Ben Waller
... (sensory portions of the cerebral cortex) and movement (the cerebellum, substantia nigra, globus pallidus). When THC activates cannabinoid receptors, it interferes with the normal functioning of these brain areas. ...
... (sensory portions of the cerebral cortex) and movement (the cerebellum, substantia nigra, globus pallidus). When THC activates cannabinoid receptors, it interferes with the normal functioning of these brain areas. ...
- ISpatula
... usually small ligands bind to receptors of this class (gamma, magnesium, pheromones, taste molecules) ...
... usually small ligands bind to receptors of this class (gamma, magnesium, pheromones, taste molecules) ...
Adenosine - Wellington ICU
... - depression of SA & AV nodal activity - antagonises cAMP-mediated catecholamine stimulation of ventricular muscle -> negative chronotropy & dromotropy - direct agonist at specific cell membrane receptors (A1 & A2) - A1 = coupled to K+ channels by a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in supraventric ...
... - depression of SA & AV nodal activity - antagonises cAMP-mediated catecholamine stimulation of ventricular muscle -> negative chronotropy & dromotropy - direct agonist at specific cell membrane receptors (A1 & A2) - A1 = coupled to K+ channels by a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in supraventric ...
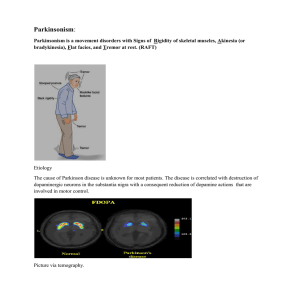
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism
... So the Strategies of drug treatment of parkinsonism involve increasing dopamine activity in the brain or decreasing muscarinic cholinergic activity in the brain (or both). A. Levodopa: precursor of dopamine. 1.Mechanisms : because dopamine has low bioavailability and does not readily cross the blood ...
... So the Strategies of drug treatment of parkinsonism involve increasing dopamine activity in the brain or decreasing muscarinic cholinergic activity in the brain (or both). A. Levodopa: precursor of dopamine. 1.Mechanisms : because dopamine has low bioavailability and does not readily cross the blood ...
THESIS OUTLINE
... were made from dopamine neurons in order to assess GABA mediated neurotransmission in the VTA in absence of µ-opioid receptors (Chapter 3). In addition, signal transduction pathways coupled to µ-opioid receptors in the VTA were explored in an in vitro study as described in Chapter 4. Slices of the V ...
... were made from dopamine neurons in order to assess GABA mediated neurotransmission in the VTA in absence of µ-opioid receptors (Chapter 3). In addition, signal transduction pathways coupled to µ-opioid receptors in the VTA were explored in an in vitro study as described in Chapter 4. Slices of the V ...
Peripheral nerve pathophysiology
... Origin of peripheral nervous system disease These diseases can be broadly classified into four major categories: Spinal dystrophies (motor neuron body) Peripheral neuropathies (nerve: body+axon) Diseases of the myoneural junction Myopathies Groups one through three are primarily diseases of ...
... Origin of peripheral nervous system disease These diseases can be broadly classified into four major categories: Spinal dystrophies (motor neuron body) Peripheral neuropathies (nerve: body+axon) Diseases of the myoneural junction Myopathies Groups one through three are primarily diseases of ...
IMS-P21 Discovery of ASP5736, a Novel 5
... Discovery Research, Astellas Pharma Inc., 2Development, Astellas Pharma Inc. ...
... Discovery Research, Astellas Pharma Inc., 2Development, Astellas Pharma Inc. ...
Important side effects to be considered when choosing antipsychotic
... Dopamine receptor blocking activity in the brain:. D1 and D5 receptors activate adenylyl cyclase, often exciting neurons, whereas D2, D3 and D4 receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase, or mediate membrane K+ channel opening leading to neuronal hyperpolarization. The neuroleptic drugs bind to these rece ...
... Dopamine receptor blocking activity in the brain:. D1 and D5 receptors activate adenylyl cyclase, often exciting neurons, whereas D2, D3 and D4 receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase, or mediate membrane K+ channel opening leading to neuronal hyperpolarization. The neuroleptic drugs bind to these rece ...
receptors
... Gave radioactively labeled nicotine to rats. Found > number of nicotinic receptors vs. controls. Unusual – receptors usually ↑ in numbers when there is a shortage of stimulation. Solution: nicotine initially exerts a stimulatory effect (agonist), and then desensitizes receptors to render them nonfun ...
... Gave radioactively labeled nicotine to rats. Found > number of nicotinic receptors vs. controls. Unusual – receptors usually ↑ in numbers when there is a shortage of stimulation. Solution: nicotine initially exerts a stimulatory effect (agonist), and then desensitizes receptors to render them nonfun ...
Pharmacology Objectives 2
... 1. Describe the chemical nature of receptors. Receptors are single macromolecules or aggregates of macromolecules (frequently proteins or glycoproteins) located in cell plasma membranes or in the cell cytoplasm that interact with hormones, neurotransmitters or drugs. 2. Explain the chemical interact ...
... 1. Describe the chemical nature of receptors. Receptors are single macromolecules or aggregates of macromolecules (frequently proteins or glycoproteins) located in cell plasma membranes or in the cell cytoplasm that interact with hormones, neurotransmitters or drugs. 2. Explain the chemical interact ...
