Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... molecular structure and function of genes and how they influence behavior. Heritability – the extent to which variation among individuals can be attributed to their differing genes. *Genes are self-regulating * Interaction – the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (environment) depen ...
... molecular structure and function of genes and how they influence behavior. Heritability – the extent to which variation among individuals can be attributed to their differing genes. *Genes are self-regulating * Interaction – the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (environment) depen ...
Biology and Psychology - Austin Community College
... Peripheral Nervous System Consists of sensory and motor neurons that transmit messages to and from CNS. Without it, we’d be isolated from the world. 2 Main Divisions: Somatic (sensory) connects CNS with sensory receptors, skeletal muscles, & surface of the body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous System Consists of sensory and motor neurons that transmit messages to and from CNS. Without it, we’d be isolated from the world. 2 Main Divisions: Somatic (sensory) connects CNS with sensory receptors, skeletal muscles, & surface of the body. ...
No Slide Title
... All the nerves that control skeletal muscles, joints, and skin. They receive and act on external stimuli are called ________ nerves. ...
... All the nerves that control skeletal muscles, joints, and skin. They receive and act on external stimuli are called ________ nerves. ...
module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
... Prosthetics; Hemispherectomy; The Sodium Amobarbital Test; Language on Two Sides of the Brain? Exercises: Neuroscience and Moral Judgments; The Sensory ...
... Prosthetics; Hemispherectomy; The Sodium Amobarbital Test; Language on Two Sides of the Brain? Exercises: Neuroscience and Moral Judgments; The Sensory ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Twelve
... Motor – These carry impulses to your muscles. At end of each motor neuron is a motor end plate. This attaches to an individual muscle fiber taking impulses from the brain to stimulate movement. Connector – These connect actions of other neurons. You will sometimes see these referred to as relay, tra ...
... Motor – These carry impulses to your muscles. At end of each motor neuron is a motor end plate. This attaches to an individual muscle fiber taking impulses from the brain to stimulate movement. Connector – These connect actions of other neurons. You will sometimes see these referred to as relay, tra ...
How Does the Brain Learn Through Music?
... and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
... and music among the multiple measures used for NCLB accountability.” ...
Lecture #11 Development of the Nervous System Part II
... 3. Oligodendrocytes are responsible for the production of myelin which facilitates electrical conduction. 4. While it is only 2% of total body weight, the brain consumes 20% of total oxygen taken in. It also hogs 15% of cardiac output through the internal carotid and vertebral arteries. 5. The brain ...
... 3. Oligodendrocytes are responsible for the production of myelin which facilitates electrical conduction. 4. While it is only 2% of total body weight, the brain consumes 20% of total oxygen taken in. It also hogs 15% of cardiac output through the internal carotid and vertebral arteries. 5. The brain ...
study notes quiz 1
... SENSATION (b) Autonomic Nervous System: (i) receives unconscious sensory input from internal organs (e.g., the acid content of stomach) (ii) unconcious control of movement and organs (e.g., heartbeat, breathing, reflexes) (iii) Controls itself – it is autonomic and will function without upper cognit ...
... SENSATION (b) Autonomic Nervous System: (i) receives unconscious sensory input from internal organs (e.g., the acid content of stomach) (ii) unconcious control of movement and organs (e.g., heartbeat, breathing, reflexes) (iii) Controls itself – it is autonomic and will function without upper cognit ...
Steele`s Top 10 Dietary Principles and Strategies For Maximizing
... Diffuse Modulatory System: A collection of neurons within the brainstem producing either noradrenaline, dopamine, or acetylcholine for release to diffuse targets throughout the central nervous system, thus ‘setting the tone’ for consciousness and cognition. Ghrelin: A hormone released by cells linin ...
... Diffuse Modulatory System: A collection of neurons within the brainstem producing either noradrenaline, dopamine, or acetylcholine for release to diffuse targets throughout the central nervous system, thus ‘setting the tone’ for consciousness and cognition. Ghrelin: A hormone released by cells linin ...
10strategies
... Diffuse Modulatory System: A collection of neurons within the brainstem producing either noradrenaline, dopamine, or acetylcholine for release to diffuse targets throughout the central nervous system, thus ‘setting the tone’ for consciousness and cognition. Ghrelin: A hormone released by cells linin ...
