereotype behavior) ...
doc Behavioural_Neuroscience_Jan_16
... o Drugs can bind to these neurotransmitters. o These drugs can be an: An agonist, a drug that facilitates postsynaptic transmission An antagonist, a drug that blocks or inhibits postsynaptic transmission Competitive binding: o A direct agonist will attach itself to the binding site where the n ...
... o Drugs can bind to these neurotransmitters. o These drugs can be an: An agonist, a drug that facilitates postsynaptic transmission An antagonist, a drug that blocks or inhibits postsynaptic transmission Competitive binding: o A direct agonist will attach itself to the binding site where the n ...
Answers
... Glitazones: Upregulate signaling molecules downstream of the insulin receptor. Useless for type I diabetes due to a complete lack of insulin production! 4) What is the “Minimal Alveolar Concentration (MAC)”? How does the MAC relate to the lipophilicity of the drug? (10) The MAC is the concentration ...
... Glitazones: Upregulate signaling molecules downstream of the insulin receptor. Useless for type I diabetes due to a complete lack of insulin production! 4) What is the “Minimal Alveolar Concentration (MAC)”? How does the MAC relate to the lipophilicity of the drug? (10) The MAC is the concentration ...
Huang Poster
... evolutionarily conserved function of a potassium channel in promoting brain tumor growth and metastasis, delineate downstream pathways and uncover a co-option mechanism for different ion channels to regulate mitotic cell volume and tumor progression. By candidate drug screening we identify an FDA-ap ...
... evolutionarily conserved function of a potassium channel in promoting brain tumor growth and metastasis, delineate downstream pathways and uncover a co-option mechanism for different ion channels to regulate mitotic cell volume and tumor progression. By candidate drug screening we identify an FDA-ap ...
Myers Module Ten
... Alcohol is a morphoid agonist, with the added feature that the compound does not get created prior to crossing the bloodbrain barrier. It is a sedative that slows neural processing. Alcohol disrupts memory formation at the synapses, in the hippocampus, which is the most sensitive and easily damaged ...
... Alcohol is a morphoid agonist, with the added feature that the compound does not get created prior to crossing the bloodbrain barrier. It is a sedative that slows neural processing. Alcohol disrupts memory formation at the synapses, in the hippocampus, which is the most sensitive and easily damaged ...
Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters? In molecular
... - for example, drug solubility, rate of absorption, rate of metab olism. Although pharmacodynamic factors determine the specific biological effects of a drug, pharmacokinetic factors can be very important in determining how effective a drug is (ex. why not use dopamine t o treat Parkinson’s disease? ...
... - for example, drug solubility, rate of absorption, rate of metab olism. Although pharmacodynamic factors determine the specific biological effects of a drug, pharmacokinetic factors can be very important in determining how effective a drug is (ex. why not use dopamine t o treat Parkinson’s disease? ...
BP 404 T. PHARMACOLOGY-I (Theory)
... how their effects can be applied to therapeutics. The subject covers the information about the drugs like, mechanism of action, physiological and biochemical effects (pharmacodynamics) as well as absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (pharmacokinetics) along with the adverse effects, cl ...
... how their effects can be applied to therapeutics. The subject covers the information about the drugs like, mechanism of action, physiological and biochemical effects (pharmacodynamics) as well as absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (pharmacokinetics) along with the adverse effects, cl ...
![NALTREXONE[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008499817_1-96b3e8696c43dc1d94e990e6680b7eac-300x300.png)