Neurotransmitter release in the brain
... The human brain consists of around 100 billion neurons each making 100010,000 synaptic connections. The activity of the brain is electrical but the connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmit ...
... The human brain consists of around 100 billion neurons each making 100010,000 synaptic connections. The activity of the brain is electrical but the connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmit ...
Synthetic Chemistry and Medicine
... • 5-HT1A receptor that inhibits firing of serotonergic neurons. After a few weeks, of chronic overstimulation, 5-HT1A receptor becomes subsensitive due to and is downregulated – leading to therapeutic effects. ...
... • 5-HT1A receptor that inhibits firing of serotonergic neurons. After a few weeks, of chronic overstimulation, 5-HT1A receptor becomes subsensitive due to and is downregulated – leading to therapeutic effects. ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
MCDB 1041 The Brain and Addiction The Brain`s Reward Pathway
... One of the most powerful effects of alcohol is to reduce the pace of brain activity in part by decreasing the excitatory actions of the neurotransmitter glutamate at the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and boosting the action of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) a ...
... One of the most powerful effects of alcohol is to reduce the pace of brain activity in part by decreasing the excitatory actions of the neurotransmitter glutamate at the NMDA subtype of the glutamate receptor and boosting the action of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) a ...
F.Neuroleptics
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
... component of neuroleptanesthesia, promethazine is not a good antipsychotic drug, but the agent is used in pruritus because of its antihistaminic properties. Adverse Effects: 1. Parkinsonian effects due to excess of cholinergic influence may be normalized by anticholinergics but often the symptoms pe ...
Document
... • Extracellular/transmembrane domain binds to ligand • Intracellular domain binds to effector molecules (G protein) ...
... • Extracellular/transmembrane domain binds to ligand • Intracellular domain binds to effector molecules (G protein) ...
A1989U815100001
... a number of receptor subtypes. significantly, drugs that act as 5-HT,s a~Onists,such as 8-OH DPAT, augment rood intake.’ This effect is in keeping with the postulated existence of IA type autoreceptors on the cell bodies ofthe raphe nuclei. This argument keeps intact the major principle of the origi ...
... a number of receptor subtypes. significantly, drugs that act as 5-HT,s a~Onists,such as 8-OH DPAT, augment rood intake.’ This effect is in keeping with the postulated existence of IA type autoreceptors on the cell bodies ofthe raphe nuclei. This argument keeps intact the major principle of the origi ...
Pharmacology 101 (Part 3) The Grand Finale
... excretion. In this edition we will focus on the pharmacodynamic phase of pharmacology, which in essence relates to the study of how a drug acts on the body. All functions within the body are mediated by control systems which depend on enzymes, receptors on cell walls, carrier molecules, and specific ...
... excretion. In this edition we will focus on the pharmacodynamic phase of pharmacology, which in essence relates to the study of how a drug acts on the body. All functions within the body are mediated by control systems which depend on enzymes, receptors on cell walls, carrier molecules, and specific ...
Drug Abuse & Addiction
... Illegal drugs: $181 billion/year Alcohol: $185 billion/year Tobacco: $158 billion/year Total: $524 billion/year Surgeon General’s Report, 2004; ONDCP, 2004; Harwood, 2000. ...
... Illegal drugs: $181 billion/year Alcohol: $185 billion/year Tobacco: $158 billion/year Total: $524 billion/year Surgeon General’s Report, 2004; ONDCP, 2004; Harwood, 2000. ...
Chemically Modifying Behaviors
... – How drugs interact with the brain and nervous system receptors – The different types of drugs most commonly used and how they affect behavior – Drug tolerance and addiction ...
... – How drugs interact with the brain and nervous system receptors – The different types of drugs most commonly used and how they affect behavior – Drug tolerance and addiction ...
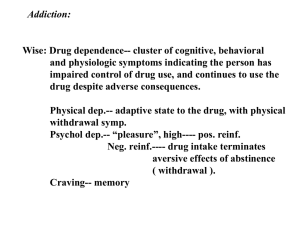
Addiction
... Blum et al (1990, 1996); Spear (2000): Reward deficiency syndrome Nader et al. (2002) ...
... Blum et al (1990, 1996); Spear (2000): Reward deficiency syndrome Nader et al. (2002) ...
Schizophrenia - Beauchamp College
... also reported to alter serotonin neurotransmission and to effect several other neurotransmitters, including, acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and ...
... also reported to alter serotonin neurotransmission and to effect several other neurotransmitters, including, acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... – Increase levels of norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine by preventing their metabolism – Use is declining due to side effects (can cause fatal hypertensive crisis) => Last choice of treatment today (only if other drugs fail) – Possibility of severe food-drug interaction (“cheese reaction”: Tyram ...
... – Increase levels of norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine by preventing their metabolism – Use is declining due to side effects (can cause fatal hypertensive crisis) => Last choice of treatment today (only if other drugs fail) – Possibility of severe food-drug interaction (“cheese reaction”: Tyram ...
