File
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
Chapter 3 outline
... I. Communicating Internally: Connecting World and Brain A. Main components of the nervous system ...
... I. Communicating Internally: Connecting World and Brain A. Main components of the nervous system ...
Characterization of GPR101 transcripts structure, expression and
... GPR101 expression was seen in human fetal pituitary. GPR101 was also expressed in several brain areas during zebrafish and rat development. While GPR101 over-expression strongly activates the cAMP pathway in basal conditions, only a very modest increase in Gi- and no activation of Gq-mediated pathwa ...
... GPR101 expression was seen in human fetal pituitary. GPR101 was also expressed in several brain areas during zebrafish and rat development. While GPR101 over-expression strongly activates the cAMP pathway in basal conditions, only a very modest increase in Gi- and no activation of Gq-mediated pathwa ...
Chapter 2
... – Outside the Axon= positive ions – Inside the Axon= negative ions – Even positive and negative= resting potential, which acts like a gate . – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through ...
... – Outside the Axon= positive ions – Inside the Axon= negative ions – Even positive and negative= resting potential, which acts like a gate . – Depolarization= unfreezes or ungates the axon allowing the message to go through ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... __________________-Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. __________________-Degeneration of nervous tissue that can cause memory loss, loss of verbal communication, and motor skills __________________-genetic di ...
... __________________-Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. __________________-Degeneration of nervous tissue that can cause memory loss, loss of verbal communication, and motor skills __________________-genetic di ...
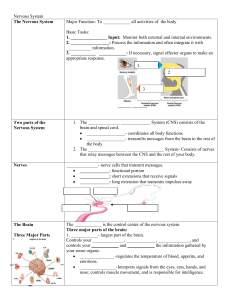
Nervous System
... In a simple reflex, only a sensory nerve and motor nerve involved – example, “kneejerk” reflex Disorders of Nervous System ...
... In a simple reflex, only a sensory nerve and motor nerve involved – example, “kneejerk” reflex Disorders of Nervous System ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... The Brain • Brainstem –responsible for automatic survival functions ...
... The Brain • Brainstem –responsible for automatic survival functions ...
The Body and the Brain
... Some neurons are as small as an inch in length. Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the ...
... Some neurons are as small as an inch in length. Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the ...
Direct Electrode Stimulation Direct electrode stimulation involves
... causes the neurons to lose their ability to fire, this is used to make specific brain areas inactive to measure temporary changes in all kinds of behaviour and mental processes. It can be used to study how the brain organises different functions such as language, memory, vision or attention. Advanta ...
... causes the neurons to lose their ability to fire, this is used to make specific brain areas inactive to measure temporary changes in all kinds of behaviour and mental processes. It can be used to study how the brain organises different functions such as language, memory, vision or attention. Advanta ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance ...
... The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance ...
Read our 2014-15 Annual Report - Nuffield Department of Clinical
... Image captions Treating congenital myasthenic syndrome: Searching for mutations in a DNA sequence Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease earlier: The basal ganglia network is in green, and the significant difference between Parkinson’s patients and the control group in red Identifying autoimmune disease: P ...
... Image captions Treating congenital myasthenic syndrome: Searching for mutations in a DNA sequence Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease earlier: The basal ganglia network is in green, and the significant difference between Parkinson’s patients and the control group in red Identifying autoimmune disease: P ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
Document
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
Brain
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... and cerebrum • associated with fear, aggression and drives for food and sex •hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus ...
... and cerebrum • associated with fear, aggression and drives for food and sex •hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus ...
Unit 3B: The Brain Messing with the Brain Scientists can electrically
... Judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds/textures Coordinates voluntary movement (coordination) Limbic System (neural system associated with emotions and drives, sits between older structures and cerebral cortex) Amygdala: influences aggression and fear including perception of them a ...
... Judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds/textures Coordinates voluntary movement (coordination) Limbic System (neural system associated with emotions and drives, sits between older structures and cerebral cortex) Amygdala: influences aggression and fear including perception of them a ...
Temporal Lobe
... o Definition: A brain abscess is a collection of immune cells, pus, and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection. • Brain abscesses commonly occur when bacteria or fungi infect part of the brain. Swelling and irritation (inflammation) develops in response. Infected b ...
... o Definition: A brain abscess is a collection of immune cells, pus, and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection. • Brain abscesses commonly occur when bacteria or fungi infect part of the brain. Swelling and irritation (inflammation) develops in response. Infected b ...
Module 6 Powerpoint
... Whole-brain Association Activity Whole-brain association activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...
... Whole-brain Association Activity Whole-brain association activity involves complex activities which require communication among association areas across the brain such as: memory language attention meditation and spirituality consciousness ...