... Diffuse Modulatory System: A collection of neurons within the brainstem producing either noradrenaline, dopamine, or acetylcholine for release to diffuse targets throughout the central nervous system, thus ‘setting the tone’ for consciousness and cognition. Ghrelin: A hormone released by cells linin ...
Brain Development - Pottstown School District
... also drive the very rapid growth of learning that occurs immediately after birth. At birth, a baby’s brain contains 100 billion neurons, roughly as many nerve cells as there are stars in the Milky Way. Before birth, the brain produces trillions more neurons and “synapses” (connections between the br ...
... also drive the very rapid growth of learning that occurs immediately after birth. At birth, a baby’s brain contains 100 billion neurons, roughly as many nerve cells as there are stars in the Milky Way. Before birth, the brain produces trillions more neurons and “synapses” (connections between the br ...
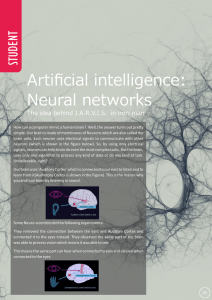
Artificial intelligence: Neural networks
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... Chapter 12-13 NOTE: This was originally prepared for BIOL 2404, however many parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
... Chapter 12-13 NOTE: This was originally prepared for BIOL 2404, however many parts overlap with 2401. I’ve added additional references. Use this knowing it may not cover everything. Nervous System: (These are very important chapters.) ...
Nervous
... -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism’s ...
... -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism’s ...
Document
... • Aristotle and his emphasis on the relationship between structure and function marked the beginning of physiology in Ancient Greece. • Galen was the to use experiment to probe the function of the body. Also the founder of experimental physiology. • Ibn -al- Naifs, was the first physician to correc ...
... • Aristotle and his emphasis on the relationship between structure and function marked the beginning of physiology in Ancient Greece. • Galen was the to use experiment to probe the function of the body. Also the founder of experimental physiology. • Ibn -al- Naifs, was the first physician to correc ...
Nervous System
... - a different kind of neurotransmitter....NO is a gas released by some neurons locally in erectile tissue, causes vasodilation. Viagra blocks an enzyme that ...
... - a different kind of neurotransmitter....NO is a gas released by some neurons locally in erectile tissue, causes vasodilation. Viagra blocks an enzyme that ...
CNS
... • Outer layer not connected to bone rather space filled with fat, connective tissue and blood serving as padding for when spine is bent ...
... • Outer layer not connected to bone rather space filled with fat, connective tissue and blood serving as padding for when spine is bent ...
DOC
... Neurotransmitters are brain chemicals that control the action between nerve cells – and therefore they control everything our bodies do. Visitor experience: Users will experience the action as if they are inside the brain of the main character. Users will control the action by making choices at key ...
... Neurotransmitters are brain chemicals that control the action between nerve cells – and therefore they control everything our bodies do. Visitor experience: Users will experience the action as if they are inside the brain of the main character. Users will control the action by making choices at key ...
Organization of the nervous system
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
... A Neuron is a very special cell: You have about 100 billion of them! •Cell body: Keeps the neuron alive and determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... -Passes on both sensory and motor information -Maintains normal muscle tone, posture and balance -Makes sure all skeletal muscles function together for smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
... -Passes on both sensory and motor information -Maintains normal muscle tone, posture and balance -Makes sure all skeletal muscles function together for smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
Presentation - Ch 2 Sections Demo-6-7
... Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. How do the brain structures change when the brain has a ...
... Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. How do the brain structures change when the brain has a ...
The Evolution of the Brain Neurons are quite distinct from other body
... more complex brains are able to sense and control much more complex aspects of their surroundings. This capacity for increased environmental control is nowhere more striking than in our species. Using the advanced perceptual-behavioral capacities of our brain together with our culturally evolved kn ...
... more complex brains are able to sense and control much more complex aspects of their surroundings. This capacity for increased environmental control is nowhere more striking than in our species. Using the advanced perceptual-behavioral capacities of our brain together with our culturally evolved kn ...