Drugs and Consciousness
... ➤ ActivePsych: Digital Media Archive, 2nd ed.: The Brain's Reward Center ...
... ➤ ActivePsych: Digital Media Archive, 2nd ed.: The Brain's Reward Center ...
Lecture-13-2013-Bi
... treatment with base: ammonia or Na bicarbonate, then heat to drive off HCl ...
... treatment with base: ammonia or Na bicarbonate, then heat to drive off HCl ...
experiments with enzymes involved in neurotransmission
... 1. Neuronal communication, neuronal synapse Neurons communicate with each other via synapses, where the axon terminal of one cell impinges upon another neuron's dendrite, soma or, less commonly, axon. The human brain has a huge number of synapses. Each of the 1011 (one hundred billion) neurons has o ...
... 1. Neuronal communication, neuronal synapse Neurons communicate with each other via synapses, where the axon terminal of one cell impinges upon another neuron's dendrite, soma or, less commonly, axon. The human brain has a huge number of synapses. Each of the 1011 (one hundred billion) neurons has o ...
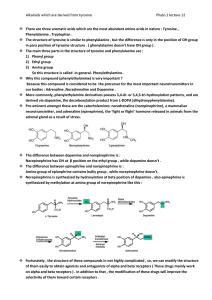
Norepinephrine
... duration of action. But this property doesn’t convert the agonist to antagonist. So, any change on alkylation can’t convert agonist to antagonist. In general, antagonist needs more hydrophobicity and bulkiness than agonist, so they said if we change the hydroxyls in catechol to something more hydrop ...
... duration of action. But this property doesn’t convert the agonist to antagonist. So, any change on alkylation can’t convert agonist to antagonist. In general, antagonist needs more hydrophobicity and bulkiness than agonist, so they said if we change the hydroxyls in catechol to something more hydrop ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... each of the cerebral hemispheres? 30. What’s the importance of the corpus callosum? You can skip the section on the Endocrine System – pages 67-68 31. How are genetic factors related to several aspects of behavior? (Look to ...
... each of the cerebral hemispheres? 30. What’s the importance of the corpus callosum? You can skip the section on the Endocrine System – pages 67-68 31. How are genetic factors related to several aspects of behavior? (Look to ...
Variability in Drug Response 1
... Dependence refers to a complex and poorly understood set of changes in the homeostasis of an organism that causes a disturbance of the homeostatic set point of the organism if the drug is stopped. This disturbance often is revealed when administration of an opioid is stopped abruptly, resulting in w ...
... Dependence refers to a complex and poorly understood set of changes in the homeostasis of an organism that causes a disturbance of the homeostatic set point of the organism if the drug is stopped. This disturbance often is revealed when administration of an opioid is stopped abruptly, resulting in w ...
L1: Intro to Pharm- Objectives Describe what is meant by a drug`s
... contraindicated in asthmatics), 2) Co-administration with other drugs may produce undesirable/altered effects ...
... contraindicated in asthmatics), 2) Co-administration with other drugs may produce undesirable/altered effects ...
Synapses - KScience
... control the information that passes around the nervous system. They make sure that the information passes in the right direction. They use chemical transmitters. 1. How many synapses are on the diagram? 2. What type of nerve cells are cell X and cell Z? 3. In what form does information pass to cell ...
... control the information that passes around the nervous system. They make sure that the information passes in the right direction. They use chemical transmitters. 1. How many synapses are on the diagram? 2. What type of nerve cells are cell X and cell Z? 3. In what form does information pass to cell ...
Mechanisms of drug action
... β1 receptors are a sub group of adrenoceptors. Endogenous adrenaline and nor adrenaline act on these receptors in heart and increase heart rate and cardiac contractility there by increasing the cardiac work load and the blood pressure. Propranolol is a β receptor antagonist. It binds to β1 receptors ...
... β1 receptors are a sub group of adrenoceptors. Endogenous adrenaline and nor adrenaline act on these receptors in heart and increase heart rate and cardiac contractility there by increasing the cardiac work load and the blood pressure. Propranolol is a β receptor antagonist. It binds to β1 receptors ...
agonist - Buffalo State
... Drug effect is directly proportional to number of receptors occupied Drug effect ceases as drug-receptor complex dissociate Ariens & Stephenson theory introduced terms of "affinity" & "efficacy" Affinity: ability of the drug to combine with receptor to create drug-receptor complex Efficacy: ability ...
... Drug effect is directly proportional to number of receptors occupied Drug effect ceases as drug-receptor complex dissociate Ariens & Stephenson theory introduced terms of "affinity" & "efficacy" Affinity: ability of the drug to combine with receptor to create drug-receptor complex Efficacy: ability ...
The pharmacology of type I hypersensitivity
... IgE-mediated reactions affect both the respiratory and the cardiovascular systems. This usually respond rapidly to the parenteral administration of epinephrine. Epinephrine is the physiological antagonist of histamine on smooth muscles,and it acts on different receptors. It is the drug of choice in ...
... IgE-mediated reactions affect both the respiratory and the cardiovascular systems. This usually respond rapidly to the parenteral administration of epinephrine. Epinephrine is the physiological antagonist of histamine on smooth muscles,and it acts on different receptors. It is the drug of choice in ...