Lecture 4
... • Nicotine activates nicotinic acetylcholine ionotropic receptors (nAChR). It has a higher affinity for nAChR in the brain than those in skeletal muscle, so it primarily affects the nAChR in the brain. • Nicotine is named after the French ambassador in Portugal, Jean Nicot de Villemain, who sent tob ...
... • Nicotine activates nicotinic acetylcholine ionotropic receptors (nAChR). It has a higher affinity for nAChR in the brain than those in skeletal muscle, so it primarily affects the nAChR in the brain. • Nicotine is named after the French ambassador in Portugal, Jean Nicot de Villemain, who sent tob ...
Biological therapies of schizophrenia
... However the appropriateness of drug treatment is debatable. While it may be a more humane approach than ECT or restraints that were used in the past and they are relatively cheap (they are free at point of delivery in the UK) and can allow schizophrenics to live a relatively normal life, it is quest ...
... However the appropriateness of drug treatment is debatable. While it may be a more humane approach than ECT or restraints that were used in the past and they are relatively cheap (they are free at point of delivery in the UK) and can allow schizophrenics to live a relatively normal life, it is quest ...
MS Word - Graphic Science
... stimulants used to treat ADHD. Of other drugs used to treat the condition, modafinil is particularly significant in cognitive enhancement. The drug increases noradrenaline and dopamine levels in a similar way to amphetamines, but unlike amphetamines, which affect the whole brain, its action seems to ...
... stimulants used to treat ADHD. Of other drugs used to treat the condition, modafinil is particularly significant in cognitive enhancement. The drug increases noradrenaline and dopamine levels in a similar way to amphetamines, but unlike amphetamines, which affect the whole brain, its action seems to ...
GABA - the Houpt Lab
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel protein, causing it to open and allow ions to move into the cell. 2. G-Protein Coupled Receptors Neurotransmitter binds to receptor protein, which activates a complex of G-proteins (interact with GTP). Activated G-proteins i. can interact with ion channels in membra ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel protein, causing it to open and allow ions to move into the cell. 2. G-Protein Coupled Receptors Neurotransmitter binds to receptor protein, which activates a complex of G-proteins (interact with GTP). Activated G-proteins i. can interact with ion channels in membra ...
Nervous System Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System The
... 1. The fundamental cell of the nervous system is the neuron. 2. The neuron has functionally specialized ...
... 1. The fundamental cell of the nervous system is the neuron. 2. The neuron has functionally specialized ...
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
... (e.g. Alzheimer’s Disease is related to loss of cholinergic function in brain) 5. Endorphins - thought to modulate pain relief and to be associated with naturally occurring pleasures or “highs” 6. GABA - (gamma-aminobutyric acid) referred to as an inhibitory transmitter because when it binds to rece ...
Pharmacokinetics - The Cambridge MRCPsych Course
... But initial effects at pre-synaptic 5HT1A receptors reduces postsynaptic serotonin release Down-regulation of pre-synaptic receptors allows increase in serotonin (delayed response to antidepressant) Side-effects include nausea (5HT2A) and sexual dysfunction ...
... But initial effects at pre-synaptic 5HT1A receptors reduces postsynaptic serotonin release Down-regulation of pre-synaptic receptors allows increase in serotonin (delayed response to antidepressant) Side-effects include nausea (5HT2A) and sexual dysfunction ...
What do you know about Drugs
... tablet, or capsule. • These pills come in different colors and sizes. • They are sometimes inserted into the anus (known as "shafting" or "shelving"). ...
... tablet, or capsule. • These pills come in different colors and sizes. • They are sometimes inserted into the anus (known as "shafting" or "shelving"). ...
DRUG RECEPTOR INTERACTIONS
... 1. Cell-membrane embedded proteins 2. Ligand-gated Ion Channel 3. G –protein coupled Receptor Systems 4. Transcription Factors ...
... 1. Cell-membrane embedded proteins 2. Ligand-gated Ion Channel 3. G –protein coupled Receptor Systems 4. Transcription Factors ...
Drug-Receptor Interactions
... G-protein-linked receptors compose a large class of membrane-bound receptors. The protein structure of these receptors includes a common seven-membered transmembrane domain. In general, receptors linked to G proteins greatly amplify the biologic signal because they activate G proteins, which in turn ...
... G-protein-linked receptors compose a large class of membrane-bound receptors. The protein structure of these receptors includes a common seven-membered transmembrane domain. In general, receptors linked to G proteins greatly amplify the biologic signal because they activate G proteins, which in turn ...
Pharmacology
... Drug-Receptor Interactions •Drug-receptor interactions serve as signals to trigger a cascade of events. This cascade or signaling pathway, is a collection of many cellular responses which serve to amplify the signal and produce a final effect. •Effectors are thus the molecules that translate the dr ...
... Drug-Receptor Interactions •Drug-receptor interactions serve as signals to trigger a cascade of events. This cascade or signaling pathway, is a collection of many cellular responses which serve to amplify the signal and produce a final effect. •Effectors are thus the molecules that translate the dr ...