Synapses and Integration
... Neuropeptides as Neuromodulators – Release mechanism uncertain • Act as autocrine or paracrine agents – Bind to presynaptic cell to affect amount of neurotransmitter released when an action potential occurs in that presynaptic – Bind to post synaptic cell to affect number of receptors for the neurot ...
... Neuropeptides as Neuromodulators – Release mechanism uncertain • Act as autocrine or paracrine agents – Bind to presynaptic cell to affect amount of neurotransmitter released when an action potential occurs in that presynaptic – Bind to post synaptic cell to affect number of receptors for the neurot ...
Drug - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... muscle movement and organ is epinephrine and norepinephrine. The receptors are alpha and beta ...
... muscle movement and organ is epinephrine and norepinephrine. The receptors are alpha and beta ...
week3pm
... ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified (large and diverse family) ◦ control many cellular processes ◦ Involved in synaptic effects of many nt ...
... ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified (large and diverse family) ◦ control many cellular processes ◦ Involved in synaptic effects of many nt ...
TOXICOLOGY – TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE
... Second messenger systems - These systems are activated when the drug comes in contact w/ receptors for it. This results in many processes being activated or inhibited. - Examples of 2ND messengers include cAMP, cGMP, IP3 - 2ND messengers open/close ion channels Definitions - Affinity – This is the s ...
... Second messenger systems - These systems are activated when the drug comes in contact w/ receptors for it. This results in many processes being activated or inhibited. - Examples of 2ND messengers include cAMP, cGMP, IP3 - 2ND messengers open/close ion channels Definitions - Affinity – This is the s ...
PDF - ClaimSecure
... ability to reduce the cardinal motor features of the disorder i.e. tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia . In fact, virtually all PD patients will require l-dopa therapy at some stage of their illness. When it was first marketed, large amounts of ldopa were required to produce a good clinical response. ...
... ability to reduce the cardinal motor features of the disorder i.e. tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia . In fact, virtually all PD patients will require l-dopa therapy at some stage of their illness. When it was first marketed, large amounts of ldopa were required to produce a good clinical response. ...
Stimulants - CT Clearinghouse
... Amphetamines, such as methamphetamine, also act on the pleasure circuit by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters present in the synapse, but the mechanism is different from that of cocaine. Chemically, methamphetamine is closely related to amphetamine, but it has greater effects on the b ...
... Amphetamines, such as methamphetamine, also act on the pleasure circuit by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters present in the synapse, but the mechanism is different from that of cocaine. Chemically, methamphetamine is closely related to amphetamine, but it has greater effects on the b ...
Slide 1
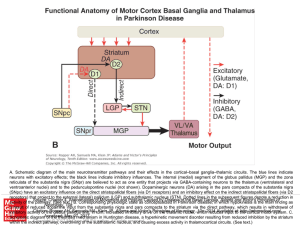
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
Module 22 Notes
... Found in beer, wine, and liquor The _____ most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) Slows thinking, and impairs _______ activity Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) A measure of how much _______ is in a person’s bloodstream Alcohol _______ the parts of the brain responsible for controlling ________ and m ...
... Found in beer, wine, and liquor The _____ most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) Slows thinking, and impairs _______ activity Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) A measure of how much _______ is in a person’s bloodstream Alcohol _______ the parts of the brain responsible for controlling ________ and m ...
Sites of drug metabolism
... of a cell (or inside a cell) that receives chemical signals from outside the cells and when such chemical signals bind to a receptor , they cause some form of cellular /tissue response . ...
... of a cell (or inside a cell) that receives chemical signals from outside the cells and when such chemical signals bind to a receptor , they cause some form of cellular /tissue response . ...
Lorem Ipsum - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... Levodopa Tachycardia - Dopamine has beta1 effects on the cardiovascular ...
... Levodopa Tachycardia - Dopamine has beta1 effects on the cardiovascular ...
Drugs of Abuse
... dopamine (DA) neurons. Left: Cocaine inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT), decreasing DA clearance from the synaptic cleft and causing an increase in extracellular DA concentration. Right: Since amphetamine (Amph) is a substrate of the DAT, it competitively inhibits DA transport. In addition, onc ...
... dopamine (DA) neurons. Left: Cocaine inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT), decreasing DA clearance from the synaptic cleft and causing an increase in extracellular DA concentration. Right: Since amphetamine (Amph) is a substrate of the DAT, it competitively inhibits DA transport. In addition, onc ...
Carol Dwan
... • GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. When this molecule binds to it’s receptor it makes the neuron less likely to fire. • Complex molecule with multiple receptor sites ...
... • GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. When this molecule binds to it’s receptor it makes the neuron less likely to fire. • Complex molecule with multiple receptor sites ...
Psychology
... • The process whereby neurons communicate with each other • Neurotransmission, especially in the brain and spinal cord, helps explain the effects of psychoactive drugs. • Psychoactive drugs interfere with normal neurotransmission. ...
... • The process whereby neurons communicate with each other • Neurotransmission, especially in the brain and spinal cord, helps explain the effects of psychoactive drugs. • Psychoactive drugs interfere with normal neurotransmission. ...
Module 55: The Biomedical Therapies, Summary Notes
... They reduce tension and anxiety without causing drowsiness and in combination with psychotherapy (such as systematic desensitization) can help a person with phobias and other fear triggering stimuli (obsessive compulsive disorders). ...
... They reduce tension and anxiety without causing drowsiness and in combination with psychotherapy (such as systematic desensitization) can help a person with phobias and other fear triggering stimuli (obsessive compulsive disorders). ...
Psychology
... • The discomfort and distress that follow when a person who is dependent on a drug discontinues the use of the drug • Drug Rebound Effect -Withdrawal symptoms are usually the opposite of the drug’s effects – “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction” ...
... • The discomfort and distress that follow when a person who is dependent on a drug discontinues the use of the drug • Drug Rebound Effect -Withdrawal symptoms are usually the opposite of the drug’s effects – “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction” ...
Possible Test Questions
... - M1 – Muscarinic cholinergic receptors – blockade of these receptors leads to many common side effects fitting into the classic anti-cholinergic caterogory - such as dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision. - 5-HT receptors = The Serotonin Receptors modulate the release of many other neurotransmi ...
... - M1 – Muscarinic cholinergic receptors – blockade of these receptors leads to many common side effects fitting into the classic anti-cholinergic caterogory - such as dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision. - 5-HT receptors = The Serotonin Receptors modulate the release of many other neurotransmi ...
Unit 3 health studies
... Animal research backs up human research findings. Research using mice has shown a correlation between cocaine use and renal (kidney) failure. The same correlation was not found for heroin. Jaffe (2006) found a similar correlation with human drug users. This suggests it is the action of a specific dr ...
... Animal research backs up human research findings. Research using mice has shown a correlation between cocaine use and renal (kidney) failure. The same correlation was not found for heroin. Jaffe (2006) found a similar correlation with human drug users. This suggests it is the action of a specific dr ...
Slide ()
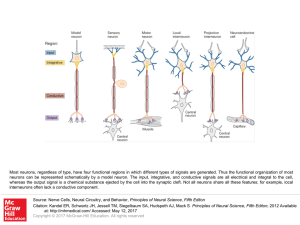
... Most neurons, regardless of type, have four functional regions in which different types of signals are generated. Thus the functional organization of most neurons can be represented schematically by a model neuron. The input, integrative, and conductive signals are all electrical and integral to the ...
... Most neurons, regardless of type, have four functional regions in which different types of signals are generated. Thus the functional organization of most neurons can be represented schematically by a model neuron. The input, integrative, and conductive signals are all electrical and integral to the ...
Document
... • A drug has an affinity for a particular type of receptor if it binds to that receptor. – Can vary from strong to weak. • The efficacy of the drug is its tendency to activate the receptor. • Drugs can have a high affinity but low efficacy. ...
... • A drug has an affinity for a particular type of receptor if it binds to that receptor. – Can vary from strong to weak. • The efficacy of the drug is its tendency to activate the receptor. • Drugs can have a high affinity but low efficacy. ...
OCD-like behavior linked to genetic mutation
... evidence suggesting how neural dysfunction in a certain region of the brain can lead to obsessive and repetitive behaviors much like obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD). Both in humans and in mice, there is a circuit in the brain called the corticostriatal connection that regulates habitual and repet ...
... evidence suggesting how neural dysfunction in a certain region of the brain can lead to obsessive and repetitive behaviors much like obsessivecompulsive disorder (OCD). Both in humans and in mice, there is a circuit in the brain called the corticostriatal connection that regulates habitual and repet ...
Drugs and the Synapse
... • A drug has an affinity for a particular type of receptor if it binds to that receptor. – Can vary from strong to weak. • The efficacy of the drug is its tendency to activate the receptor. • Drugs can have a high affinity but low efficacy. ...
... • A drug has an affinity for a particular type of receptor if it binds to that receptor. – Can vary from strong to weak. • The efficacy of the drug is its tendency to activate the receptor. • Drugs can have a high affinity but low efficacy. ...
What is Parkinson`s Disease?
... area of the brain called the substantia nigra begin to malfunction and die. These cells in the substantia nigra produce a chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger, that sends information to the parts of the brain that control movement and coordination. When a p ...
... area of the brain called the substantia nigra begin to malfunction and die. These cells in the substantia nigra produce a chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger, that sends information to the parts of the brain that control movement and coordination. When a p ...